
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has become an increasingly central component of architecture and the building trades. Modern BIM software has moved beyond the simple 2D and 3D modeling tools of the past to incorporate simulation, analysis, project management, and more. BIM Handbook: A Guide to Building Information Modeling for Owners, Designers, Engineers, Contractors, and Facility Managers has long served as the essential introduction to this subject and its ever-expanding applications. Now fully updated to reflect the increasing standardization of BIM practices and its cutting-edge industry frameworks, the latest edition of this key text remains the fundamental tool for understanding the backbone of innovation in construction technology.







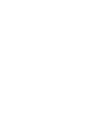
This paper presents a systematic review of generative artificial intelligence (AI) use in architectural design from 2014 to 2024, focusing on 1) AI models and theory-application gaps, 2) design phases, tasks, and objectives, 3) data types and contents, and 4) evaluation methods. Based on 161 journal papers selected using preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analysis (PRISMA), the analysis reveals the theory-application gap has been reduced by 96.09 %, from 62 to 2.5 years, highlighting rapid AI adoption since 2021 with generative adversarial networks (GANs) leading, and transformers and diffusion models gaining traction. For its application, AI is employed in schematic design phases in 68.94 %, while later phases remain underexplored. Regarding types of data used, images dominate at both input (52.8 %) and output (68.32 %), with multimodal and graph data showing promise. For evaluation, comparative evaluation was most utilized (60.9 %) supported by subjective assessment by authors (34.2 %) and third parties (17.4 %).
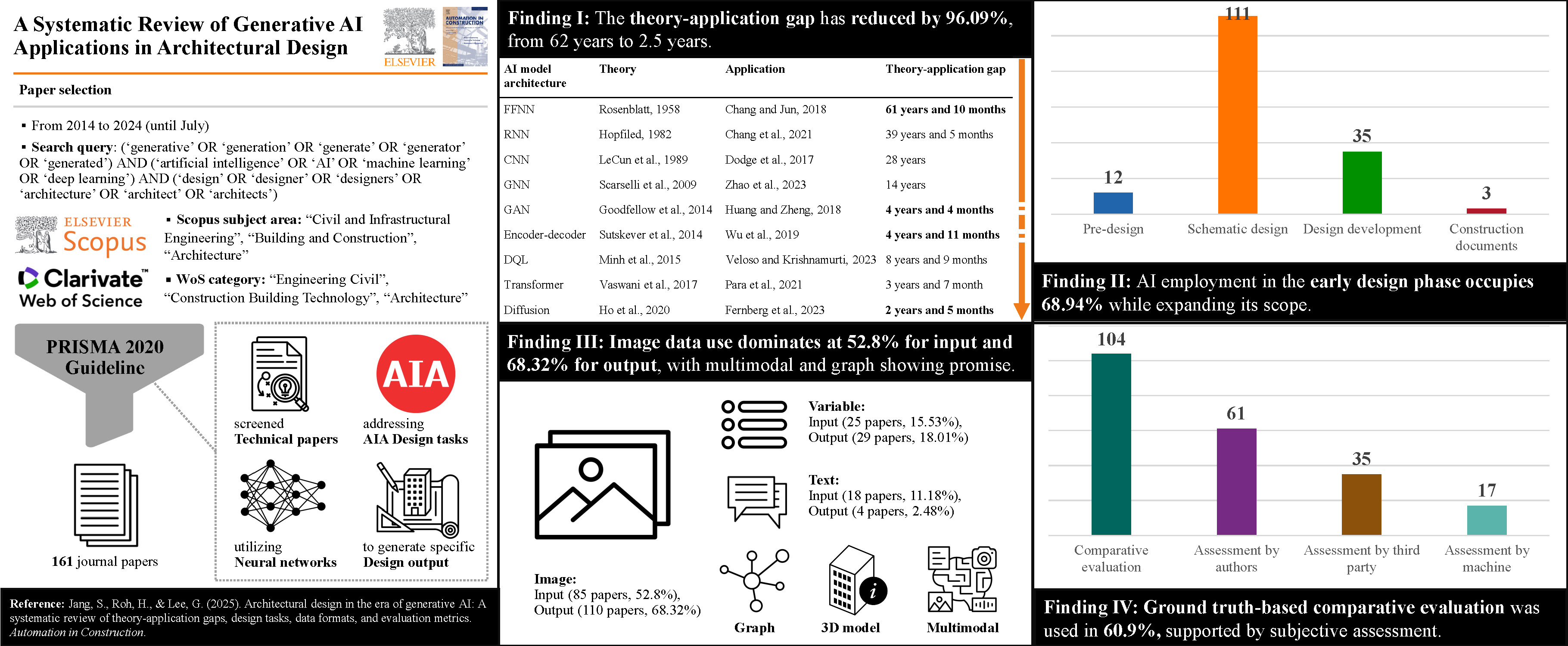
This study aims to propose a large language model (LLM)-enhanced defect question-answering (QA) method that can secure private and sensitive data while yielding high performance. Prompt responses to residents’ complaints are crucial for preventing recurring defects. However, traditional defect analysis and response methods rely on the expertise of a few skilled workers, making it difficult to ensure timely responses. The rapid advancement of LLMs offers a potential solution for improving defect QA tasks. However, many companies prohibit the use of closed-source LLM services, such as ChatGPT, due to concerns about potential data breaches. One possible solution is to use open-source LLMs like Llama and BERT, which can be locally installed and used. However, open-source LLMs typically perform worse than closed-source LLMs. Although the performance of open-source LLMs can be greatly improved through fine-tuning, the preparation of training datasets requires a significant amount of time and labor. To address these challenges, this study proposes a hybrid defect QA method that deploys an open-source LLM for defect management to secure sensitive information, and a closed-source LLM for generating a training dataset to reduce both the time and labor required. To validate the proposed method, we compare it to the state-of-the-art LLMs, GPT-4o and Llama 3, as well as graph retrieval-augmented generation (GraphRAG)-based QA systems, which have been extensively studied recently. Our results show that the hybrid LLM-based QA method achieved the highest ROUGE score of 81.6%. These findings demonstrate superior practical applicability, enabling cost-effective data generation and reliable domain adaptation within a secure data environment. This approach is beneficial for domain-specific tasks beyond defect management, where the accurate provision of specialized information and integration of historical knowledge are essential.
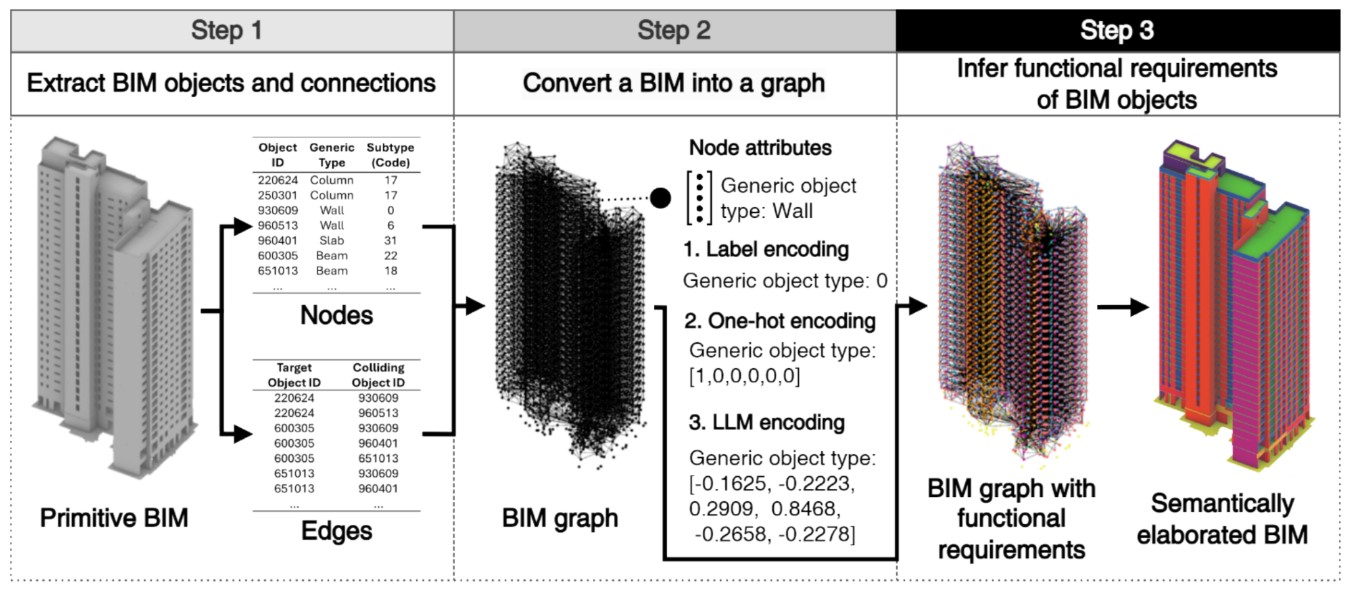
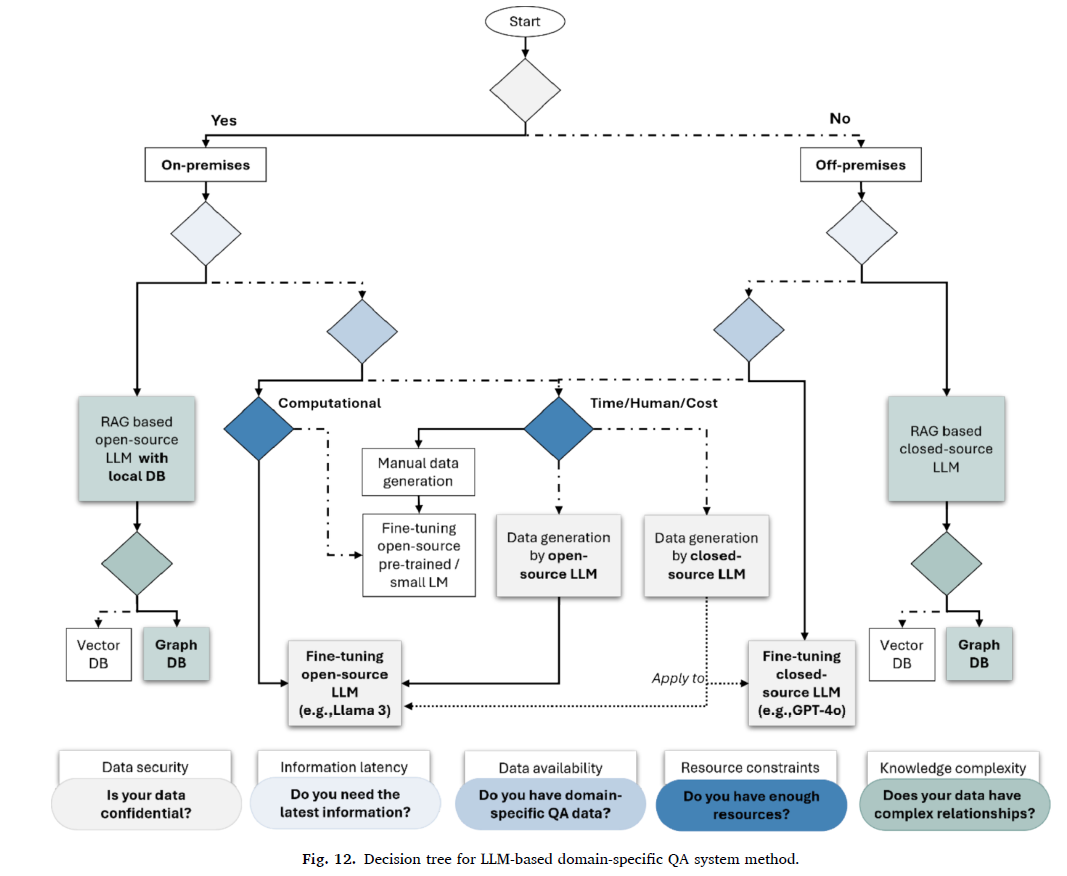
This study proposes a method to automatically subcategorize early object types in low levels of development (LODs) into detailed types (i.e., subtypes) with distinct functional requirements, such as insulation, waterproofing, and load-bearing. While rough cost estimation is possible in the early design phase without detailed object classifications, its accuracy is often limited. Subcategorizing generic objects like walls and columns into more detailed types enhances the precision of early-stage engineering analyses, including cost estimation, load assessments, and material takeoffs. Existing automated object subclassification methods rely on information extracted from highly detailed models, which are unavailable in early-stage building information models (BIMs) due to a lack of geometric and attributive distinctions. This study addresses these limitations by leveraging functional requirements inferred from object connections and placement in early BIMs, achieved using a graph neural network (GNN). To convert BIMs into graphs, a novel threshold-enhanced triangle intersection (TETI) algorithm is introduced, overcoming inaccuracies and exception-handling issues in existing methods. The study explores two GNN-based approaches: node property prediction and node prediction. The former distinguished generic object types into 14 detailed categories, but cost estimation required greater specificity. The latter successfully classified objects into 42 subtypes, with the best results achieved using semantically rich embeddings from a large language model (LLM) and GraphSAGE with three SAGE convolution layers, three hops, and 1,024 dimensions, yielding a weighted F1-score of 0.8766. This approach significantly reduces input data requirements compared to existing methods, enabling more accurate early identification of functional requirements in lowLOD BIMs and supporting both early engineering analyses and detailing processes.
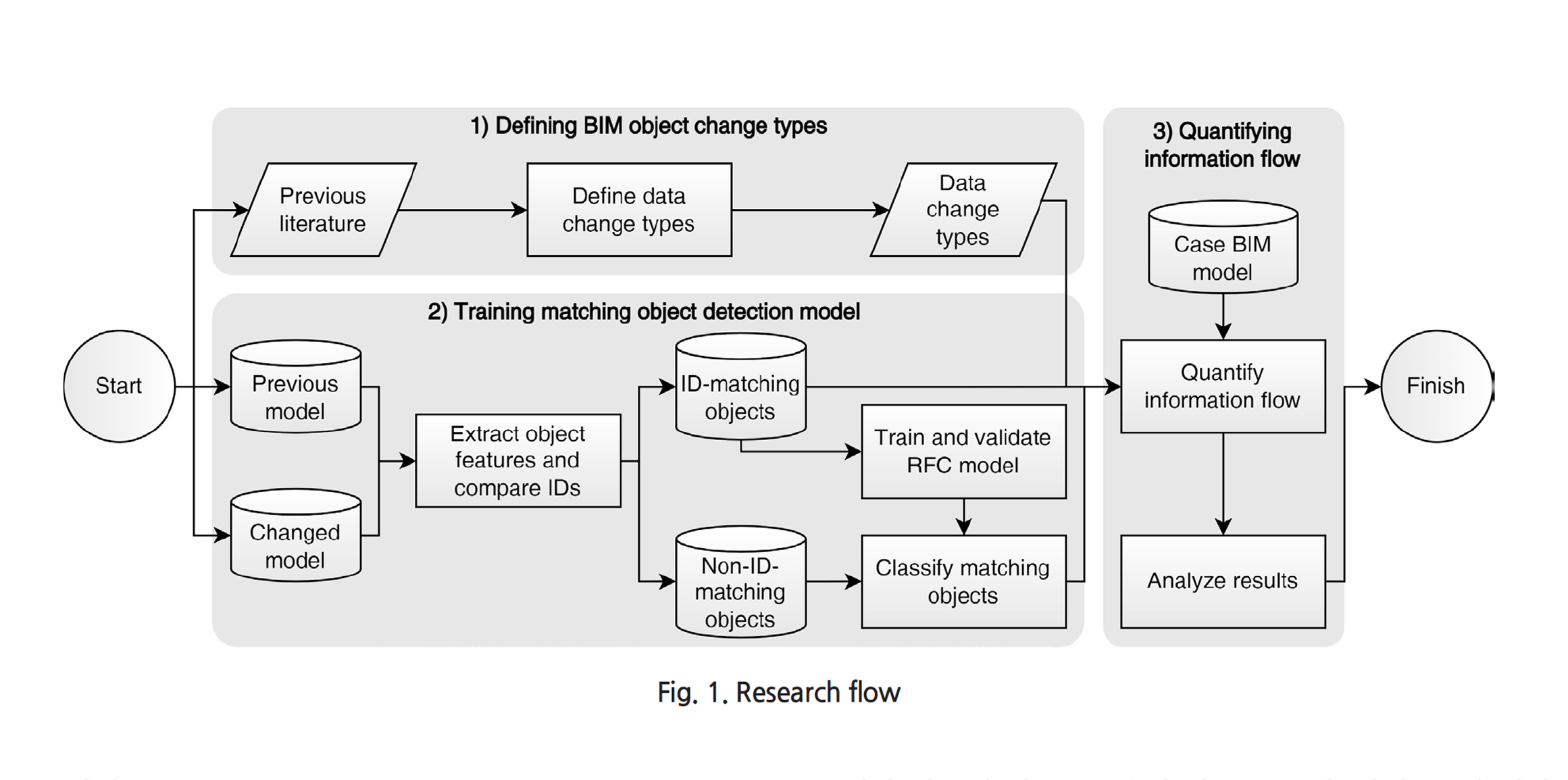
This paper introduces a novel method for quantifying changes in Building Information Modeling (BIM) object data during BIM-enabled design detailing process. A significant advantage of BIM is its ability to improve information flow, a crucial element in managing the design process. However, despite the importance of this capability, existing research lacks robust quantitative methods for monitoring the detailed stages of BIM authoring. To bridge this gap, we propose a systematic approach that involves three key steps: 1) defining the types of data changes, 2) developing a classifier to match and track BIM objects across consecutive models, and 3) applying a weighted Level of Development (LOD) framework to quantify the extent and significance of these changes. The proposed method was applied in a case study analyzing BIM models from the Schematic Design (SD), Design Development (DD), and Construction Documentation (CD) phases of a project. The results demonstrate that our approach effectively reflects and quantifies the progression of design changes between these phases. Moreover, the findings highlight the potential of this method to serve as a decision support tool, enhancing the management of the design process by providing detailed insights into the evolution and development of design details.
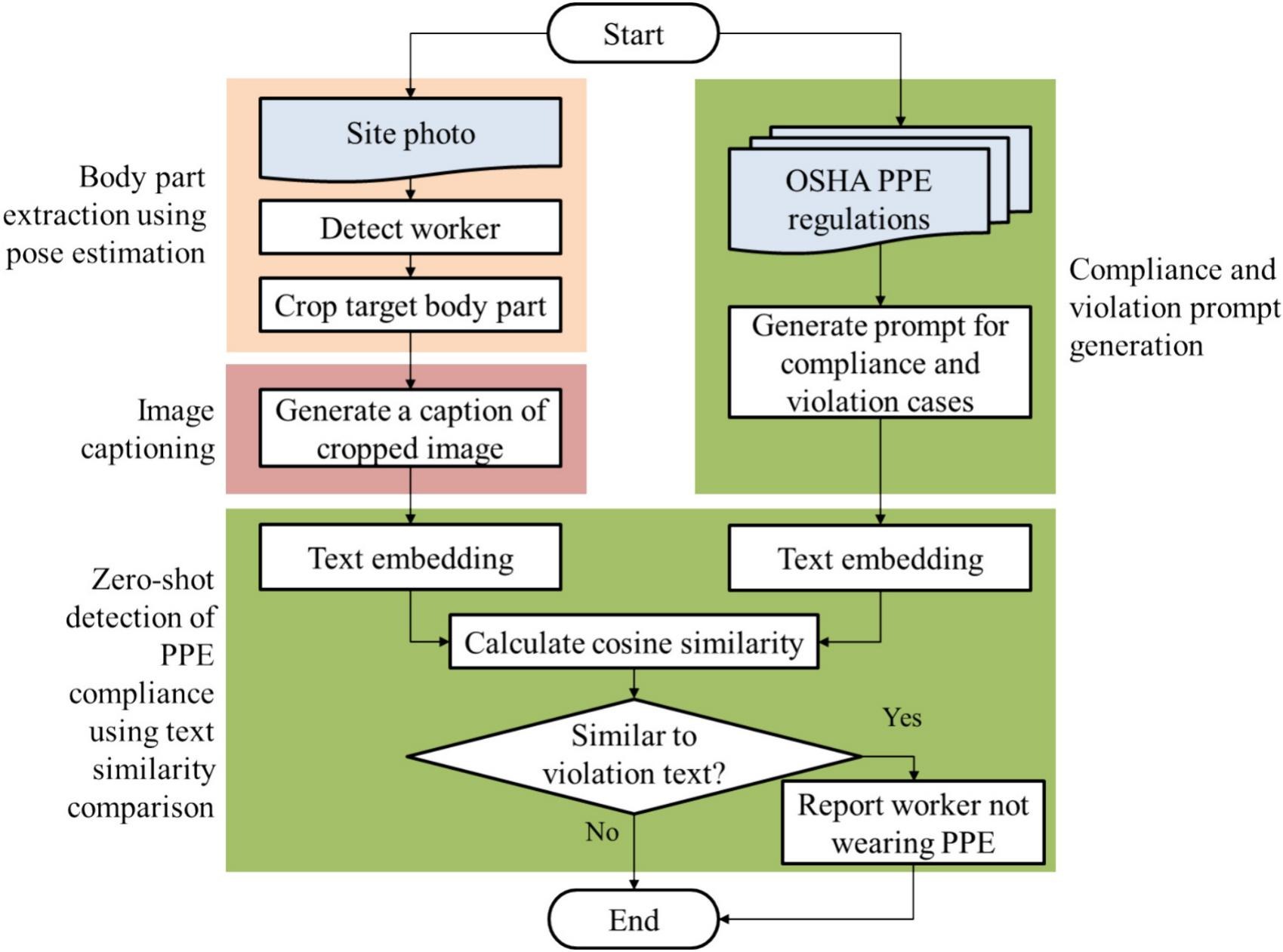
Previous studies have deployed object-detection-based approaches to automate personal protective equipment (PPE) safety monitoring. However, previously proposed methods require large amounts of labeled data for different PPE items. This study proposes a zero-shot PPE monitoring method that does not require a training process to overcome this problem. The proposed method comprises three steps. First, it detects workers onsite from images and crops body parts using human-body key points. Next, the cropped body images are described in text using image captioning. Finally, the extracted text is compared with prompts describing body parts wearing PPE, and safety is determined based on cosine similarity. Compared to the F1-score of 73.5% achieved by traditional object detection approaches trained on 50 images for hardhat monitoring, the proposed zero-shot approach demonstrates significant improvement with an F1-score of 82.6%. It also surpasses the previous zero-shot monitoring performance (an accuracy of 53%).
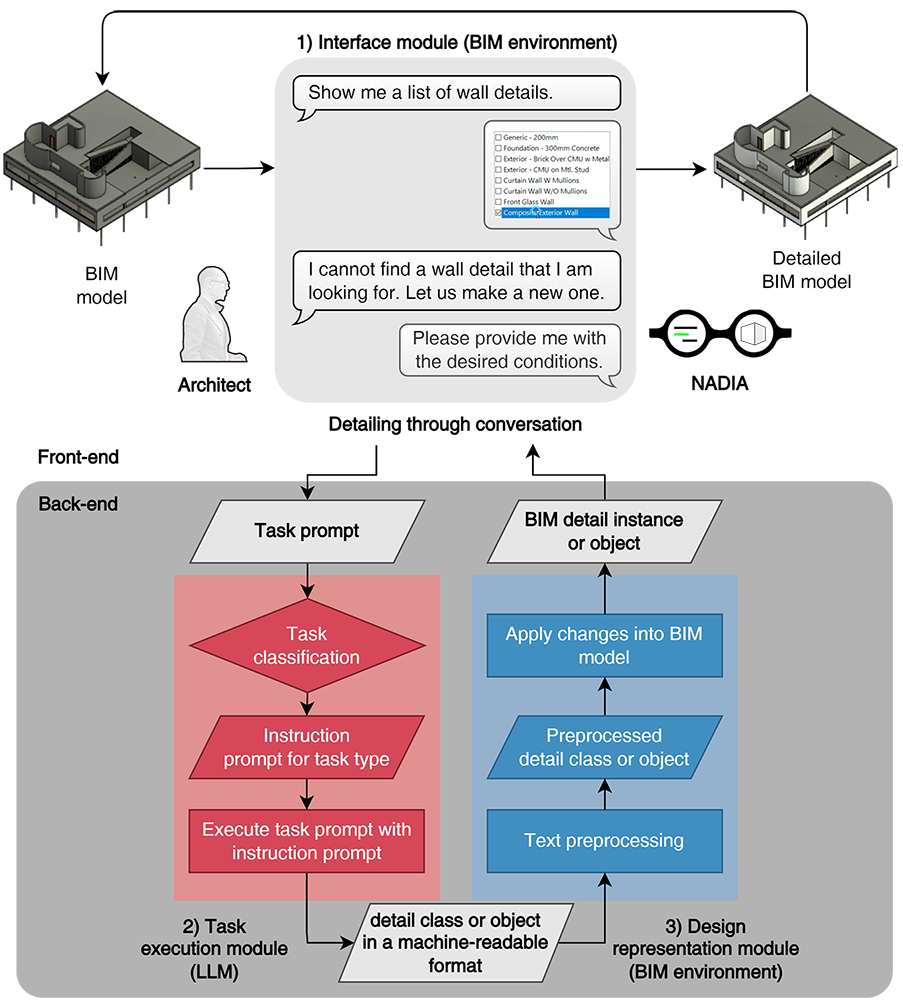
Learning building information modeling (BIM) systems has always been a challenge for BIM adoption. Although groundbreaking performances of large language models (LLMs) have inspired many researchers to consider an LLM as a potential BIM control method using natural language, a specific method of utilizing LLMs for automated BIM model detailing has not yet been proposed. This paper proposes an LLM-BIM chaining framework to enable architectural design detailing using natural language, instead of using menu-based user interfaces, named “Natural-language-based Architectural Detailing through Interaction with AI (NADIA)”. The NADIA framework is based on three main approaches: 1) separating the specification of the wall layers from the creation of the wall layers; 2) appropriate instruction prompting to guide the LLM to minimize irrational responses and produce engineering rational details; and 3) LLM-BIM chaining to seamlessly link a BIM authoring tool and an LLM. The effectiveness of NADIA was validated based on two main aspects: its accuracy in generating details that adhere to specified design requirements from users—as a design assistant—and its compliance with general engineering requirements—as a design consultant. The validation was achieved through tasks that involved generating 240 and 1,920 exterior wall details, respectively. NADIA achieved an average accuracy of 83.33% in generating logically coherent details in line with the required design conditions. For thermal performance requirements, it demonstrated a mean accuracy of 98.54% in complying with the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) 20.1-2019 standard. Despite being in its early stages, NADIA’s potential for developing and refining architectural details through natural language-based interactions between architects and machines is promising.
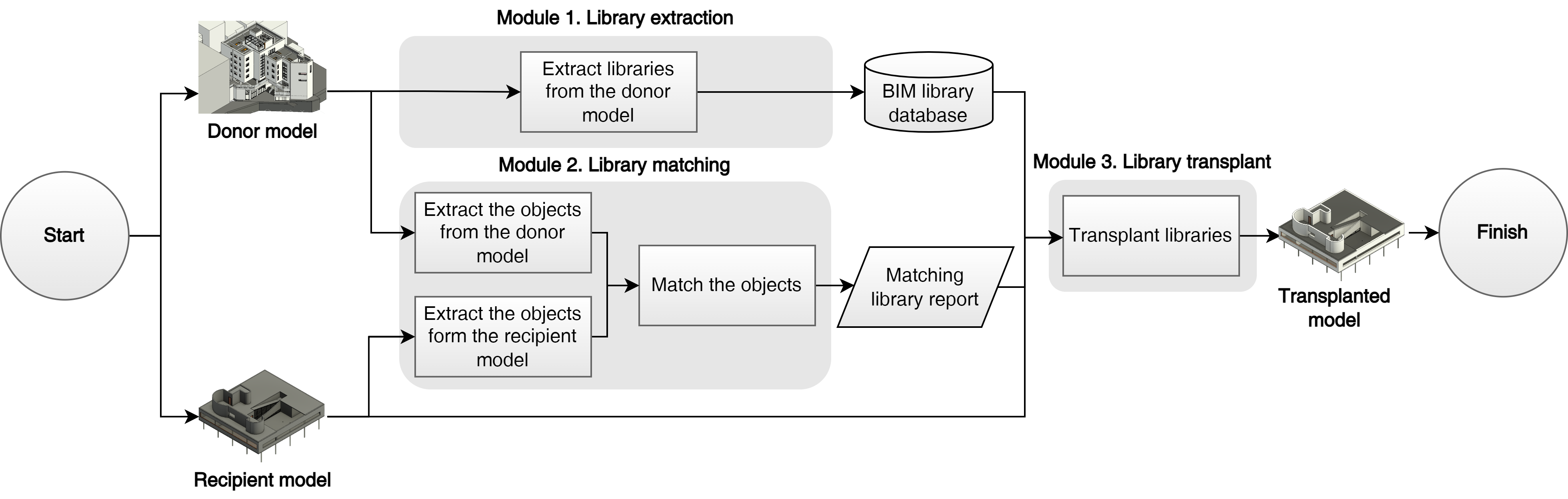
This study introduces a framework for transplanting a building information modeling (BIM) library. Design detailing constitutes 50% to 60% of the total design time, even within the BIM context. Previous studies have highlighted the potential of integrating BIM and artificial intelligence (AI) for enhanced productivity. However, challenges arise due to architects’ preferences for unique project-specific details when applying generalized AI approaches based on big data. To address this, we propose a BIM library transplant framework. This framework automatically identifies objects at a high level of development (LOD) from a selected existing BIM model (i.e., a donor model) and matches them with low-LOD objects in a new model (i.e., a recipient model). Subsequently, it replaces the low-LOD objects with corresponding high-LOD objects. The framework involves three steps: 1) extracting the library from the donor model, 2) matching the library, and 3) transplanting the library from the donor to recipient model. To validate its efficacy, we implemented the BIM library transplant framework as a Revit add-on, employing the random forest classifier as the library-matching AI model. Our results indicate that the implemented framework has the potential to reduce detailing time by approximately 60% to 70%, while achieving an accuracy range of 65% to 80%.
Large amounts of data are often categorized using different systems. In such cases, few-shot and unsupervised text classification are the two main approaches for dynamically classifying text into a single classification. Unsupervised text classification typically exhibits lower performance but requires significantly less data preparation effort and computing resources than the few-shot approach. This study proposes two methods to enhance unsupervised text classification for domain-specific non-English text using improved domain corpus embedding: 1) weighted embedding-based anchor word clustering (wean-Clustering), and 2) cosine-similarity-based classification using a defect corpus that is vectorized by fine-tuned pretrained language models (sim-Classification-ftPLM). The proposed methods were tested on 40,765 Korean building defect complaints and achieved F1 scores of 89.12% and 84.66% respectively, outperforming the state-of-the-art zero-shot (53.79%) and few-shot (72.63%) text classification methods, with minimal data preparation effort and computing resources.
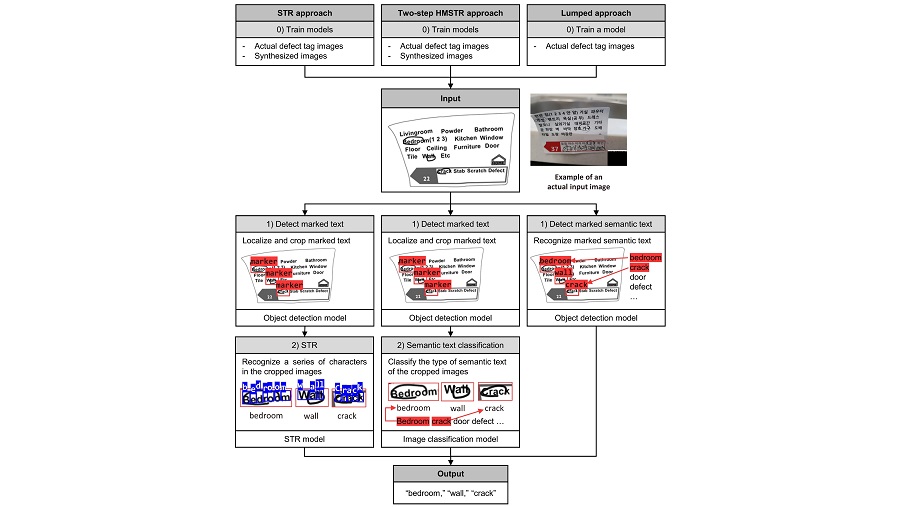
Automated text recognition techniques have made significant advancements; however, certain tasks still present challenges. This study is motivated by the need to automatically recognize hand-marked text on construction defect tags among millions of photographs. To address this challenge, we investigated three methods for automating hand-marked semantic text recognition (HMSTR)—a modified scene text recognition-based (STR) approach, a two-step HMSTR approach, and a lumped approach. The STR approach involves locating marked text using an object detection model and recognizing it using a competition-winning STR model. Similarly, the two-step HMSTR approach first localizes the marked text and then recognizes the semantic text using an image classification model. By contrast, the lumped approach performs both localization and identification of marked semantic text in a single step using object detection. Among these approaches, the two-step HMSTR approach achieved the highest F1 score (0.92) for recognizing circled text, followed by the STR approach (0.87) and the lumped approach (0.78). To validate the generalizability of the two-step HMSTR approach, subsequent experiments were conducted using check-marked text, resulting in an F1 score of 0.88. Although the proposed methods have been tested specifically with tags, they can be extended to recognize marked text in reports or books.
This paper provides an overview of South Korea's 20-year journey in adopting building information modeling (BIM) and future direction. It first discusses the six phases of BIM adoption in South Korea, starting from the use of BIM as a marketing tool to its current intelligent BIM phase. The government's support for BIM-related research and development projects is also highlighted, with a focus on the artificial intelligence (AI)-based architectural design automation project. As the future direction, it explores the integration of AI with BIM in both local and global contexts. The paper presents AI-powered architectural design methods, including AI-powered early architectural design generation and architectural detailing. Compared to AI-based early architectural design generation, architectural detailing is an unexplored research topic. This paper introduces two AI- and BIM-based architectural detailing methods, being developed at Yonsei University: namely, BIM library transplant and Natural language-based Architectural Detailing through Interaction with AI (NADIA). These methods demonstrate how AI-enhanced BIM can enable architects to interactively develop building details using a language model as a conversational AI and a knowledge base, and a BIM authoring tool as a design platform, in the near future.
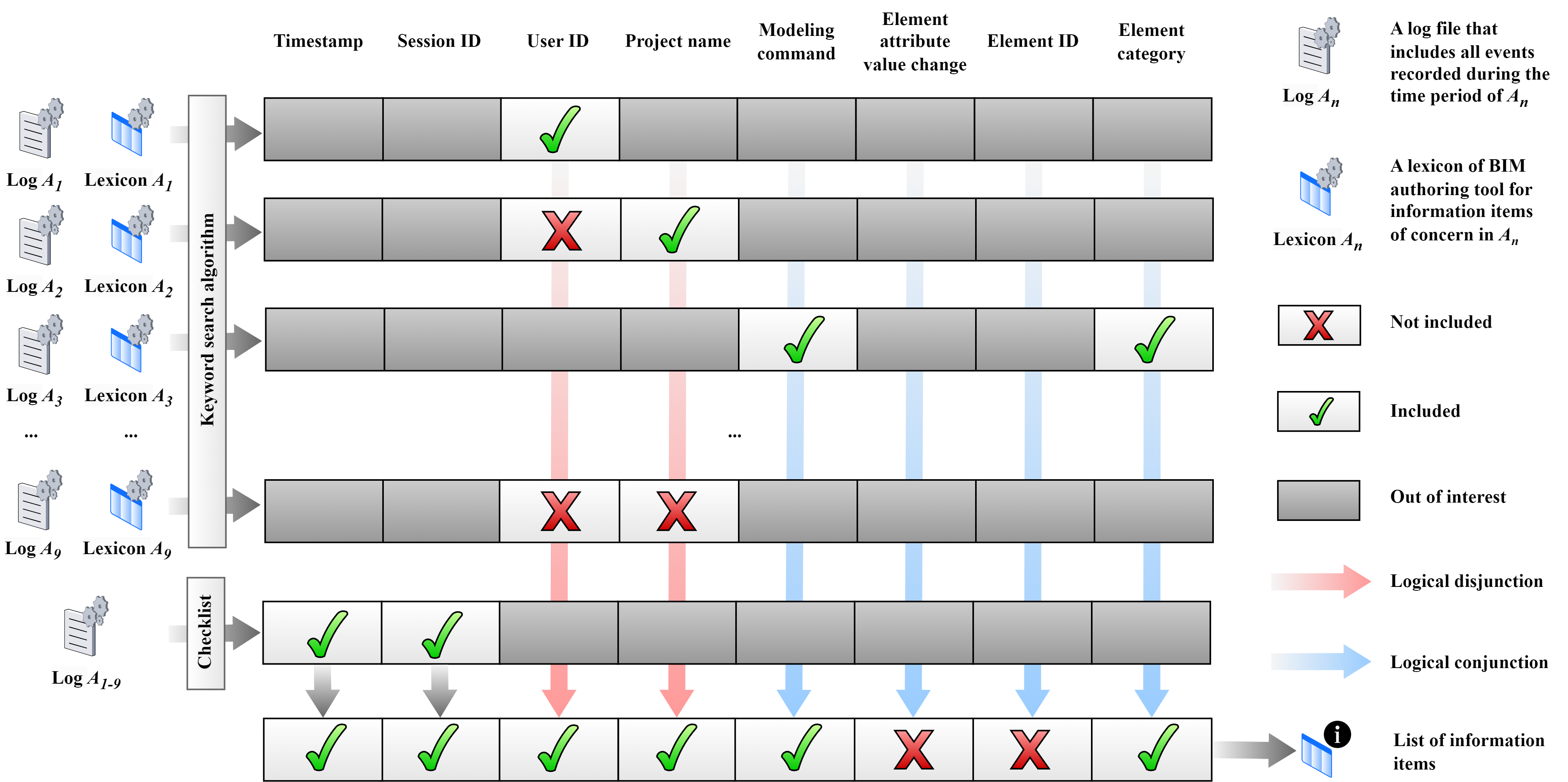
This study conducted a lexicon-based content analysis of building information modeling (BIM) logs from four major BIM authoring tools and four custom-developed BIM loggers to understand whether the BIM logs satisfy the information requirements for various BIM log mining use cases, as well as to assess their potential for future development and research. First, through a critical review of previous studies, 19 different ways of using BIM logs were identified, including authoring and collaborative pattern discovery, authoring process modeling, collaboration pattern analysis, command predictions, and team optimization; however, most of the uses concerned process discovery. The analysis also revealed that BIM log mining has mainly been used for the design phase, with a few examples of being used for the construction phase. For BIM log mining, various techniques ranging from simple frequency analyses via social network analyses to advanced pattern discovery were deployed. In terms of BIM log sources, native BIM logs from Revit were dominantly used almost in all studies, aside from a few studies that used custom-developed BIM logs. The content analysis of BIM logs showed that the contents of native BIM logs provided by major BIM authoring tools varied, but commonly lacked model-element-specific information; this limitation prevents in-depth analyses of BIM processes. Overall, the current disproportionate focus on process discovery in the design phase of BIM log mining suggests that the application of BIM log mining is still in its early stages and holds significant potential for other project phases if adding model-element-specific information is incorporated.
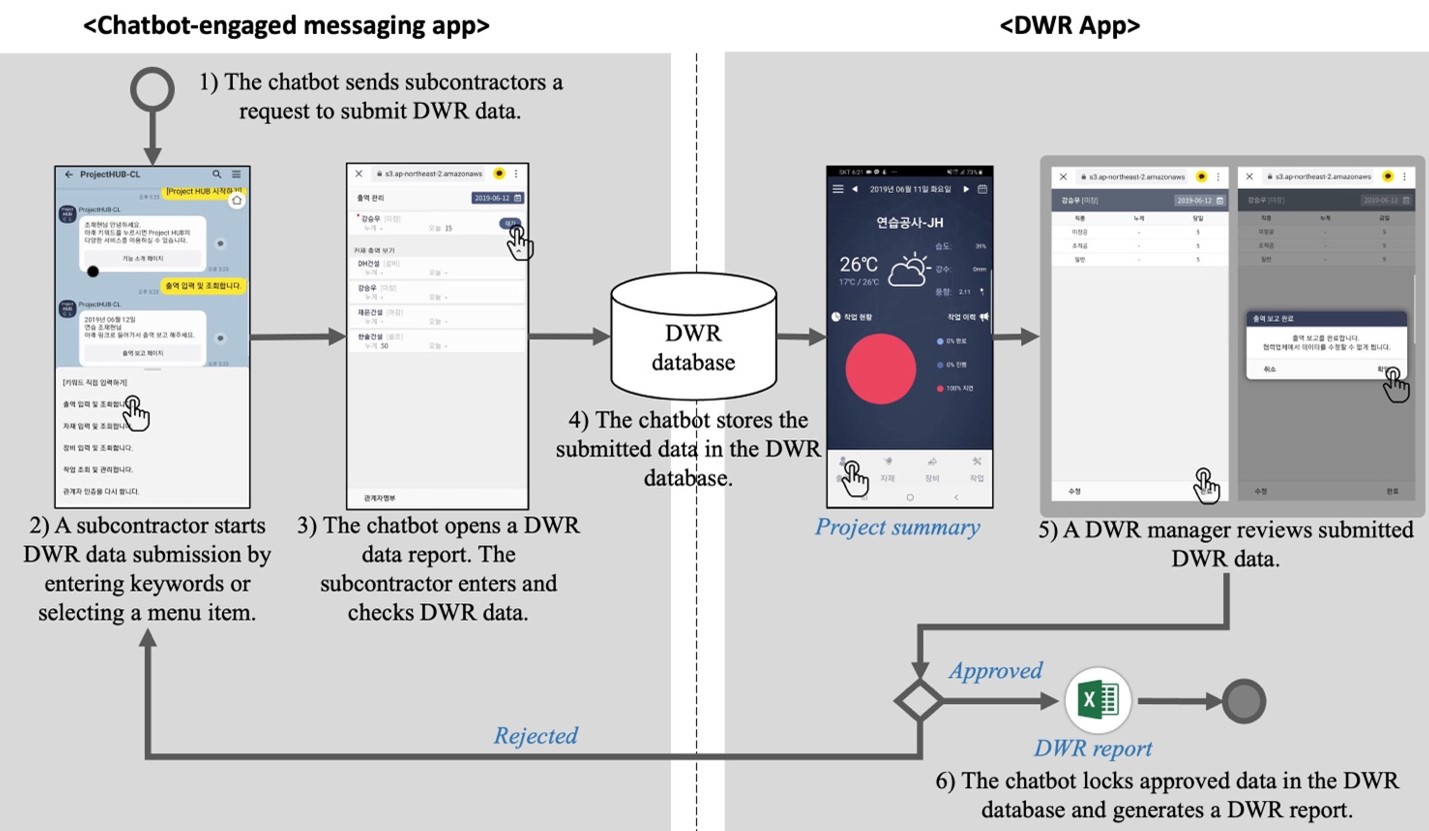
This paper proposes a chatbot-engaged system for supporting construction daily work reports (DWR) using a mobile messenger. Although mobile messengers are commonly used by project participants, they do not provide functions for capturing, managing, and storing DWR data. To address these limitations, the authors developed a chatbot-engaged messenger and a mobile app that allow general contractors (GCs) to interactively collect and manage data from subcontractors (SCs). A field applicability test of the proposed system was conducted at three construction sites. The results of the functionality test confirmed that the chatbot-engaged messenger fully supports DWR tasks, while significantly reducing the time spent. The usability test revealed that a two-pronged approach, involving a chatbot-engaged messenger for SCs and a mobile DWR management app for GCs, is an effective solution. Key considerations as well as information requirements for a messenger-based DWR system are also identified.
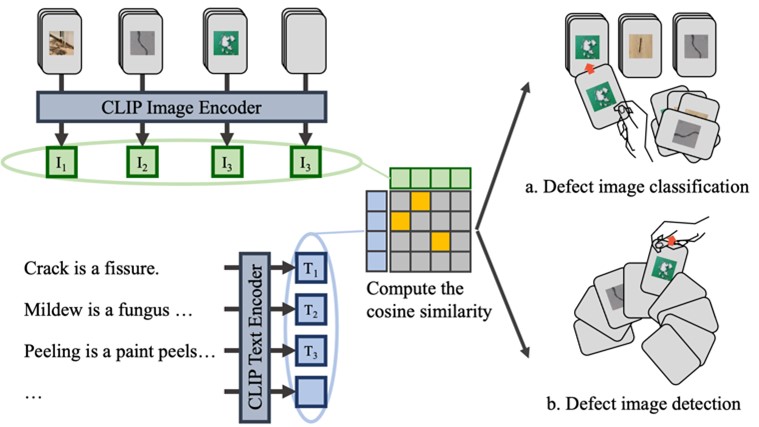
Zero-shot learning, applied with vision-language pretrained (VLP) models, are expected to be an alternative to existing deep learning models for defect detection, under insufficient dataset. However, VLP models, including contrastive language-image pre-training (CLIP), showed fluctuated performance on prompts (inputs), resulting in research on prompt engineering—optimization of prompts for improving performance. Therefore, this study aims to identify the features of a prompt that can yield the best performance in classifying and detecting building defects using the zero-shot and few-shot capabilities of CLIP. The results reveal the following: (1) domain-specific definitions are better than general definitions and images; (2) a complete sentence is better than a set of core terms; and (3) multimodal information is better than single-modal information. The resulting detection performance using the proposed prompting method outperformed that of existing supervised models.
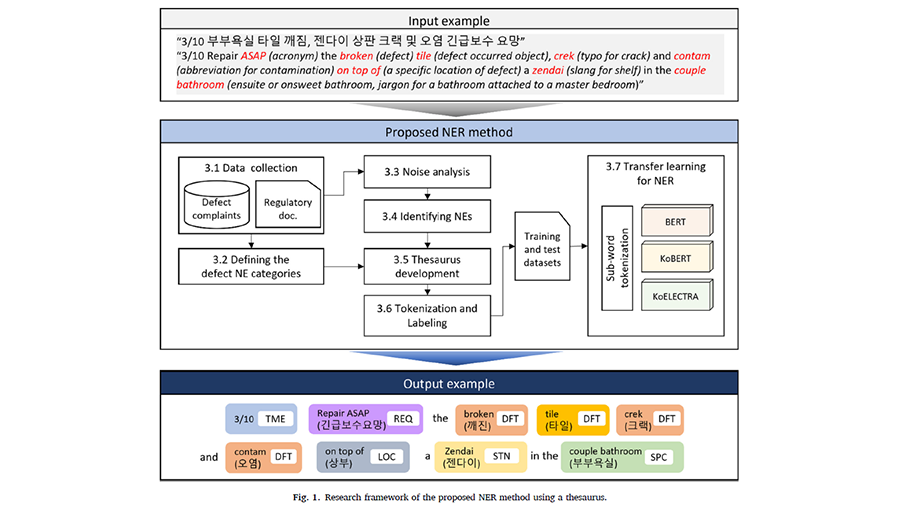
Neither traditional rule-based named entity recognition (NER) nor the latest language models perform well in information extraction from noisy text—the text that contains linguistic errors, slang, loanwords, and jargon. Building defect complaints filed by residents via online systems is a representative example of such noisy text. This paper proposes an NER method for automatically extracting defect information from noisy text using a defect thesaurus and transfer learning. The thesaurus built herein included 1097 defect named entities in 23 categories. The NER performance was tested using 69,750 defect complaints through transfer learning of three representative pre-trained language models: Multilingual Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT), Korean BERT (KoBERT), and Korean Efficiently Learning an Encoder that Classifies Token Replacements Accurately (KoELECTRA). The proposed method achieved an average F1 score of 91.0% using KoBERT. This NER performance was higher than that of the open benchmark NER performance for clean text (86.1%).
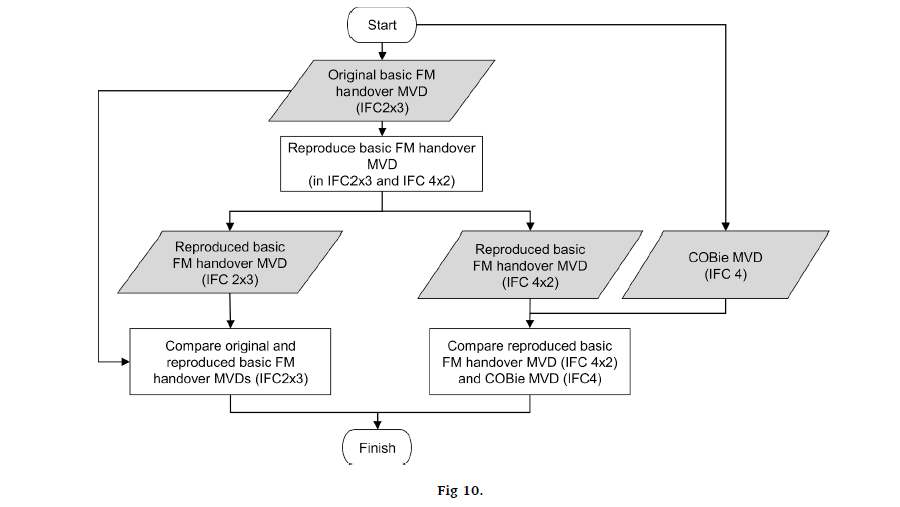
The development of an integrated information delivery manual (IDM) and model view definition (MVD) using the buildingSMART Data Dictionary (bSDD) as a lexicon has been identified as an ideal way of developing IDMs and MVDs. Several previous studies proposed methods to integrate the IDM and MVD development process. However, they were inherently limited in various ways because they were proposed before the core relevant technologies were ready. This study proposes an integrated IDM and MVD development method using bSDD as a lexicon based on three international standards—ISO 12006-3, ISO 16739-1, and ISO 29481-3. In particular, ISO 29481-3 is deployed as a core data schema to integrate the entire process. ISO 29481-3, of which the authors were the main developers, is a new ISO standard that specifies the information delivery manual XML schema definition (idmXSD). In addition, the concept-based MVD generation algorithm was adopted to generate a syntactically valid MVD. The proposed method was validated against the basic Facility Management (FM) Handover MVD and the Construction–Operations Building Information Exchange (COBie) MVD. The proposed approach is expected to help facilitate the development of IDM and MVD by allowing developers to utilize bSDD as a common lexicon and share and repurpose existing IDMs and their relationships to MVDs in a machine-readable format using idmXSD.
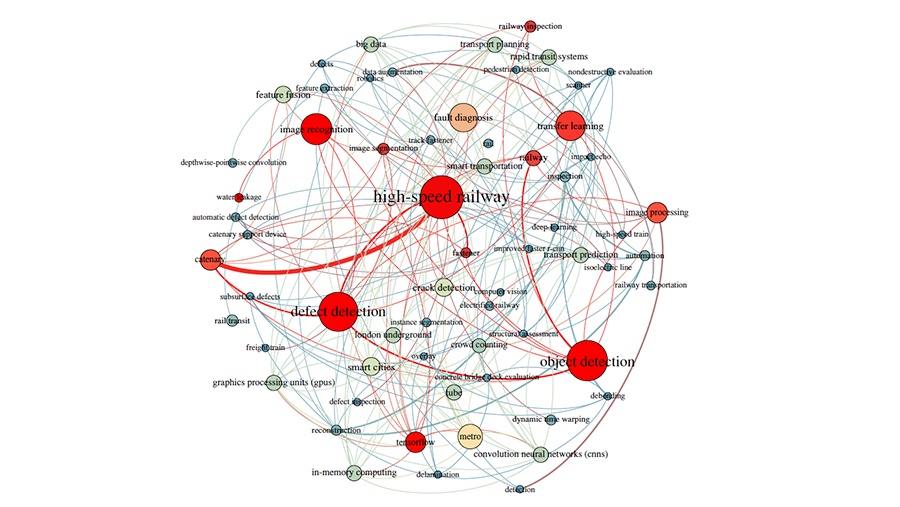
This study reviewed the status quo of research on machine learning (ML), including deep learning, in the rail industry. This study conducted a scientometric analysis and critical review of 640 papers selected from 12,675 web-crawled papers. The extensive and complex networks of topics, researchers, and countries were analyzed using the Louvain method, a co-occurrence keyword analysis, a degree centrality analysis, and other network analysis methods. The results indicate that the majority of studies of ML in the rail industry focused on maintenance activities and traffic management, and mainly targeted rolling stock, rails, and passengers. Overhead contact systems, including catenaries, are a high-demand objective for ML-based maintenance. Although analyses of tunnels and stations remain rare, passenger flow prediction, station air quality estimation, shield tunneling performance improvement, and ground settlement are areas of high importance. Geographically, China, the US, and the United Kingdom lead ML studies in the rail industry, and the level of collaboration is higher among European countries than among countries on other continents. Future challenges include ensuring the security and stability of ML, along with considering novel mindsets, the black-box effect, improvements in ML techniques, and resource overload when introducing ML technologies.
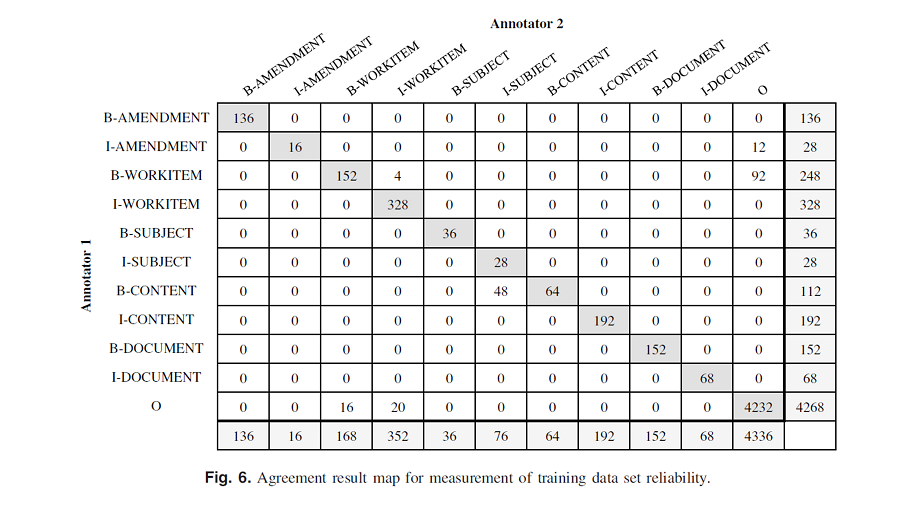
Change orders are documents that describe a specific contract amendment to the original scope of work. Historical change orders are invaluable information sources that can provide practical and proven solutions for developing new change orders from similar cases. However, current change order management systems are not efficient in searching for and finding the most related and similar change orders due to inherent weaknesses in current archiving and search processes, such as keyword-based or reason code–based search. This study proposes and develops a natural language processing (NLP)–driven model that can significantly improve the accuracy and reliability of searching cases by restructuring how each change order’s information is stored and retrieved in change order management systems. The NLP-driven model proposed in this study can automatically detect change reasons and altered work items through text representation pattern analysis and training. The proposed model applies semantic frames to define essential semantic components and determines syntactic features for text representation pattern analysis. The model also utilizes a conditional random field (CRF) classifier, which can consider contexts in sequential texts at the model training stage. The proposed model can significantly improve the accuracy and relevancy of the search process to find the most similar cases by allowing context-driven classification, archiving, and retrieval of change orders.
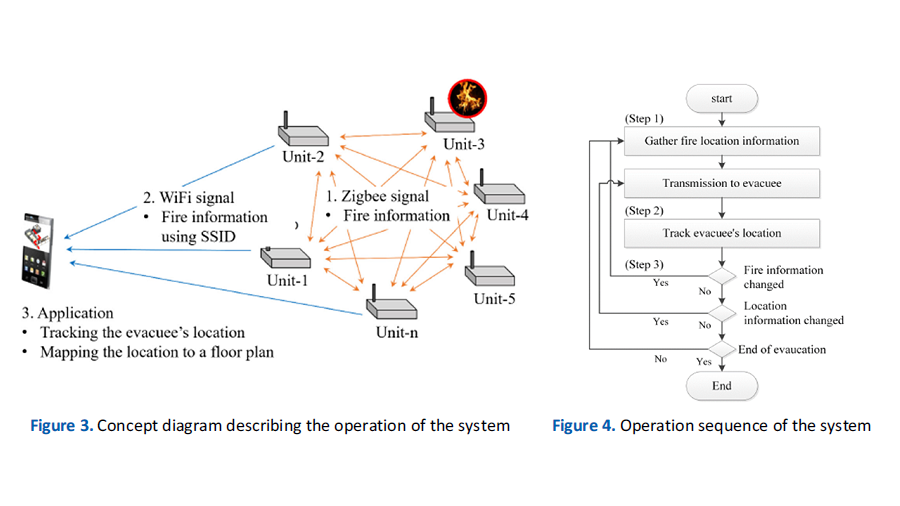
If a fire breaks out in a building, occupants can evacuate more rapidly if they are able to identify the location of the fire, the exits, and themselves. This study derives the requirements of system development, such as distance non-limitation, a non-additional device, a non-centralized server system, and low power for an emergency, to identify information about the fire and the location of evacuees. The objective is to receive and transmit information and reduce the time and effort of the database for location tracking. Accordingly, this study develops a server-independent system that collects information related to a building fire and an evacuee’s location and provides information to the evacuee on their mobile device. The system is composed of a transmitting unit to disseminate fire location information and a mobile device application to determine the locations of the fire and the evacuee. The developed system can contribute to reducing the damage to humans because evacuees can identify the location of the fire, exits, and themselves regardless of the impaired server system by fire, the interruption of power source, and the evacuee’s location. Furthermore, this study proposes a theoretical basis for reducing the effort required for database construction of the k-nearest neighbor fingerprint.
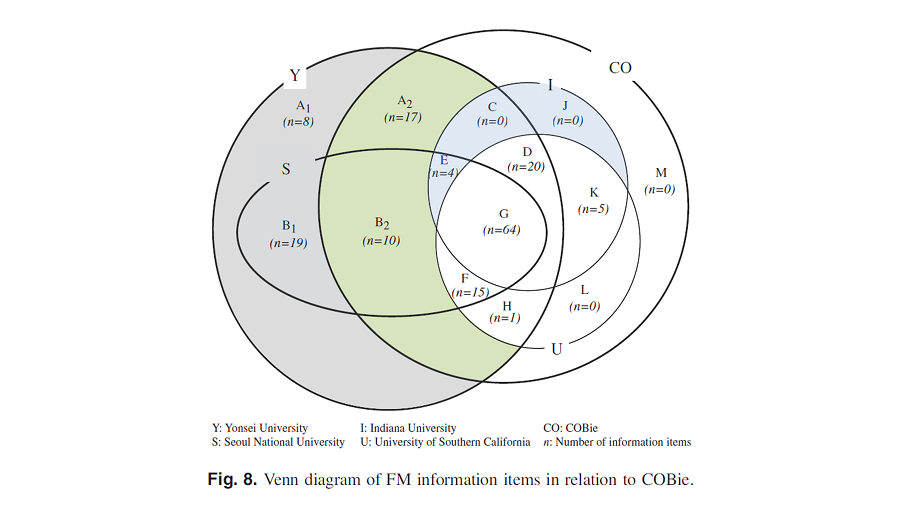
This study analyzes in detail the information requirements for managing higher education facilities by building information modeling (BIM). This is achieved by conducting a job shadowing quarterly for a year, a document content analysis of facility management (FM) documents, expert interviews, and a comparative analysis of the FM information obtained from two universities each in the US and South Korea. The comparative analysis involves mapping the information requirements specified in different formats from the construction operations building information exchange (COBie) data format. The analysis reveals that although there are certain differences between the information required in the US and South Korea, most of the FM information requirements (83.4%, 136 items) can still be supported by COBie. The remainder of the unsupported information (16.6%, 27 items) is ignorable because it is associated with the information only acquirable during the FM phase and cannot be supported by the BIM handover or COBie. This finding increases the possibility of mandating COBie as data requirements for higher education facilities in extended regions.
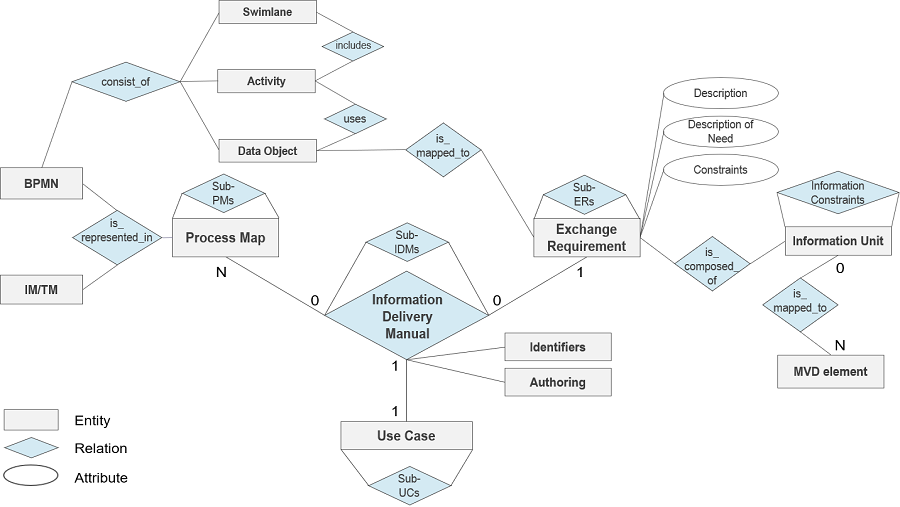
This study proposes a relational framework for standardized machine-applicable, readable, and transferable (smart) information delivery manual (IDM) specifications. As the demand for projects using building information modeling (BIM) increases, there is a more acute awareness and need for clearly defined information requirements to support the BIM projects. The ISO 29481-1 IDM standard defines how to specify exchange requirements (ERs) and their use cases (UCs) using a process map (PM). However, IDM specifications are currently not easily sharable or reusable due to the lack of a commonly accepted standard data schema. This study overcomes this problem by identifying definitions and relationships of IDM components to develop the relational framework for an IDM data schema. An extensive review of existing IDM-related documents and standards, and iterative international meetings, were conducted by 46 international IDM experts from 16 countries. A consensus on the relational framework was then reached through three Delphi survey rounds. The formalized relational IDM framework lays a foundation for further developing an IDM data schema as an international standard.
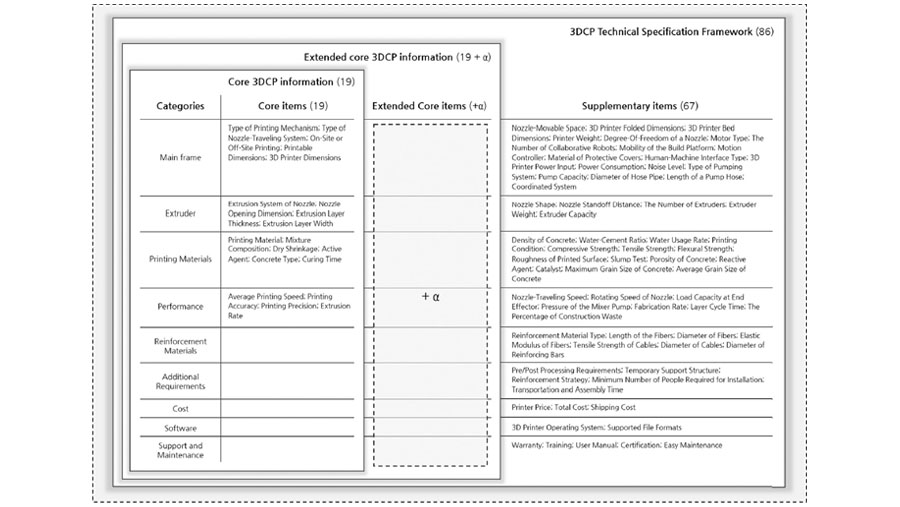
In this paper, we propose a technical specification framework for three-dimensional concrete printers (3DCPs) by analyzing 139 academic papers from 1997 to 2020, 98 3DCPs, and a Delphi survey with 22 3DCP experts. Despite the rapid growth of 3DCP research and market, there is no commonly acceptable technical specification framework for comparative analysis of 3DCPs with diverse characteristics. For deriving a common technical specification framework for various 3DCPs, this study first compiled 1604 technical specification items through a literature review. The technical specification items were restructured into nine categories and 90 items by removing identical terms, merging synonyms, and excluding items that appeared only once. The 3DCP expert panel reached a consensus on 86 items as significant 3DCP properties following three rounds of a Delphi survey. Finally, a 3DCP technical specification framework with 19 core and 67 supplementary technical specification items in nine categories was proposed based on the analysis.
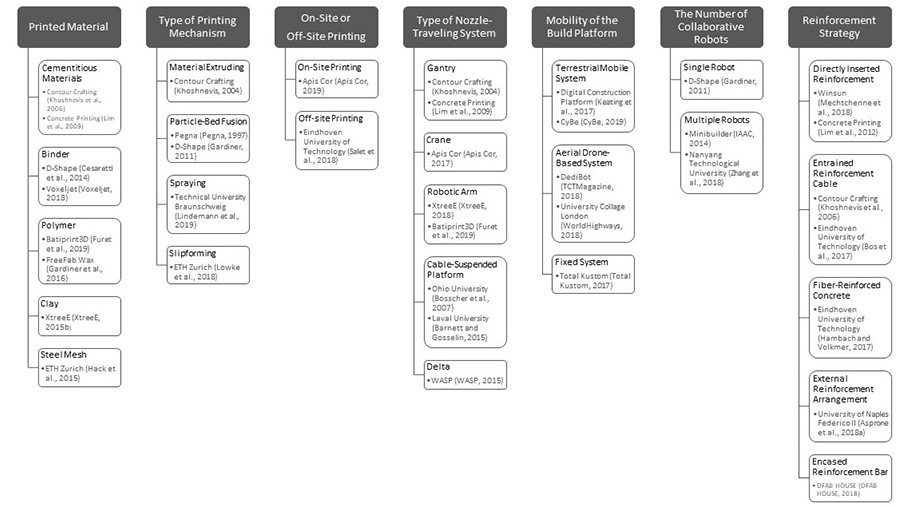
This study reviews and comparatively analyzes existing classification systems for 3D concrete printers to propose a classification system for 3D concrete printers. Several classifications for existing 3D printers have been proposed and used in the market. Nevertheless, quite a few of the printer types such as fused deposition modeling (FDM) and selective laser melting (SLM) are not suitable for characterizing 3D concrete printers. To derive the properties that distinguish one 3D concrete printer type from the others, this study reviews existing 3D concrete printers and comparatively analyzes the properties of 3D concrete printers identified in previous studies. The results show that existing classifications do not reflect the states-of-the-art of 3D concrete printers, the classification terms are ambiguous, and the entire printing processes are not considered. A new classification system was proposed based on the essential properties of the 3D concrete printers identified through the analysis of related work. The result of this study can be used as a basis for classifying commercial 3D concrete printers as well as studies related to 3D concrete printers.

This is an editorial for the special issue on "BIM policy and management" of Construction Management and Economics. This article reviews BIM from the people, process, technology, and policy (PPTP) points of view, introduces the articles in the special issue, and discusses the future directions and issues.
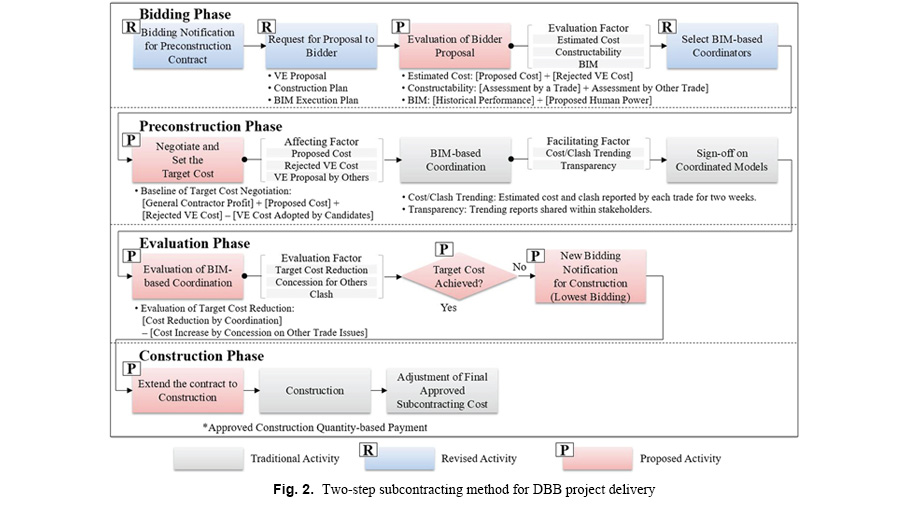
This paper introduces a two-step subcontracting process for building information modeling (BIM)–based design coordination under a design-bid-build (DBB) contract. Although integrated project delivery (IPD) is known to be an ideal contractual method for BIM projects, DBB still has been the dominant contracting method, owing to the complexity of IPD, as well as regional regulations. BIM-based design coordination under DBB can effectively reduce design errors through the value engineering process. However, in practice, the cost reduction realized under DBB is minimal because, unlike under IPD, DBB contracts do not provide incentives for subcontractors to reduce costs. This study proposes that subcontracting be divided into two phases: preconstruction and construction. Only subcontractors who meet the target costs during BIM-based design coordination in the preconstruction phase win the right to work during the construction phase. From case studies, this study finds quantitative cost reductions from this change in the preconstruction process. This study also reveals the manner in which this two-phase process impacts subcontractors’ attitudes toward cost-reduction efforts. These findings contribute to maximizing the efficiency of BIM-based design coordination, which will eventually contribute to more efficient delivery of construction projects.
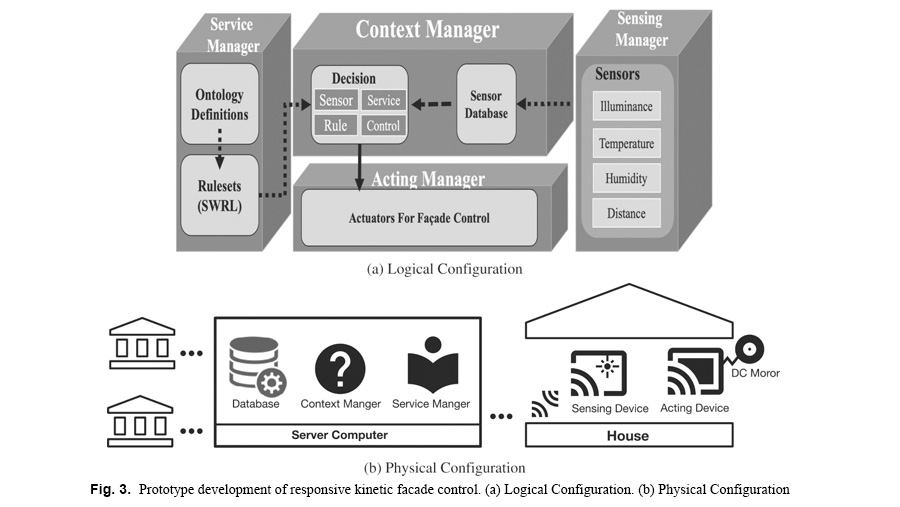
The elderly suffer from discomfort in social life owing to the decline of their physical, psychological, and social functions. The elderly who spend a lot of time indoors requires an intelligent system to extend their time to live independently in a residential environment. Recently, the Ambient Assisted Living (AAL) concept was introduced to commercialize various technologies and apply them to urban and architectural environments. However, AAL’s connection to architectural elements is insufficient. This study intends to build a residential environment platform that integrates Internet of Things (IoT) technology and architectural elements to support the independence of the elderly based on the AAL concept. The proposed platform is designed to be applied to various scenarios and services. A responsive façade system was designed to verify the platform, and the usefulness of the system was evaluated through the interaction of the designed façade and an acting manager.
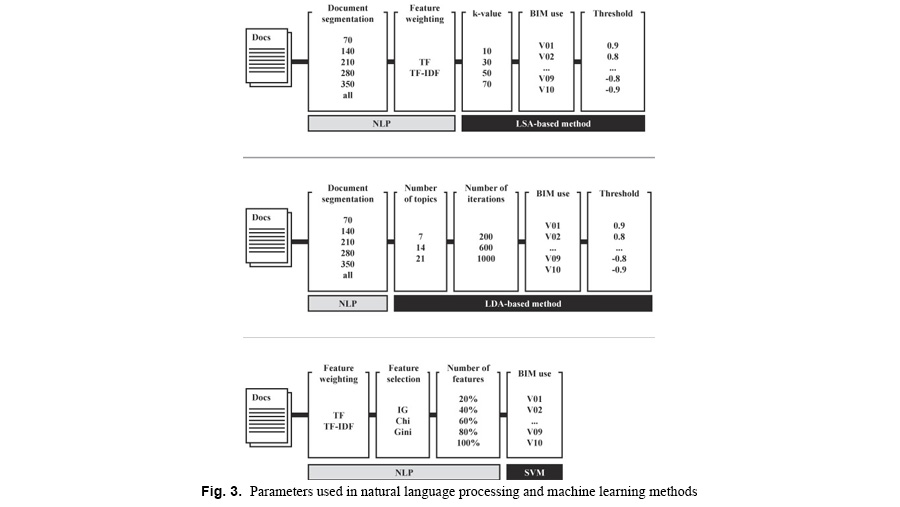
This paper comparatively analyzes a method to automatically classify case studies of building information modeling (BIM) in construction projects by BIM use. It generally takes a minimum of thirty minutes to hours of collection and review and an average of four information sources to identify a project that has used BIM in a manner that is of interest. To automate and expedite the analysis tasks, this study deployed natural language processing (NLP) and commonly used unsupervised learning for text classification, namely latent semantic analysis (LSA) and latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA). The results were validated against one of representative supervised learning methods for text classification—support vector machine (SVM). When LSA and LDA detected phrases in a BIM case study that had higher similarity values to the definition of each BIM use than the threshold values, the system determined that the project had deployed BIM in the detected approach. For the classification of BIM use, the BIM uses specified by Pennsylvania State University were utilized. The approach was validated using 240 BIM case studies (512,892 features). When BIM uses were employed in a project, the project was labeled as “1”; when they were not, the project was labeled as “0.” The performance was analyzed by changing parameters: namely, document segmentation, feature weighting, dimensionality reduction coefficient (k-value), the number of topics, and the number of iterations. LDA yielded the highest F1 score, 80.75% on average. LDA and LSA yielded high recall and low precision in most cases. Conversely, SVM yielded high precision and low recall in most cases and fluctuations in F1 scores.
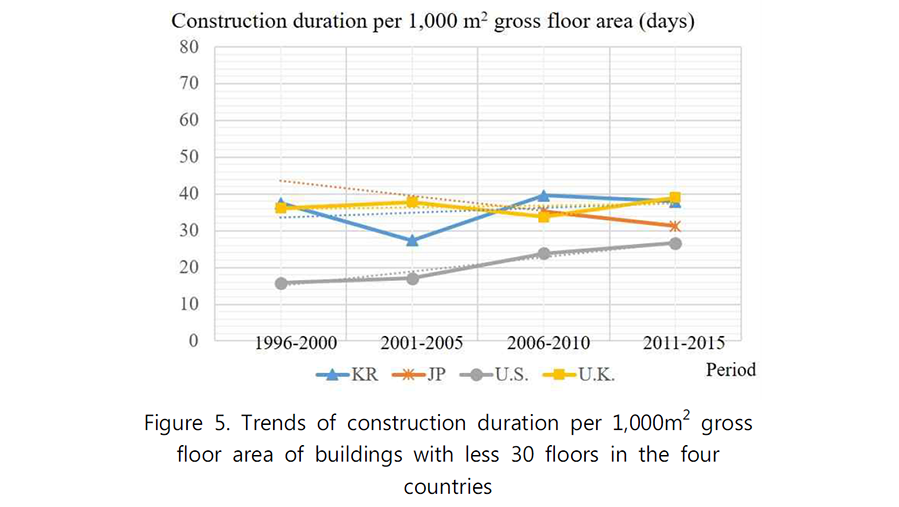
To improve productivity in the architecture, construction and engineering industry, it is critical to understand both current and historic trends in construction productivity. This study analyzes and compares construction productivity trends of South Korea, the U.S., the U.K., and Japan 1995 to 2015 using the following three measures: construction labor productivity, construction duration per floor, and construction duration per 1,000 m2 floor area. As the results, the international competitiveness of each country varied according to which measures were used to analyze them. Among the four countries, the construction labor productivity of the U.S. was the highest, followed by that of South Korea. South Korea also had the second highest productivity growth rate, following that of Japan. On the other hand, when analyzed from the perspective of construction duration, the construction productivity in South Korea appeared relatively lower than those of other countries. There were differences in the location of construction competitiveness of each country analyzed by various measures. Therefore, to accurately diagnose and improve the construction competitiveness in South Korea, strategies based on various measures are need to established simultaneously.
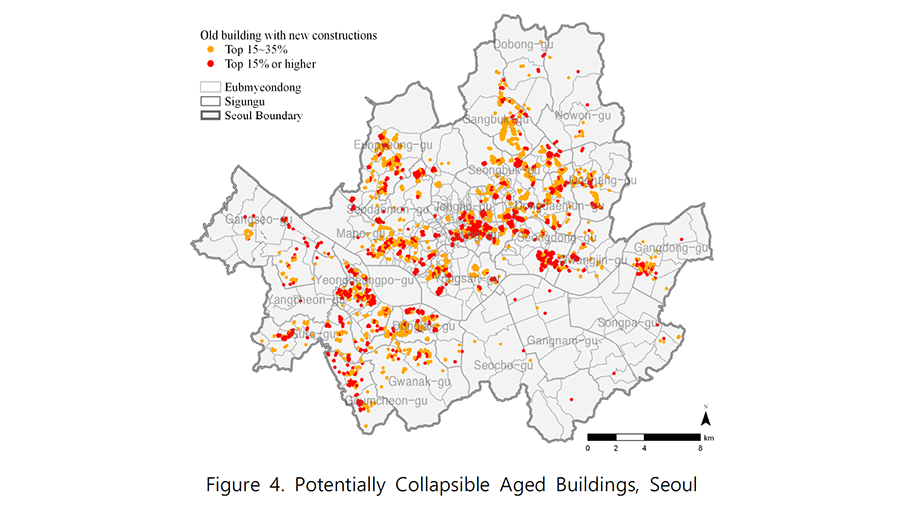
The purpose of this study is to derive an improved method for analyzing old buildings with risk of collapse using public big data. Previous studies on the risk of building collapse focused on internal factors such as building age and structural vulnerability. However, this study suggests a method to derive potentially collapsible buildings considering not only internal factors of buildings but also external factors such as nearby new construction data. Based on the big data analysis, this study develops a system to visualize vulnerable buildings that require safety diagnosis and proposed a future utilization plan.
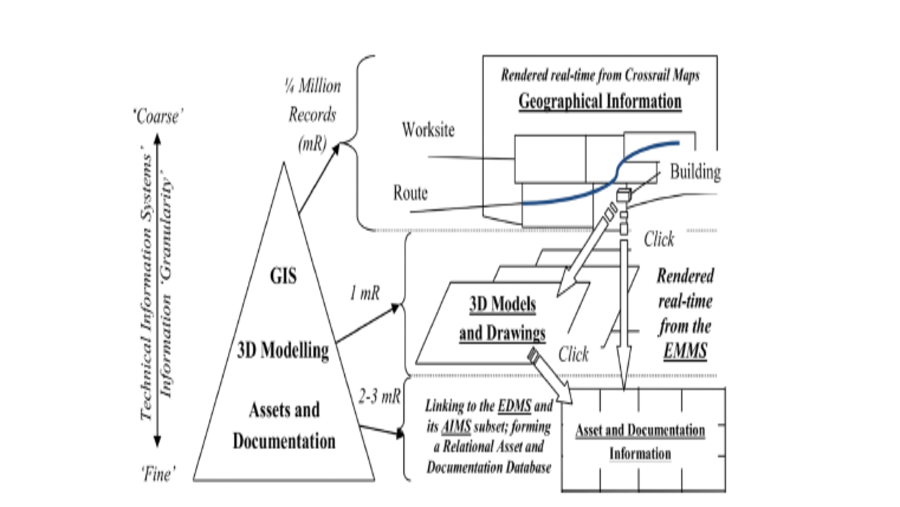
Building information modeling (BIM) is expanding its scope from the building industry to the infrastructure industry. The Korean government is also preparing for the transition. The public procurement service of Korea (PPS) announced that, from 2016, all public projects custom-managed by PPS must use BIM. The Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport of Korea (MOLIT) also announced a goal that, by 2020, 20% of all infrastructure projects will adopt BIM. The rail industry has recently begun a pilot BIM project and deployed 3D visualization, quantity check, 4D simulation, etc., but without any strategy plan, although it is essential for owner to have a strategy BIM adoption plan for successful BIM diffusion. Through literature review, an interview, a survey, and a case study of a pilot BIM project, this paper proposes a public owner’s perspective strategy for adopting BIM in the Korean rail industry.
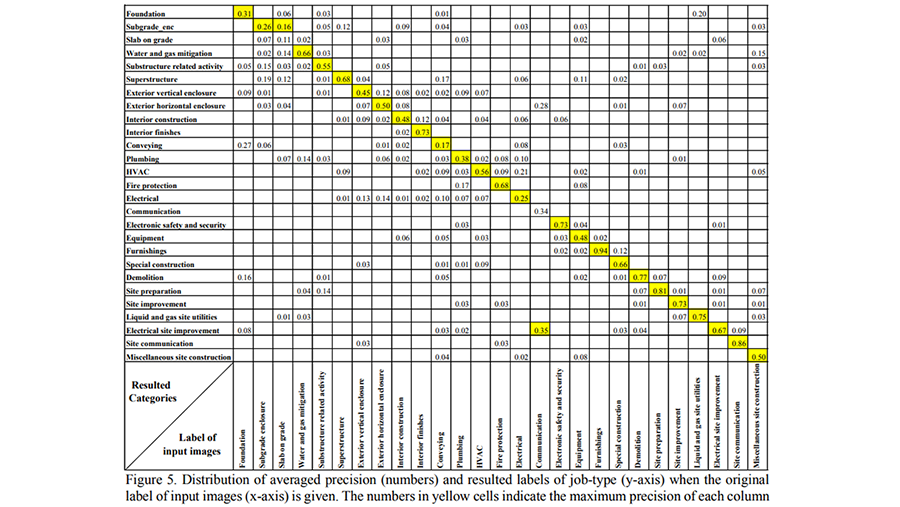
Field engineers take and collect several pictures from construction sites every day, and these pictures serve as records of a project. However, many of these images are loaded to and remain on computers in an unorganized manner because tagging, renaming, and organizing them is a time-consuming process. This paper proposes a method for automatically classifying construction photographs by job-type using a deep-learning algorithm. The first goal of this study is to classify construction images according to 27 job-types based on OmniClass Level 2. Google Inception v3—a deep learning algorithm used in this study as an image classifier—was trained using 1,208 construction pictures labeled by job-type. To improve the performance of the classifier, the optimized number of trainings was determined by examining the changes of accuracy and cross-entropy during trainings. The first result shows the incidence of several trainings over 50,000 was not meaningful. The retrained Google Inception as a construction image classifier was validated using a total of 235 images. The validation result shows that the classifier demonstrates an accuracy of 92.6% in classifying inputs properly and an average precision of 58.2% in correct classification. This means that retrained classifier can classify approximately nine out of every ten images correctly and that the deep-learning algorithm has high potential for use in the automatic classification of images from construction sites. © ISARC 2018 - 35th International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction and International AEC/FM Hackathon: The Future of Building Things. All rights reserved.
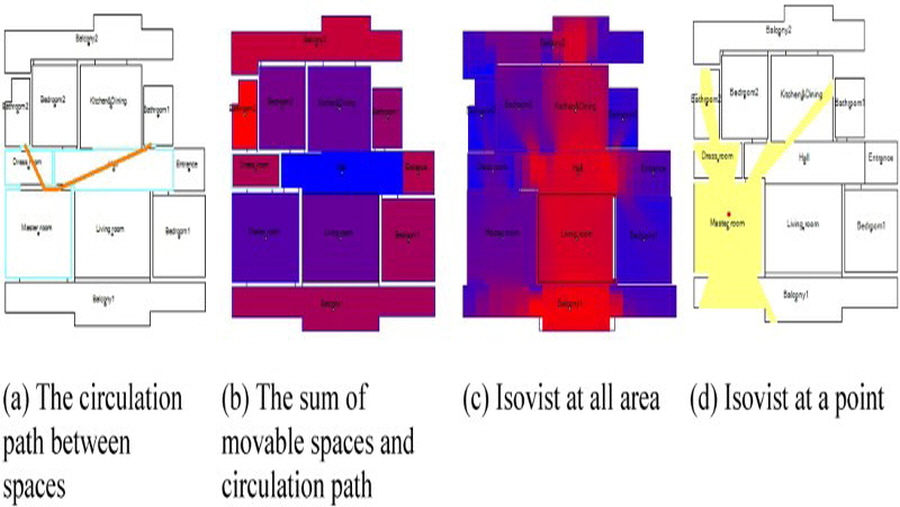
This study suggests a new spatial network model, called the space-connector model, for improving the representation of relations between spaces. Previous models have proved incapable of expressing the differences in the geometric and visual relations between spaces, such as the type and size of openings, the length of corridors, or the transparency of walls. New notations for explicitly representing these differences are proposed. This study suggests a modified process and map for calculating isovist, pedestrian route, based on the space-connector model. The space-connector model was implemented in the ‘ASpace’ tool and its functionality has been validated through an integrated analysis of space syntax and spatial properties as well as isovist and pedestrian route analysis.
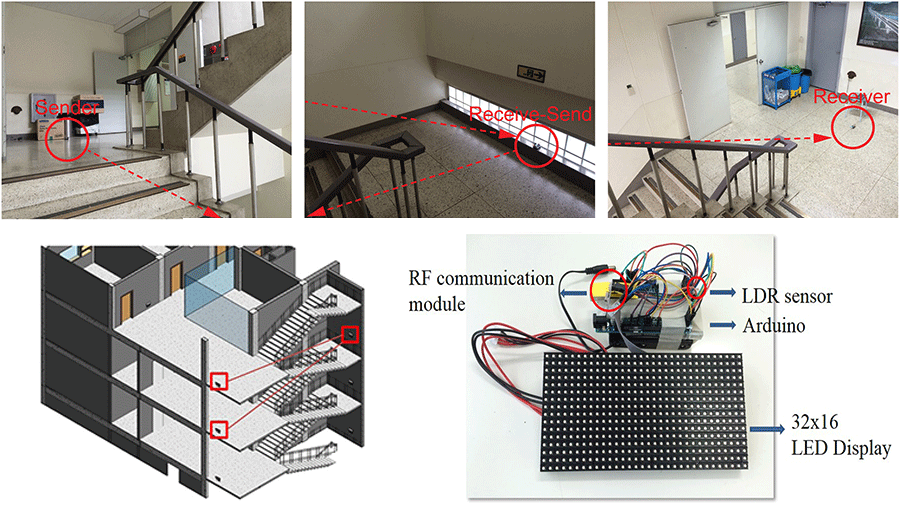
This study introduces the first working prototype of a server-independent smart exit sign system (SISES) and validates its communication reliability. A smart exit sign system (SES) is a new type of evacuation guidance system that changes the directions of exit signs toward safe paths. Thus far, only a handful of SESs have been proposed on a conceptual level and assumed that each sign node was controlled by a central server. They are, however, complex and expensive to install and vulnerable during a fire. To overcome these limitations, an SISES, which communicates over a wireless sensor network without a central server, was proposed. This study tests the communication reliability and speed of the SISES—the most critical factors for stable operation. The results show that the SISES can communicate reliably in various conditions and that it takes less than 4 s to update the entire system installed at a 3392 m2 building.
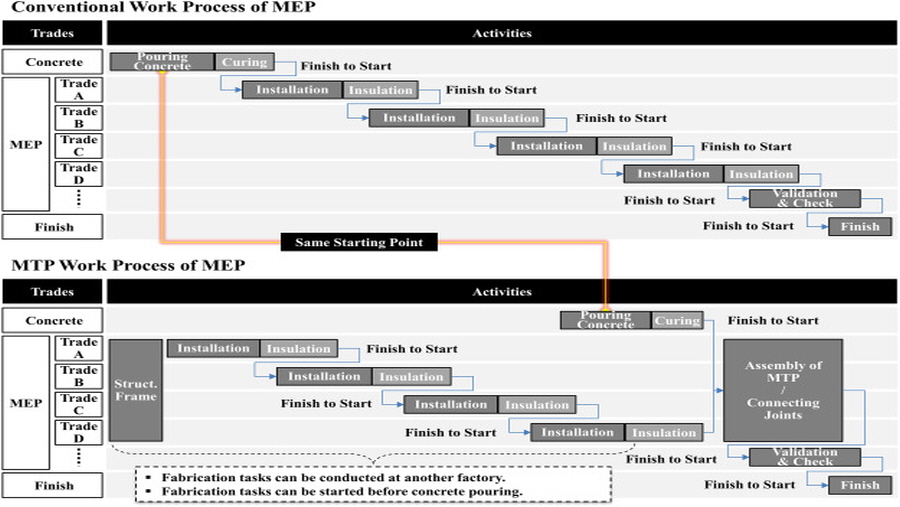
Previous studies yielded contradicting results regarding the benefits of multi-trade prefabrication (MTP) based on building information modeling (BIM). This study investigates the causes of the contradicting results by analyzing the process, productivity, and economic benefits of BIM-based MTP through a case study. The process analysis results indicate that coordinating mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) systems took longer in MTP than in the conventional method because of the newly added offsite coordination activities. Nevertheless, the overall project duration was reduced because of the parallel execution of MTP and concrete work. The productivity analysis shows that the newly added MTP activities also increased person-hours. However, as the assembly process was repeated, the required person-hours decreased by 40% from that of the initial stage because of the learning effect. The case study revealed that the management of coordination activities and the selection of projects were critical for the successful implementation of BIM-based MTP.
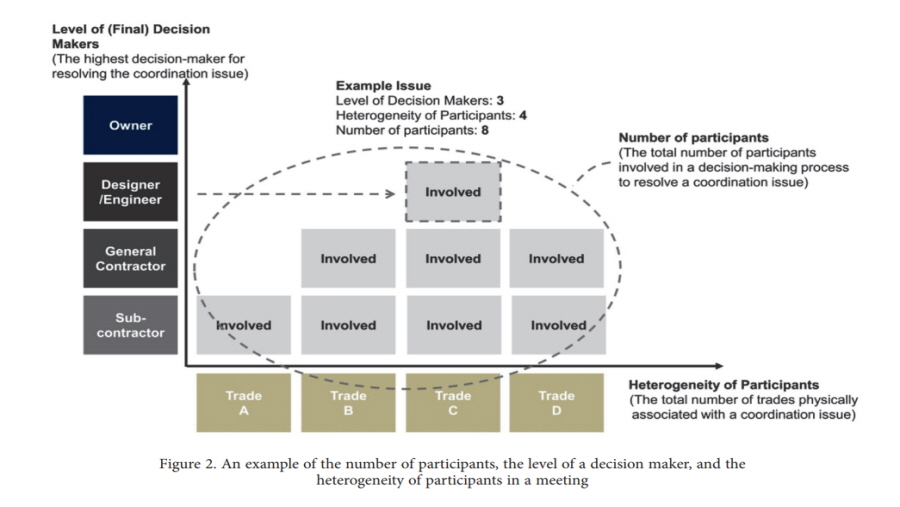
This study analyzed the impact of organizational factors on delays in building information modeling (BIM)- based coordination for mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) systems from the decision-making perspective. Recently BIM-based coordination has been regarded as a critical phase in project delivery but suffers from delays during the coordination process. This study investigated three complexity factors that often contribute to coordination delays: the number of participants – the total number of participants involved in a decision-making process for resolving a coordination issue; the level of the decision makers – the highest decision-maker involved in a problem-resolution process; and the heterogeneity of participants –the number of trades related to an issue. Using 95 major coordination issues derived from 11,808 clashes in a case study, the correlations between the coordination time and the complexity factors were analyzed. The coordination time linearly increased as each factor increased. The number of participants had the highest correlation with the coordination time, followed by the level of decision makers and the heterogeneity of participants. The findings stress the significance of integration between BIM and lean approaches, such as Obeya (big room) and Shojinka (flexible manpower line), during BIM-based coordination to expedite decision-making processes and eventually to reduce the coordination time.
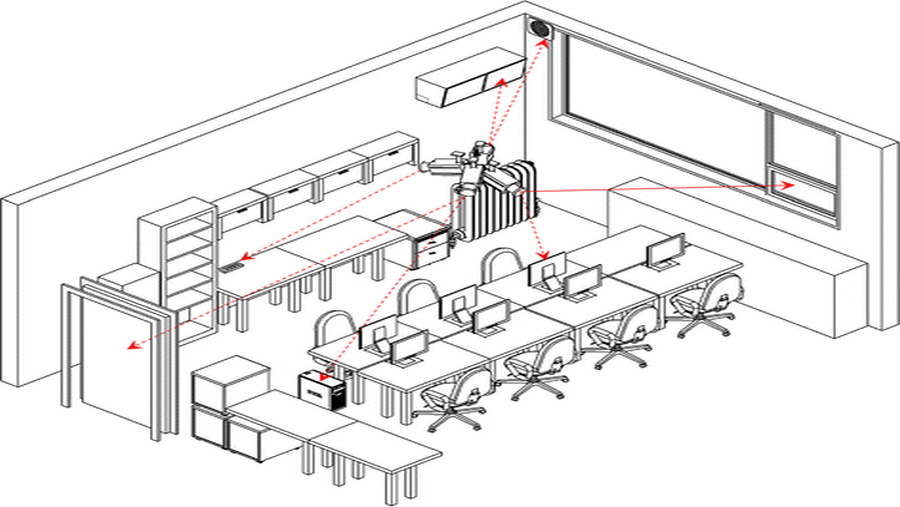
This paper describes a fire monitoring system, based on a thermographic camera, for electrical appliances in interior spaces. These appliances are at particular risk because they are vulnerable to the carelessness of users (46% of electrical appliances fires are caused this way). The system compromises a thermographic camera, rotating on a two-axis robotic arm, controlled by a fire monitoring algorithm that detects the appliances’ status. Once the system’s accuracy and ability to identify the status of each appliance had been tested, the camera’s rotation sequence was planned. To achieve the best efficiency, bearing in mind that fires can break out very quickly, the sequence was based on the distance between monitored appliances. Over a nine-hour period, monitoring six appliances, the proposed method resulted in about 295 (about 7%) more rotations than those produced by a method of arbitrary ordering. This effectiveness increases when more appliances are monitored over greater periods. The system’s main contribution to fire safety is the application and full utilization of the thermal camera, detecting the beginnings of a fire before it can break out.
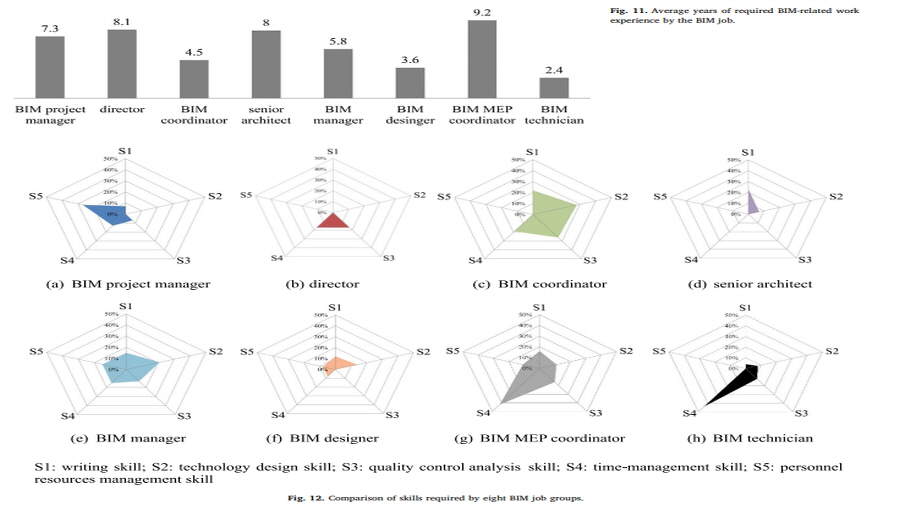
The emergence of building information modeling (BIM) has generated several BIM jobs. However, despite opinions by BIM experts, questions regarding BIM jobs and their competencies still have no clear solution. This paper addresses this question by the collection and analysis of 242 online job postings, written in English, from the US, the UK, and China. These 242 job postings comprised a total of 32,495 words, from which 35 types of job titles and 5,998 terms related to job competency were extracted. Sequentially, the 35 job types were classified into eight BIM job types by analyzing the relations between the job titles using the role and position analysis of social network analysis. The eight BIM job types were BIM project manager, director, BIM manager, BIM coordinator, BIM designer, senior architect, BIM mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) coordinator, and BIM technician. The 5,998 competency-related terms were categorized into 43 competency elements using the O*NET classification as a framework for analysis. The 43 competencies were then subcategorized into essential, common, and job-specific competencies for the eight BIM job types. The findings of this paper could contribute to the research, industry, and academia by a) providing researchers with a scientific foundation for conducting studies related to BIM jobs and competence in the future; b) setting up guidelines for recruiting and training BIM experts in the industry; and c) allowing universities to develop BIM-related courses depending on their educational goals.

This study has identified factors stimulating creative ideas, transforming creative ideas to products, and continuing creative performance in the field of architecture based on interviews with 10 creative and successful architects. Having a penchant for liberal arts and reading books on a broad range of topics on arts, humanities, social sciences, and engineering were two major sources of creative inspirations for these architects. The interview data showed that creative inspirations occurred with a variety of artistic and cultural experiences outside the field of architecture, while it got blossomed in forms of creative architecture by means of architectural knowledge and skills, commitment with efficient problem solving and interpersonal skills, and great mentors in the field. Constraints imposed on by architectural regulations and other people, including clients, had a positive impact on creative productivity. Despite constant challenges and difficulties, the architects showed psychological strengths and positivity that enabled them to stay and survive in the field.
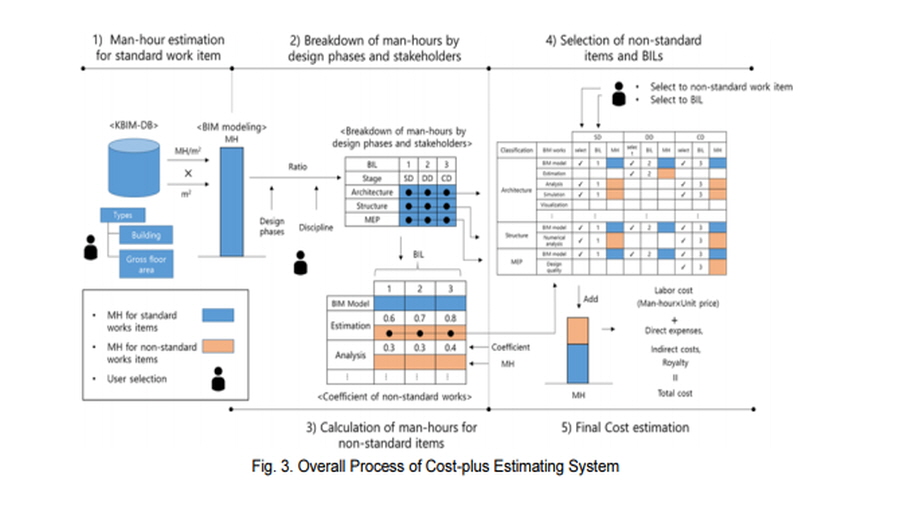
More than ten years have passed since Building Information Modeling (BIM) was introduced in Korea, but the industry lacks established approaches to assist firms in estimating the costs of providing additional BIM services in the design phases of a project. The deficiency also inhibits government agencies to allocate discrete and reasonable budgets when requesting BIM related services. This research focuses on the Architecture and Engineering (AE) industry and provides a framework to estimate costs for BIM design services based on the cost-plus pricing approach. The framework utilizes cost data from 54 projects to estimate average man-hours, and ‘man-hour coefficients’ for standard and non-standard work items. The man-hours can further be broken down to different design phases, disciplines and at different levels of development. The framework was implemented in an Excel-based system, which allows users to produce estimates for 11 different building project types, while providing flexibility in selecting preferred BIM services. Validation showed that the system produces accurate estimates for specific projects with customized requirements. By providing an objective approach for estimating the costs of BIM services, it allows clients and AE firms to agree upon a fair cost, and thus expedite its adoption in Korea.

Despite the rapid spread of building information modelling (BIM), the majority of BIM projects are still conducted in a mixed-project environment: two-dimensional (2D) drawing and BIM. The design-coordination productivity and information-exchange patterns are analysed for a unique case where two towers, A and B, of a hospital project deployed two different design coordination strategies in a 2D and BIM mixed-construction environment. The tower A strategy coordinated designs using drawings as the main source of information and confirmed them using BIM (BIM-assisted coordination), whereas the tower B strategy coordinated designs using BIM and confirmed them using drawings (BIM-led coordination). The coordination productivity was 228% faster for tower B than for tower A. The frequency of design changes was much lower for tower B (0.42 times/drawing) than for tower A (2.13 times/drawing). As the result, the design coordination for tower A was delayed by 9.3 months, whereas tower B was completed rapidly and without any delay. A social network analysis revealed that the BIM-led coordination was supported by the relatively even distribution of information, the reduced control of an mechanical, electrical and plumbing (MEP) engineer over a project, and higher accessibility to the information for every project participant.
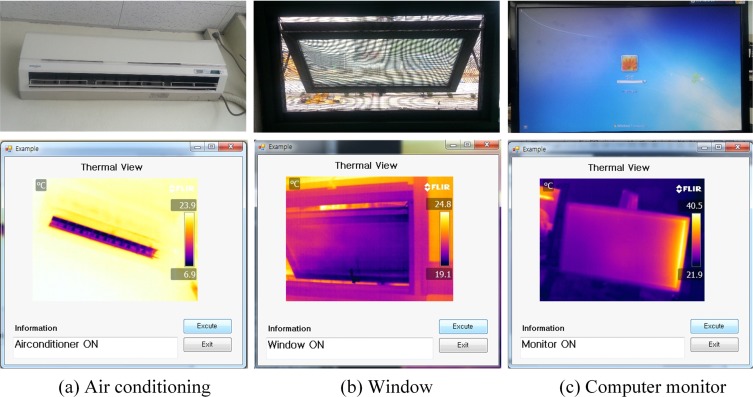
This paper presents a context-awareness system that uses a thermal camera to monitor energy wastage due to user carelessness in a large enclosed space. The users of the system can receive quantitative information of energy use and identify whether to turn an object on or off. The system is composed of a two-axis robotic arm that can manipulate the angle of a thermographic camera and software that can stitch together images received from various angles; and a context-awareness algorithm to identify objects’ situation in stitched thermographic images. The system’s performance was tested for an individual object, more than two objects close to each other, an object at long distance, and the effect of an obstacle. The context-awareness was successful except when obstacles interfered with observations. However, when obstacles interfered, the context-awareness was successful when their heat adsorption was high or when the insulation leaked. The range of spaces and situations that the system can cover will increase if it is combined with an automated device that can move it horizontally.
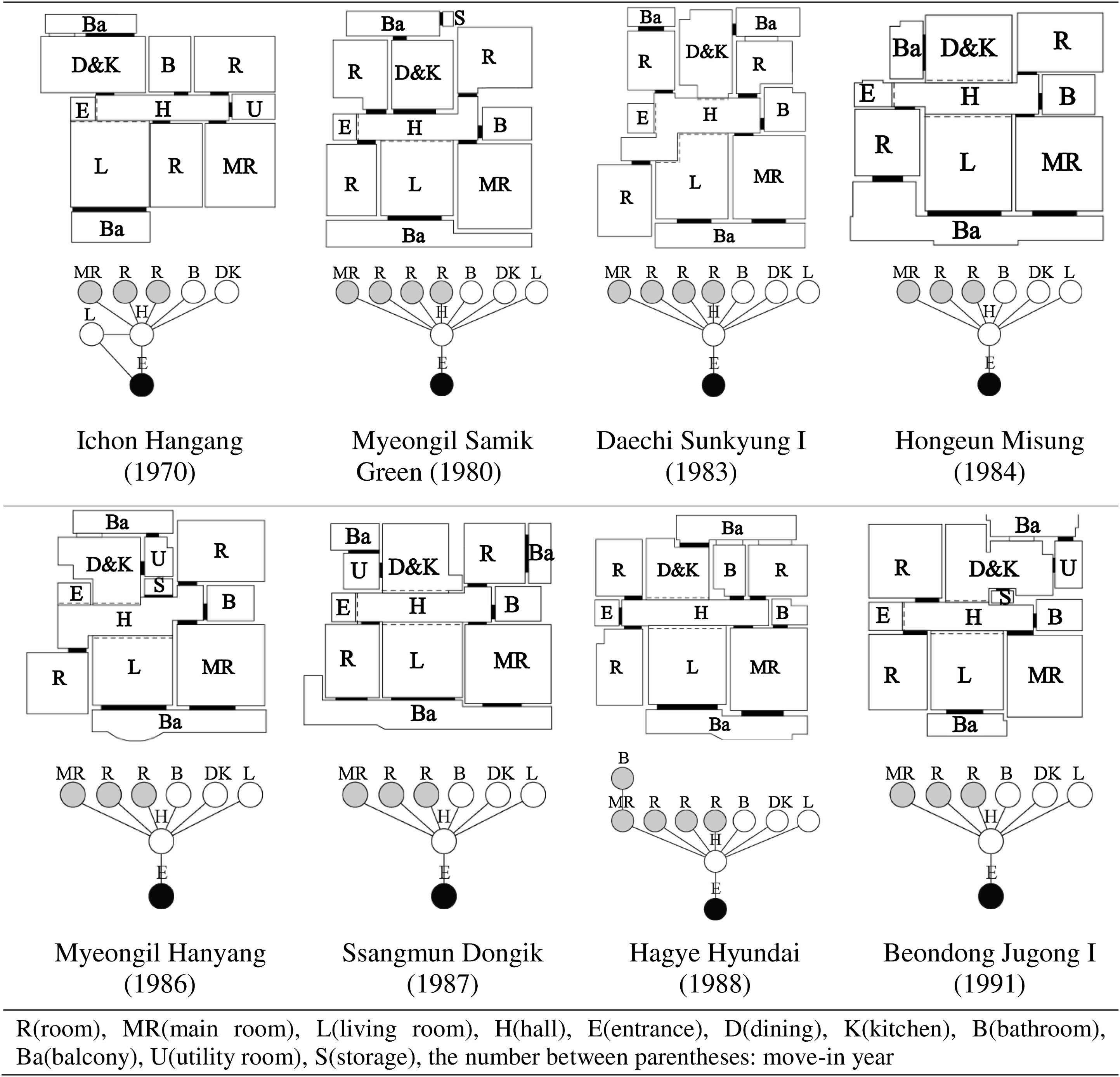
A method has been developed for automatically generating a phylogenetic tree of architectural plans based on graph theory, according to the properties of the plans and the timing of their appearance. A phylogenetic tree of architectural plans is a branching diagram that shows transitions of the architectural plans by period. In previous studies, researchers analyzed structural similarities and differences between architectural plans by comparing one floor plan to another. Such manual classification processes sometimes result in inconsistent classifications and are inefficient, especially when a large number of plans are compared and analyzed. In this paper, a new algorithmic approach is proposed, termed the time-based joining (TBJ) method, for quantitatively evaluating structural similarities between architectural plans and creating a phylogenetic tree of the analyzed architectural plans. The validity and consistency of the TBJ method’s results were tested by generating a phylogenetic tree of 422 collective housing unit plans in Seoul, South Korea, constructed from 1970 to 2010.
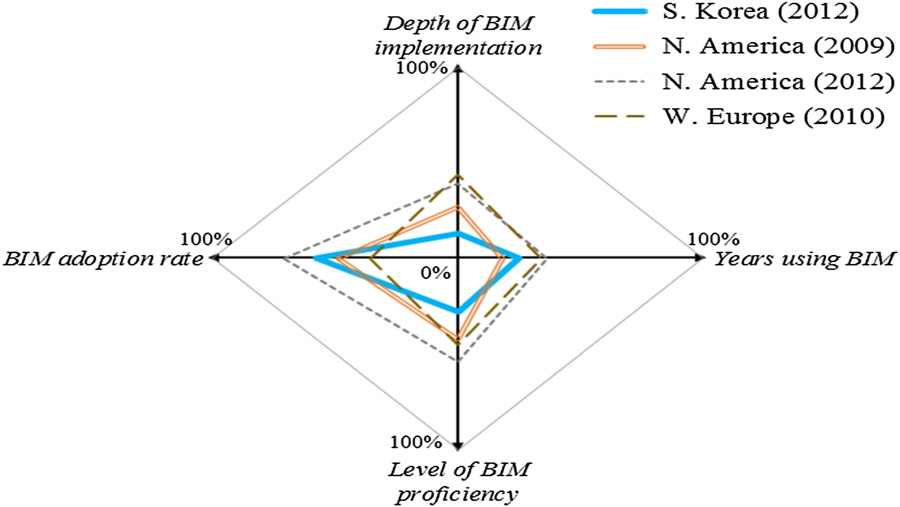
This paper proposes a simple numerical chart comprising the smallest possible number of variables to rapidly represent levels of building information modeling (BIM) adoption and implementation. The slim BIM chart employs the most widely used variables: BIM adoption rate, years of using BIM, level of proficiency, and depth of implementation. We developed three types of slim BIM charts: diamond, triangle, and ball charts, which use four, three, and two variables, respectively. We applied these slim BIM charts to three regions, namely, North America, South Korea, and Western Europe. BIM had been most widely adopted and implemented in North America in 2012 but most deeply in Western Europe in 2010. In 2012, South Korea had widely adopted BIM, but implementation had been shallow. The test cases showed that the slim BIM charts can provide BIM managers and researchers with a means to visually and quantitatively compare the different levels of BIM adoption and implementation in different regions and for different periods.

This study investigates the applicability of a success level assessment model for building information modeling (BIM) projects (SLAM BIM). SLAM BIM is a goal-driven method for the sustainable evaluation of a BIM project's success. It was developed on the premise that a project's success cannot be evaluated without first identifying its goals; thus, key performance indicators (KPIs) can vary according to project goal. SLAM BIM consists of five steps for defining BIM goals, uses, KPIs, unit measurements, and data collection forms and processes. To identify appropriate BIM KPIs, the collectability, measurability, and comparability of the candidate BIM KPIs were considered. Data related to schedule, design errors, change orders, response time, and ROI were collected and analyzed in the two projects by using the SLAM BIM process. The validity of SLAM BIM was tested by applying SLAM BIM from the beginning to the end of two construction projects.
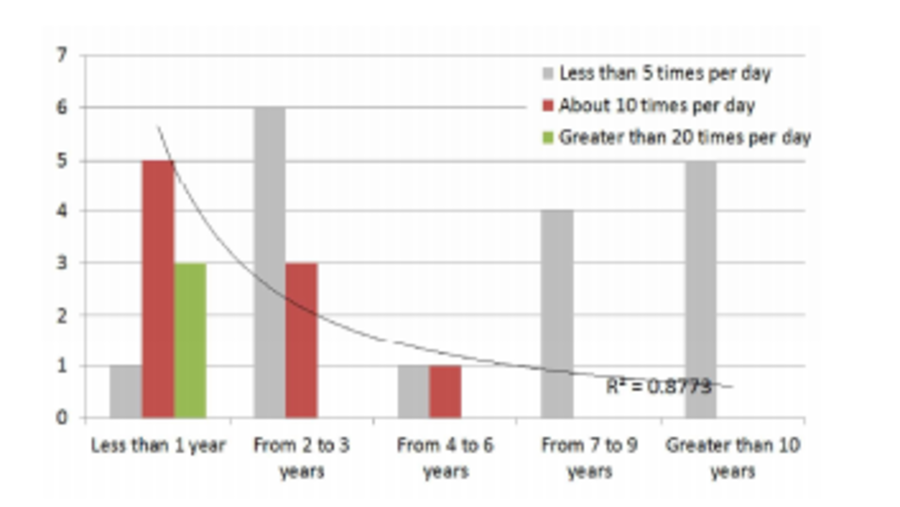
The facility management solution (FMS) has recently been introduced to a number of higher education facilities; however, the actual use rates of FMS are still low. To identify the reasons for differences between FMS experienced and unexperienced in terms of FMS evaluation, a survey was conducted with 68 facility managers from three universities using 12 questions developed on the basis of technology acceptance model3 (TAM3). For statistical analysis of the resulting data was used. The survey results show that 64.9% of FMS users were not satisfied with FMS due to lack of information, while 83.3% evaluated FMS as complicated. However, 58.9% of users replied that FMS helped to improve task efficiency. Task efficiency improvement is not only the major expectation of FMS but also the major benefit of FMS as perceived by both users and non-users. The survey also highlighted statistical differences, with FMS users stressing on-the-job relevance as a factor in considering FMS adoption, and non-users expressing an interest in the expected effects of FMS. There were also differences between users and non-users in terms of users’ attitudes and preferred assistance methods, with users indicating a more passive attitude than non-users. Finally, the results revealed a correlation between experiences of FMS and three factors (perceived job relevance, self-evaluation of the ability to operate new technology, and preferred assistance methods in the case of errors).
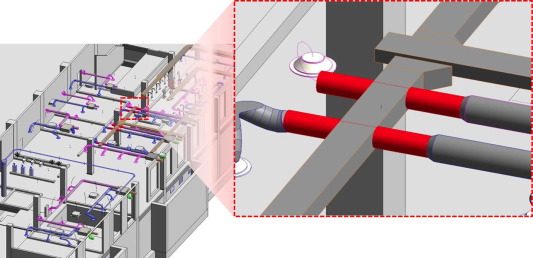
Waste generated in construction and demolition processes comprised around 50% of the solid waste in South Korea in 2013. Many cases show that design validation based on building information modeling (BIM) is an effective means to reduce the amount of construction waste since construction waste is mainly generated due to improper design and unexpected changes in the design and construction phases. However, the amount of construction waste that could be avoided by adopting BIM-based design validation has been unknown. This paper aims to estimate the amount of construction waste prevented by a BIM-based design validation process based on the amount of construction waste that might be generated due to design errors. Two project cases in South Korea were studied in this paper, with 381 and 136 design errors detected, respectively during the BIM-based design validation. Each design error was categorized according to its cause and the likelihood of detection before construction. The case studies show that BIM-based design validation could prevent 4.3–15.2% of construction waste that might have been generated without using BIM.
Globally distributed student team projects allow for complex and multifaceted learning outcomes through experiential educational settings. While the students involved may be studying built environment disciplines such as architecture, engineering and construction, distributed teams are mediated by technology, separated by time zones, and differentiated by culture. In this paper, we explore such multifaceted learning in a globally distributed team project where students from seven universities on three continents participated in a 2-week global team workshop to study rapid construction for disaster response. The participating schools included the Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IIT), National Cheng Kung University (NCKU), National Taiwan University (NTU), the University of Twente (UT), the University of Washington (UW), Washington State University (WSU), and Yonsei University (YU). For the term project students collaborated and coordinated their work in a virtual world. Upon project completion, we conducted a survey with students from two of the participating universities and analyzed their reflections as reported in their final presentations. We found that the distributed nature of the teams emphasized the importance of Building Information Modeling (BIM) execution planning and its joint development as well as the importance of shared project goals and early involvement of team members in the planning process.
This paper analyzes the duration of the construction document (CD) phase of 42 large public building projects delivered by the total solution service of Public Procurement Services in Korea from 2009 to 2014. The quality of construction documents significantly affects the quality of construction and facility management. Thus, securing appropriate time for the CD phase during project planning is important for the quality of a project. Currently, the duration of the CD phase is planned based on the construction costs of a project following a notice of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport. However, our analysis results showed that the correlation between the actual duration of the CD phase and construction costs is very weak. The actual CD phase takes 1.33-1.79 times longer than the planned duration. The practitioners who were interviewed, were already aware that the correlation between the duration of the CD phase and the construction costs is weak. They identified the complexity of the project, the extent of the design changes, project type, client characteristics, and others as more influential factors on the CD phase than the construction costs. To improve the quality of CDs, a new guideline for determining an adequate CD phase duration should be studied and developed.
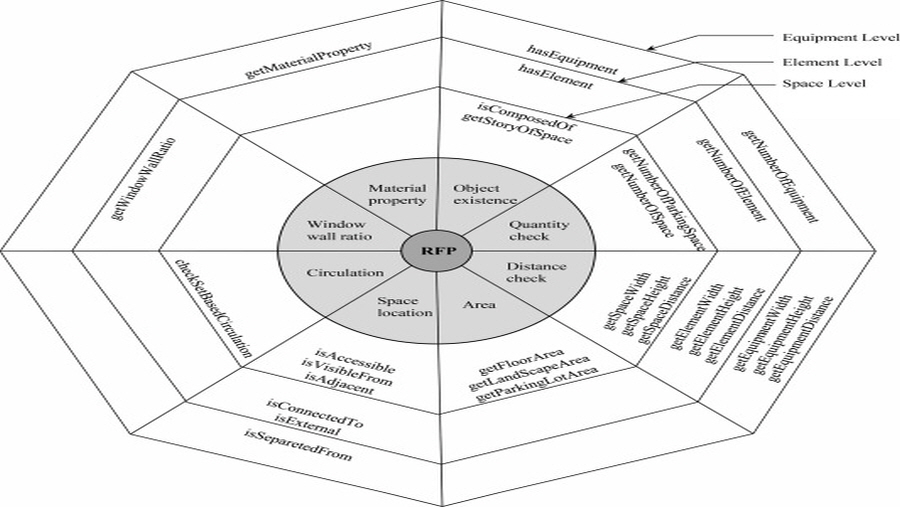
This study reports on the requirements for developing computer-interpretable rules for checking the compliance of a building design in a request for proposal (RFP), especially in the building information modeling (BIM) environment. It focuses on RFPs for large public buildings (over 5 million dollars) in South Korea, which generally entail complex designs. A total of 27 RFPs for housing, office, exhibition, hospital, sports center, and courthouse projects were analyzed to develop computer-interpreted RFP rules. Each RFP was composed of over 1800 sentences. Of these, only three to 366 sentences could be translated into a computer-interpretable sentence. For further analysis, this study deployed context-free grammar (CFG) in natural language processing, and classified morphemes into four categories: i.e., object (noun), method (verb), strictness (modal), and others. The subcategorized morphemes included three types of objects, twenty-nine types of methods, and five levels of strictness. The coverage applicability of the derived objects and methods was checked and validated against three additional RFP cases and then through a test case using a newly developed model checker system. The findings are expected to be useful as a guideline and basic data for system developers in the development of a generalized automated design checking system for South Korea.
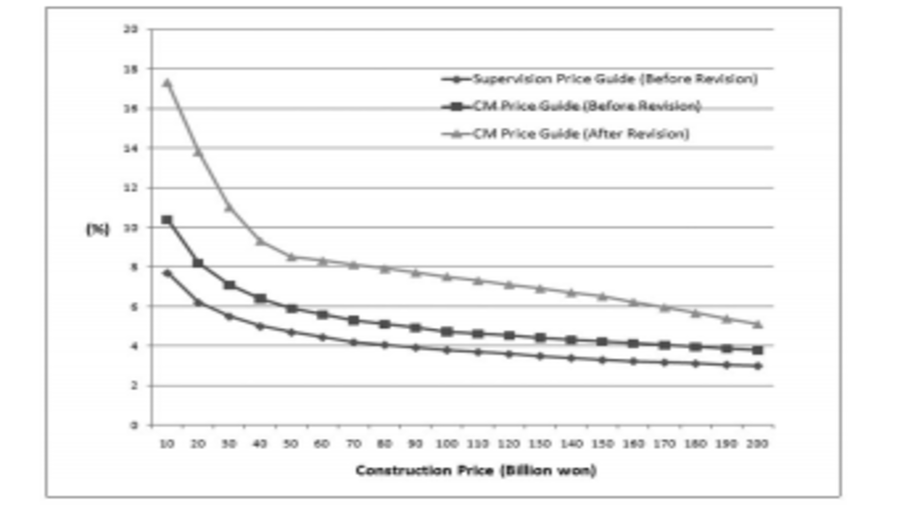
Enhancing clarity and transparency of the pricing guide for technical services for public construction works enables the prediction and reimbursement of the service cost for project owners and bidders, while it would also yield benefits for engineers who carry out the construction tasks. In order to improve the global competitiveness of construction service industry, the government revised its pricing guide for techical services for construction works recently, moving away from its previous percentage-of-construction-cost method towards the Cost Plus a Fee Method. However, since the Cost Plus a Fee Method results in the rise of the service price by 153%~197%, there is the need for a review on the method and basis of the adjustment in order to avoid controversies regarding the application of the revised method. In this context, this paper analysed the 2014 revision of the pricing guide for technical services for public construction works through comparison with foreign cases including those of the US and the UK. The analysis yielded the conclusion that, while the shift towards Cost Plus a Fee Method which is widely used in advanced economies is a very meaningful change in large measure, certain aspects still remain problematic. Unlike in advanced economies, the detailed break-down shows the direct labor cost includes certain indirect expenses. Also, indirec expenses are admitted so comprehensively as to include overhead costs and technology royalties. These problems results in redundant estimation of certain expenses, and obstructs transparency in spending details. This paper proposes various improvement measures to address these issues.
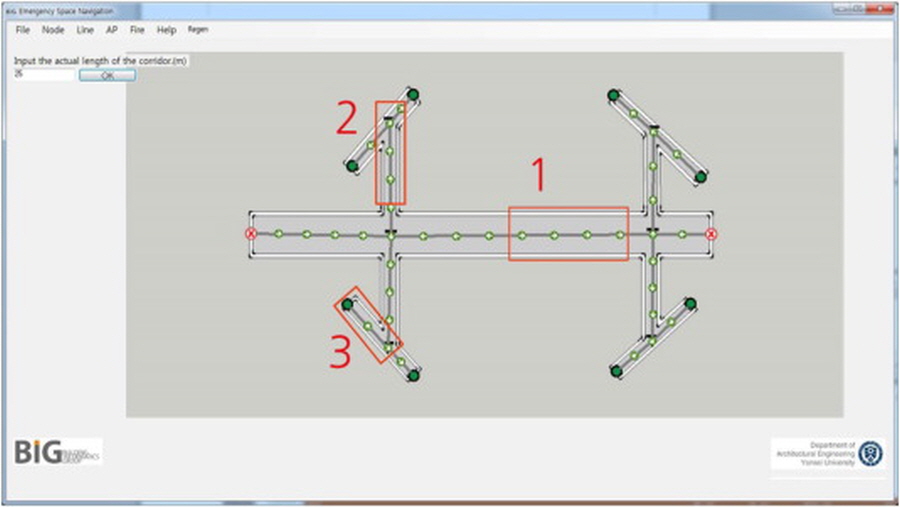
This study reports on the requirements for developing computer-interpretable rules for checking the compliance of a building design in a request for proposal (RFP), especially in the building information modeling (BIM) environment. It focuses on RFPs for large public buildings (over 5 million dollars) in South Korea, which generally entail complex designs. A total of 27 RFPs for housing, office, exhibition, hospital, sports center, and courthouse projects were analyzed to develop computer-interpreted RFP rules. Each RFP was composed of over 1800 sentences. Of these, only three to 366 sentences could be translated into a computer-interpretable sentence. For further analysis, this study deployed context-free grammar (CFG) in natural language processing, and classified morphemes into four categories: i.e., object (noun), method (verb), strictness (modal), and others. The subcategorized morphemes included three types of objects, twenty-nine types of methods, and five levels of strictness. The coverage applicability of the derived objects and methods was checked and validated against three additional RFP cases and then through a test case using a newly developed model checker system. The findings are expected to be useful as a guideline and basic data for system developers in the development of a generalized automated design checking system for South Korea.
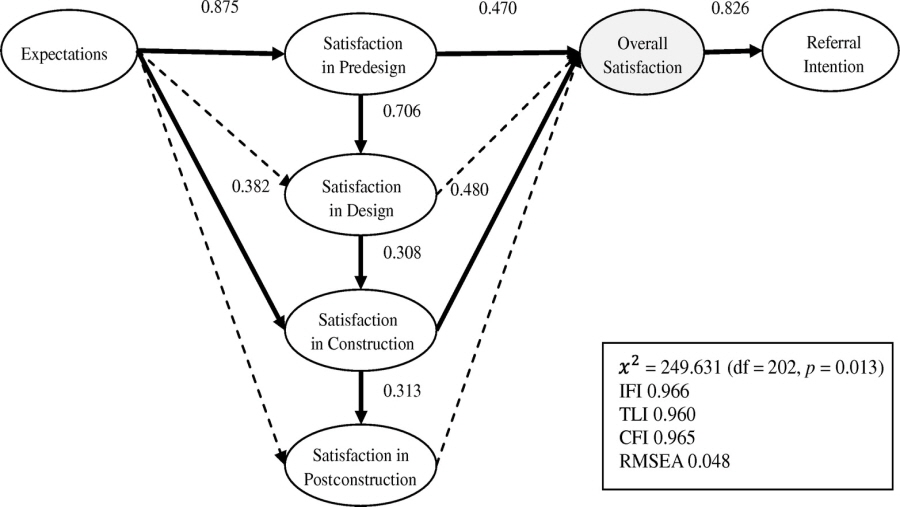
Many companies pay a great deal of attention to existing customers' referral intentions when they attempt to attract new customers. However, little is known about the necessary level of satisfaction of existing customers to understand when existing customers are likely to complete a referral and by what mechanism. This study assumed referral routes and established a model for predicting referral intentions based on the satisfaction level as described by the disconfirmation of expectation theory and the net promoter score theory. Then, the routes were verified by surveying 103 construction management #CM# clients using structural equation modeling, and the prediction model was tested by applying it to 194 CM clients using multinomial logistic regression. The results indicated that the accuracy rate of the prediction model was 79.3%. This model can be used effectively to attract new clients, particularly in fields where long-term services are provided, such as CM, because it allows service providers to predict customers' referral intentions depending on their satisfaction levels. #C# 2014 American Society of Civil Engineers.
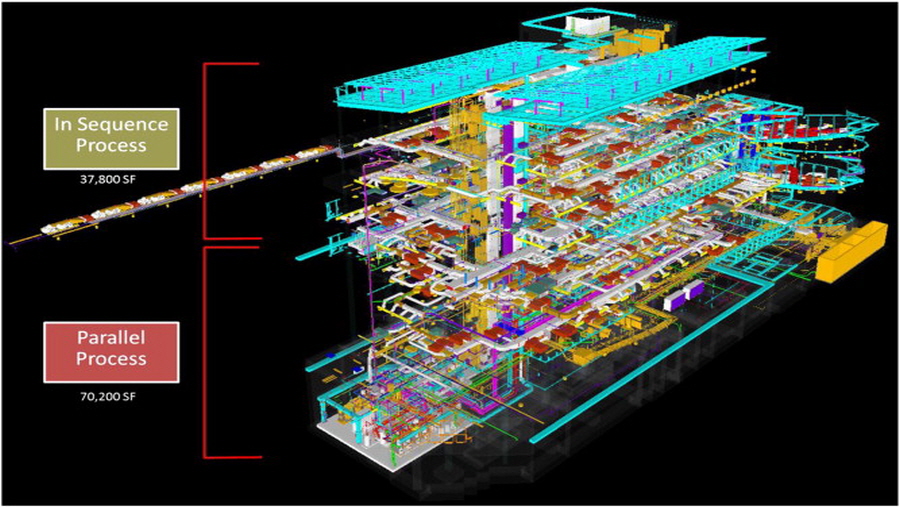
We analyze the impact of parallel vs. sequential design coordination strategies on coordination productivity and information sharing. Previous studies have shown how building information modeling (BIM) could improve interorganizational design coordination between architecture, structure, and mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) components of buildings (MEP coordination, for short) and thus improve the quality and efficiency of a design and construction project in terms of the reduced numbers of errors and requests for information. This paper presents a unique case where two MEP coordinators were hired for a BIM-assisted project, which was a pharmaceutical company headquarters office building in Silver Spring, Maryland. The first coordinator coordinated MEP designs concurrently with other trades, whereas the second coordinator coordinated MEP designs step-by-step in a sequential process. The results of our analysis showed that the two different coordination processes largely affect the number of clashes in the first run of clash detection, coordination meeting time and efficiency, ease in finding root causes of the clashes, and number of coordination cycles to complete the coordination. As such, the sequential coordination strategy was about three times faster than the parallel strategy in terms of coordination productivity. A further examination of these two processes from an information-sharing perspective showed that the sequential coordination process reduces the concentration of information, thus reducing the overload of a coordinator with decision-making tasks, and facilitates information sharing between heterogeneous project participants. The findings of this study have potential as a basis for future development of BIM-based MEP coordination best practices and strategies as well as providing the metrics for understanding, measuring, and predicting the performance of BIM-based MEP coordination and strategically planning the coordination process.
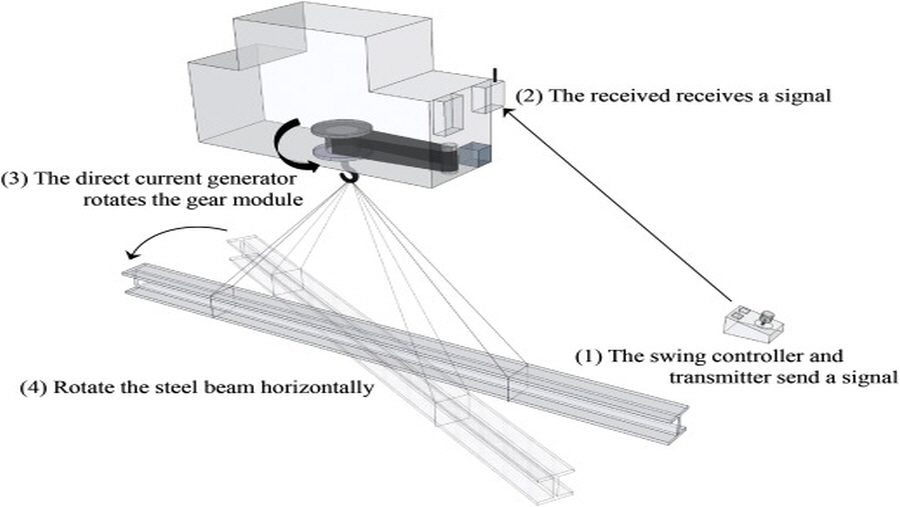
On average, approximately 90 workers are injured or killed every year while lifting and installing steel beams in South Korea. Rotation-controllable tower-crane hook-blocks (RTH) remotely rotate beams horizontally to the target position, thus helping to prevent accidents related to steel beam installation. In this study, the expected safety improvements and economic effects of the RTH were analyzed. the real discount rate, and operation and maintenance costs in accordance with the general cash flow analysis practice as well as the CO2 offset price. The results of the analysis showed that when the effects of the RTH were at their maximum and average levels, the break-even points occurred in the first year and the second year, respectively. Although the RTHmight not be profitable in the minimum case, this study demonstrated that using it would generally contribute to economic efficiency, and more importantly to worker safety.
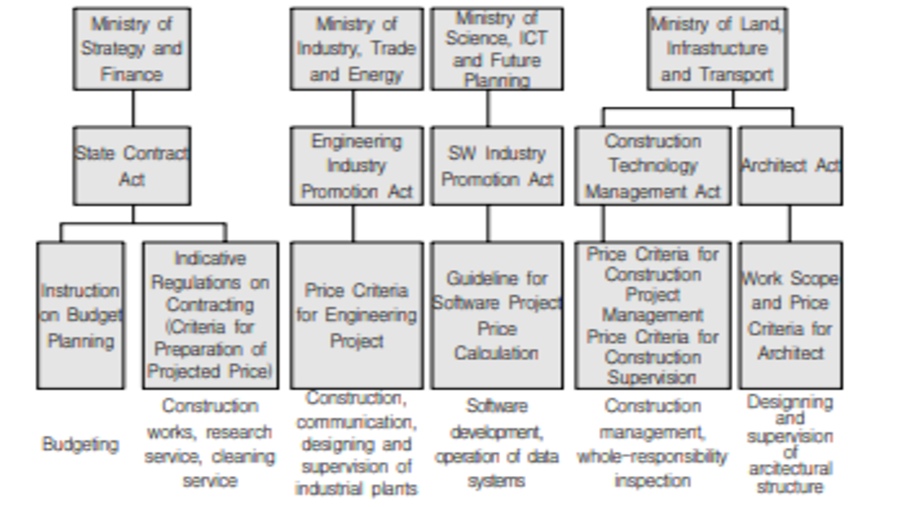
Goods, services and construction works needed by central government entities, local government entities, and other public institutions are procured with national budget. For efficient budget execution, Article 9 Paragraph 1 of the Enforcement Decree of the Act on Contracts to Which the State is a Party (hereinafter "State Contract Act") provides for the criteria for determining estimated price. Sub-paragraph 2 of the paragraph provides for the "determination of estimated price by cost calculation". On this legal basis, pricing criteria for the determination of estimated price, based on the project purpose, are announced by responsible authorities. This study analyzes the pricing criteria for technology services and proposes a price calculation methodology that can ensure transparency, as a practical improvement for more rational and efficient budget execution in the public sector.
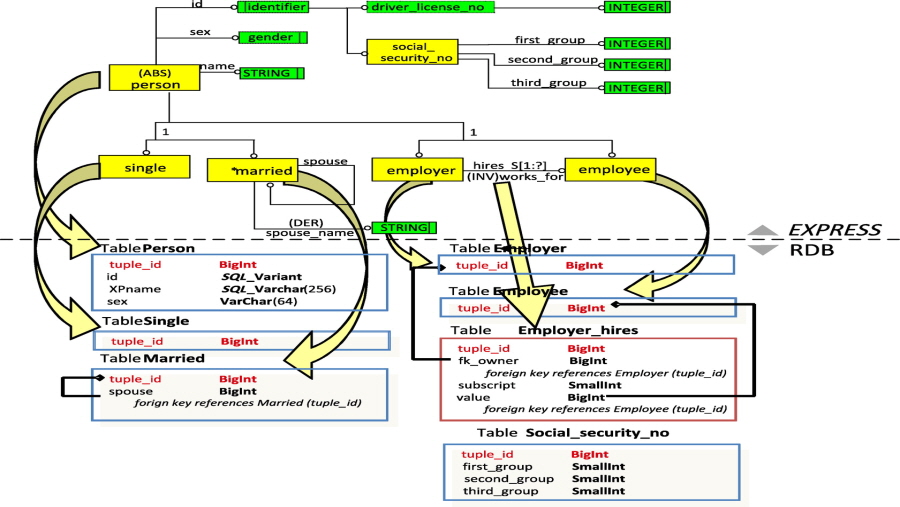
Most previous industry foundation classes (IFCs) servers were developed based on relational databases (RDBs), and many studies reported performance problems. This study developed the object-relational IFC (OR-IFC) server using the object-relational database (ORDB) approach to improve query performance by simplifying the mapping process of the inheritance structure and the aggregation concepts. In addition to the OR-IFC server, a RDB-based IFC server was also developed using mapping rules on the same database-management system as that on which the OR-IFC server was implemented to compare the performance of the ORDB- and RDB-based systems. The performance of the OR-IFC server and the RDB-based IFC server was evaluated using the Benchmark of Universal or Complex Kwery Ynterfaces benchmark method, and two test-case models with different sizes were used. The benchmark results clearly showed the query-performance improvement of the suggested OR approach. The OR-IFC server far outperformed the RDB-based server in every query related to object-oriented features such as inheritance, collection-type data, and referencing.
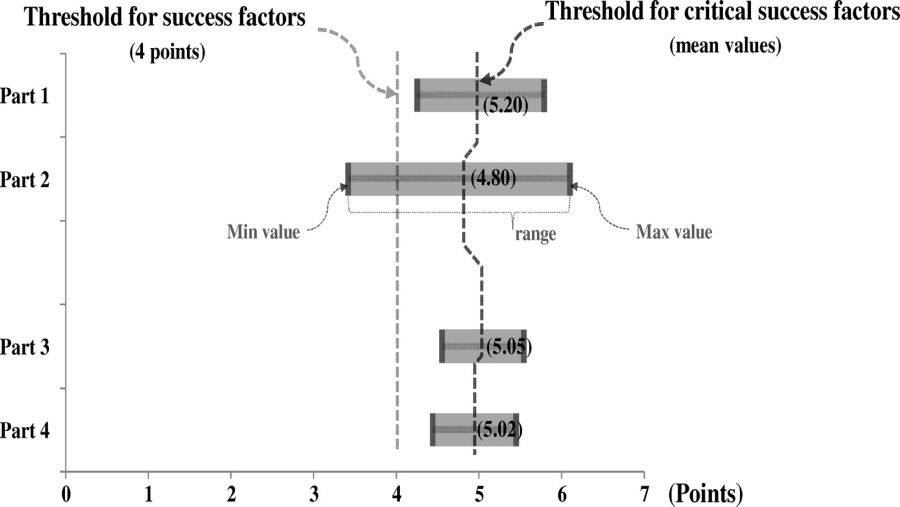
Suggestions abound for successful adoption of building information modeling (BIM); however, a company with limited resources cannot adopt them all. The factors that have top management priority for successful accomplishment of a task are termed critical success factors (CSFs). This paper aims to derive the CSFs for four questions commonly asked by companies in the first wave of BIM adoption: (1) What are the CSFs for adopting BIM in a company? (2) What are the CSFs for selecting projects to deploy BIM? (3) What are the CSFs for selecting BIM services? (4) What are the CSFs for selecting company-appropriate BIM software applications? A list of consideration factors was collected for each question, based on a literature review, and then refined through face-to-face interviews based on experiences of BIM experts. An international survey was conducted with leading BIM experts. From the 206 distributed surveys, 52 responses from four continents were collected. This study used quantitative data analysis to derive a manageable number (4–10) of CSFs for each category from dozens of anecdotal consideration factors. The derived CSFs are expected to be used as efficient metrics for evaluating and managing the level of BIM adoption and as a basis for developing BIM evaluation models in the future.
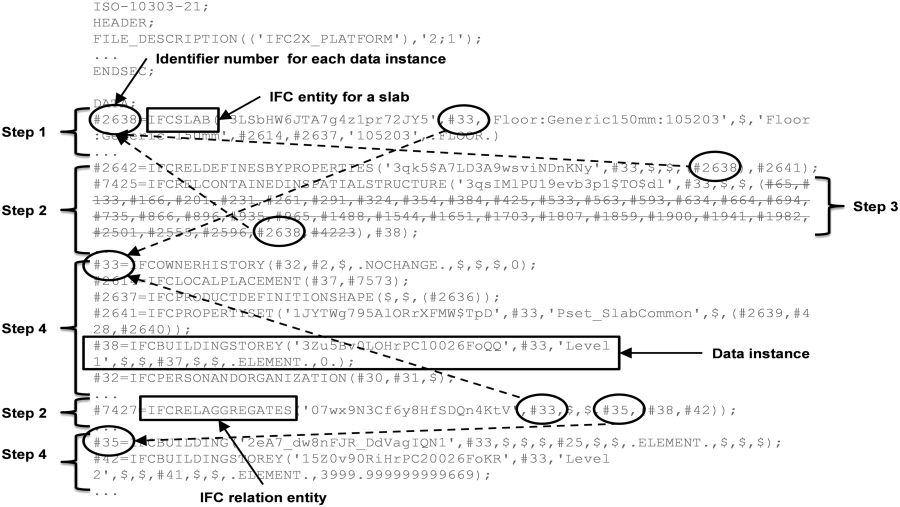
This paper proposes an algorithm for extracting a partial model from an Industry Foundation Classes (IFC) instance model without an IFC schema or a complete IFC model view definition (MVD). The methods developed in previous studies require either an IFC schema or MVD and software applications, such as an IFC model server or a building information modeling (BIM) authoring tool, to extract a partial IFC instance model. The algorithm proposed in this paper generates a partial model by recursively extracting IFC data instances in referential relations directly from an IFC instance model file, and it relies solely on the internal data structure of an IFC instance model, without an IFC schema or a MVD. The algorithm extracts physical and nonphysical data instances relevant to the user's selection of building elements by recursively iterating through data instances based on the rules specified in the algorithm. A set of required building elements is not defined on the spot; rather, a set of building elements required for a specific process is predefined as part of an information delivery manual (IDM) and can be used as input. The algorithm was tested by extracting partial models from 32 IFC 2x3 test casesinitially developed to evaluate the IFC compliancy of software applications in the construction industryand from an actual BIM project. The integrity of the extracted partial models was first validated by checking the syntax against an IFC schema and by checking the semantics of partial models using two IFC validators, namely, the Express Engine and the IfcObjectCounter. Test results showed that the proposed algorithm successfully extracts the intended partial models from the IFC instance files without using a schema. (C) 2013 American Society of Civil Engineers.
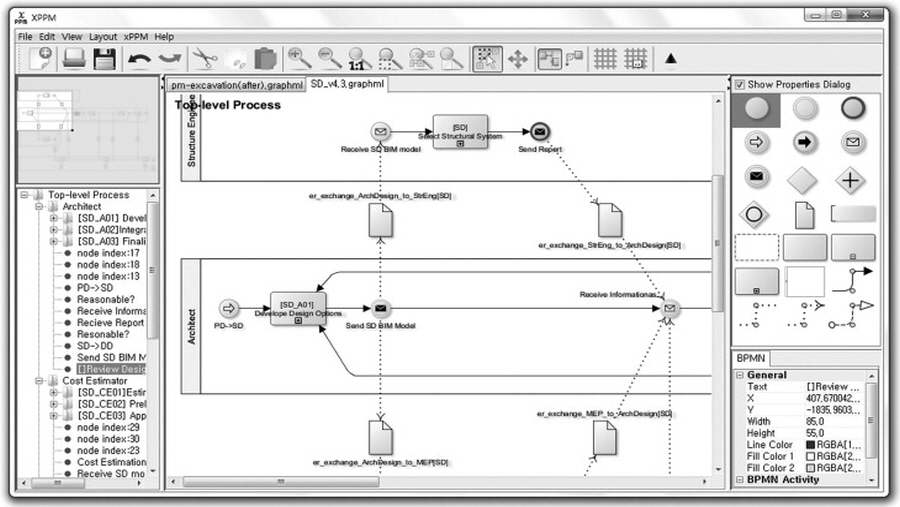
This paper proposes a new extended Process to Product Modeling (xPPM) method for integrated and seamless information delivery manual (IDM) and model view definition (MVD) development. Current IDM development typically uses Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN) to represent a process map (PM). Exchange requirements (ERs) and functional parts (FPs) specify the information required when information is exchanged between different activities. A set of information requirements, specifically defined as a subset of Industry Foundation Classes (IFC), is called an MVD. Currently however, PMs, ERs, FPs, and MVDs are developed as separate documents through independent development steps. Moreover, even though ERs and FPs are designed to be reused, tracking and reusing the ERs and FPs developed by others is practically impossible. The xPPM method is proposed to provide a tight connection between PMs, ERs, FPs, and MVDs and to improve the reusability of predefined ERs and FPs. The theoretical framework is based on the approach of the Georgia Tech Process to Product Modeling (GTPPM) to suit the IDM development process. An xPPM tool is developed, and the validity of xPPM is analyzed through the reproduction of existing IDMs and MVDs. The benefits and limitations of xPPM and lessons from the applicability tests are discussed. ? 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
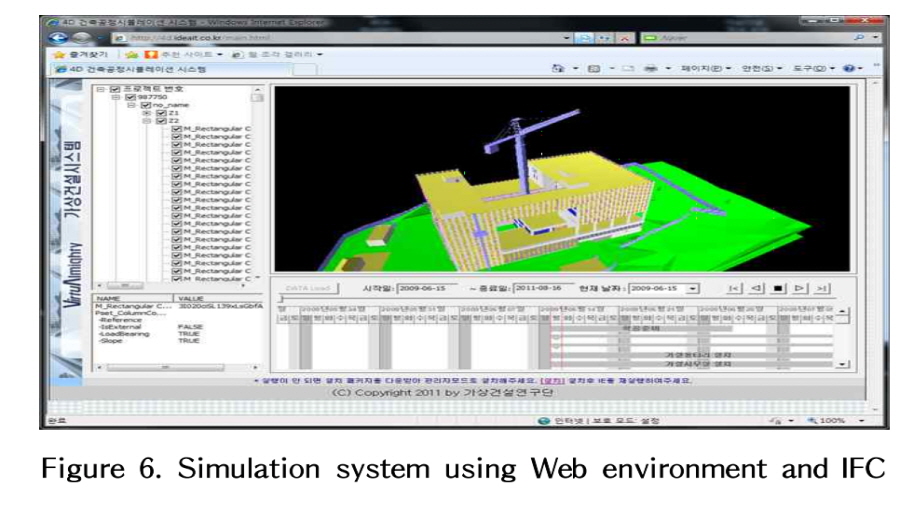
As construction projects become bigger, PMIS is being used as a project collaboration tool for project participants,owners, designers, inspectors and contractors. As the data type used in PMIS is usually text and most PMIS have no standard information classification system, there is a problem with data usability, such as the capacity for data search and analysis. BIM uses Objects and Properties, and this information might be used for relating with other construction information. As such, BIM technologies can be used with PMIS to enhance the data usability. The web environment is very convenient for multiple users, but the problem is that the data transfer speed is low for big files such as BIM model files. In this study, we suggested a Virtual Technology (VT) application to enhance the performance of BIM data exchange in PMIS, and tested and analyzed its efficiency when it is used to integrate BIM and PMIS in the web environment. The results of the study showed that VT can be used to enhance the efficiency of BIM data exchange in the web environment.
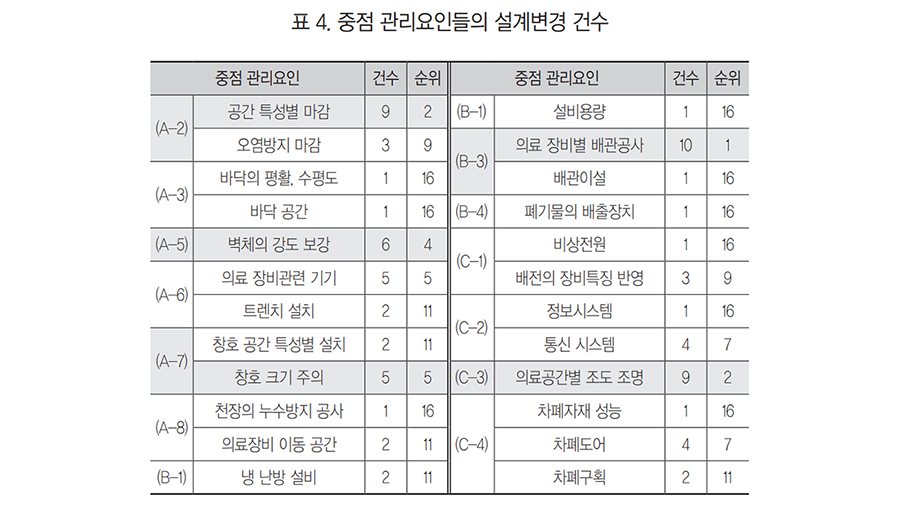
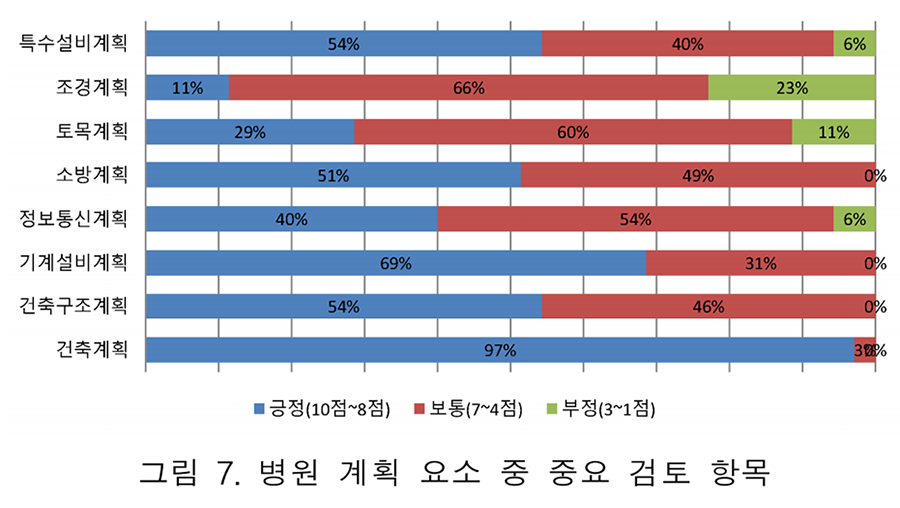
The complexity of constructing medical institutions is higher than that of general buildings, and many change orders in the design and defect repairs in the construction phase are required due to strict government regulations. The priority control of constructions and impact factors of medical institutions were analyzed in this study, and difficulties in the control in the design and construction phase were identified. First, the priority management factors that were identified were as follows: architecture, facilities, and electricity. Second, 1) priority management in constructions and factors resulting in change orders and 2) priority management in constructions involving defect repair were analyzed. Third, the importance recognized by the construction managers were analyzed. The priority management in constructions and factors that were recognized by the construction manager were deducted as having low importance, although there were many change orders and defects. The work of finishing, wall building, joining, office automation and communication function, and lighting were analyzed in the design phase, and waste, the office automation and communication function, ceilings, contamination control, and plumbing were analyzed in the construction phase. The results showed that there will be a decrease in change orders and defects if the concentration of the manager was elevated and priorities were managed.
New construction technologies, especially automated equipment, are rarely deployed on a construction site where many accidents and claims occur. This study analyzed and derived impact factors for technology adoption to improve the chance of adopting automated construction equipment to the field. First, impact factors were classified into functional and non-functional factors. Then the functional factors were divided into usability and functionality factors, and the non-functional factors into cost, construction property, and organization factors. Next, the importance and realization possibility of each impact factor were analyzed through a survey with experts. Usability and functionality were analyzed to have the highest importance and realization possibility. Lastly, the differences between construction companies and equipment development companies in the importance and realization possibility of each factor were analyzed. Construction companies recognized previous relationship, operator's attitude, members' will, and construction quality more important than equipment development companies.. The equipment development companies should consider these differences between the view of construction companies and that of equipment development companies on the impact factors. The result of this study can be used as a basis for evaluating for automated construction equipment in the preliminary development phase.
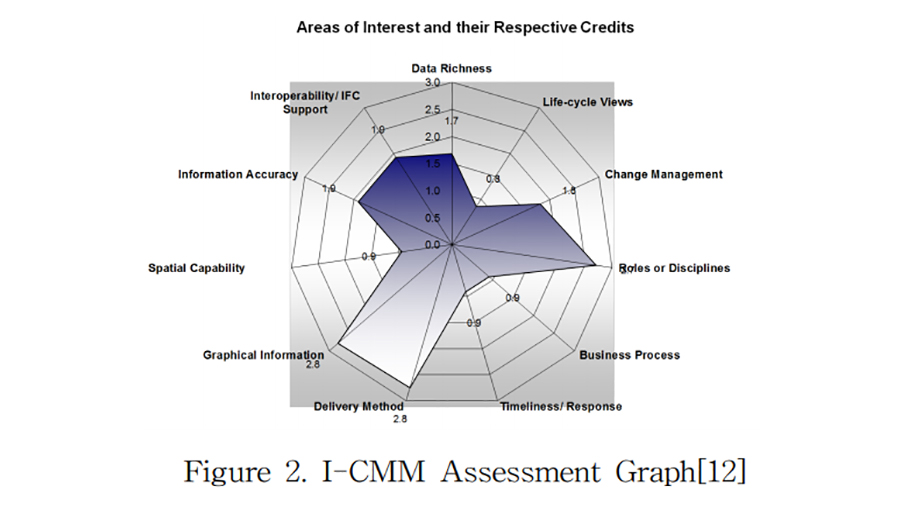
Hospital design review is challenging because design requirements for hospitals are more complex than other facilities, and many design changes occur due to changes of medical device specifications during a construction period and request from experts in various fields. Building Information Modeling (BIM) has recently been adopted in a hospital design process to improve design quality and reduce design errors. A possibility of automated check of hospital design using BIM has been demonstrated. However, the current use of BIM is too limited to satisfy the needs of practice. The main goals of this study are to survey the needs for the BIM-based hospital design validation technology and to propose the development direction and priority through a survey with experts and professionals in hospital design and construction. As the results, among various hospital-related design codes and guidelines, practitioners perceived that design change orders during a construction process and an overwhelming amount of design requirements were the most important and most repeatedly examined items. When BIM-based design validation was adopted, the central medical department, wards, and the outpatient department were regarded as the most beneficial spaces, clash detection between architectural and mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) components as the most beneficial work type, and the design development phase as the most beneficial phase. The development priority and direction of a BIM-based hospital design validation technology found in this study are expected to be used as a blueprint for developing and improving BIM-based hospital design validation systems in the future.
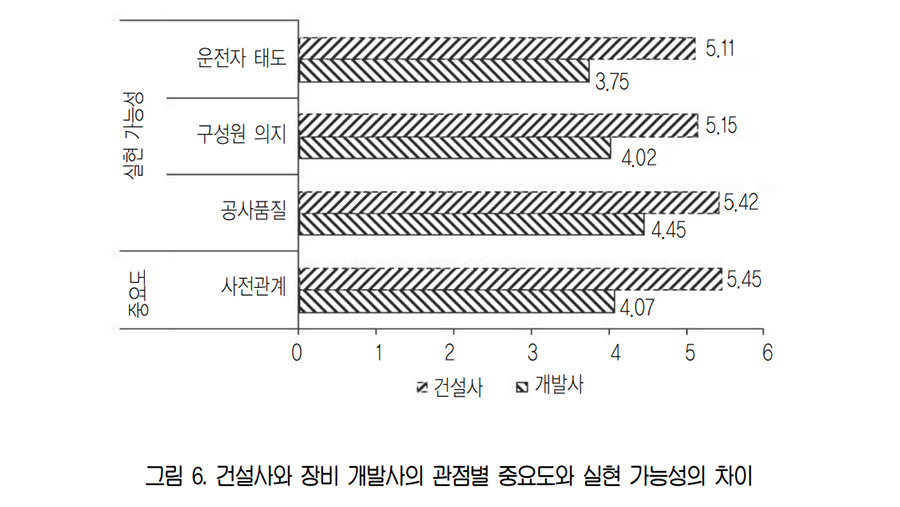
New construction technologies, especially automated equipment, are rarely deployed on a construction site where many accidents and claims occur. This study analyzed and derived impact factors for technology adoption to improve the chance of adopting automated construction equipment to the field. First, impact factors were classified into functional and non-functional factors. Then the functional factors were divided into usability and functionality factors, and the non-functional factors into cost, construction property, and organization factors. Next, the importance and realization possibility of each impact factor were analyzed through a survey with experts. Usability and functionality were analyzed to have the highest importance and realization possibility. Lastly, the differences between construction companies and equipment development companies in the importance and realization possibility of each factor were analyzed. Construction companies recognized previous relationship, operator's attitude, members' will, and construction quality more important than equipment development companies.. The equipment development companies should consider these differences between the view of construction companies and that of equipment development companies on the impact factors. The result of this study can be used as a basis for evaluating for automated construction equipment in the preliminary development phase.

Despite general perceptions, mass customization of double-curved metal panels with slight variations remains challenging. This paper reports the results of a three-year effort to develop a new hybrid sheet metal processing technique to fabricate double-curved metal panels for the Dongdaemun Design Park (DDP) building. DDP, designed by Zaha Hadid, has an unusually high percentage of double-curved panels. Among the 45,000 façade panels, approximately 22,000 panels are double curved. Despite the complexity and the large number of different types of panels, the joints are only 25 mm wide. Precision and a limited budget were the key requirements. The project team successfully developed a new and affordable sheet metal forming method called multipoint stretch forming, which is a hybrid method of multipoint forming and stretch bending, through trial and error. Several machines and prototypes were custom built and tested. The cost of fabrication of typical double-curved panels using this new method was US$260 per square meter compared with US$7,000 per square meter when die casting was used and US$3,000 per square meter when hydroforming was used. Furthermore, the average fabrication time per panel was reduced from several hours to 15 min per panel when using the new multipoint stretch forming method.
As the heights of high-rise buildings increase, their building area and elevation area also increase, consequently increasing their yearly energy consumption. Energy efficiency has become an even more important issue, especially when glass is used for a building's exterior. In this study, the life-cycle cost (LCC) of the exterior glass of high-rise buildings was analyzed from the perspective of energy efficiency and CO2 emissions. First, the LCC was analyzed according to changes in the selected types of glass. Reflective + Low-E (Type 1), double Low-E + Argon (Type 2), and triple Low-E + Argon (Type 3), which satisfy green building certification criteria and were used in the past for high-rise buildings in Korea, were selected as the exterior glass types. These types of exterior glass were applied to a case building and compared with the Low-E glass that was the existing glass type of a case building. The economic benefit of selected glasses for 40 years was greater in the order of Type 1, Type 3, and Type 2 compared to the existing glass. Second, these types of glass were applied to each orientation of the building. By changing the glass according to building orientation it is shown that in the east, west, and north, Type 1 was most economical, whereas Type 3 was most economical in the south. The results of this study will contribute to the improvement of energy efficiency, CO2 emissions reduction, and cost efficiency of future high-rise buildings. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)CO.1943-7862.0000502. (C) 2012 American Society of Civil Engineers.
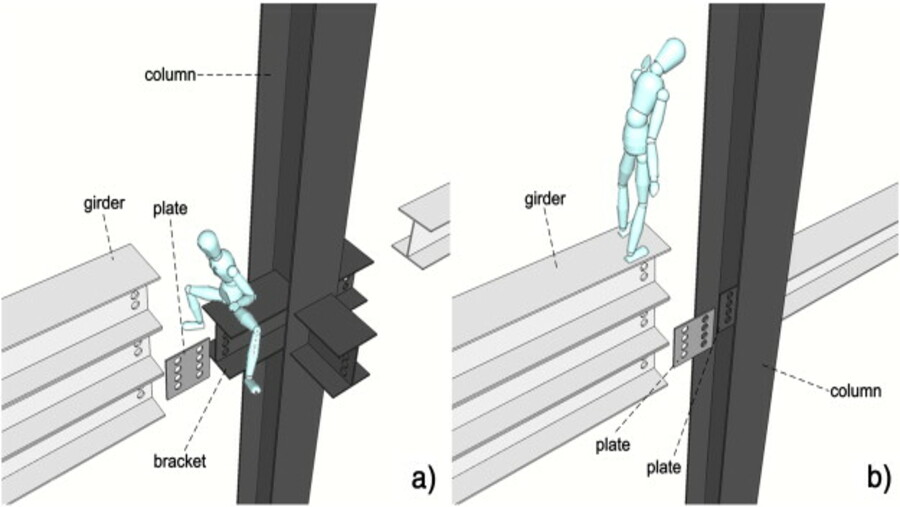
This study aims to develop a non-powered multi-beam lifting system (MLS). A MLS is a tower crane accessory that mechanically and subsequently secures and subsequently releases two to three beams in order to shorten the lifting cycle time and improve productivity. Previously proposed MLSs have been motorized systems that would require electricity and lack sufficient safety mechanisms. A non-powered MLS (NPMLS) was developed in this study and the field applicability and economic feasibility of the technology were analyzed through field tests. The analysis results showed that the elimination of lugs and the reduction of labor costs can yield considerable economic benefits. Above all, the major benefits of the NPMLS are improvements in workability and safety during steel construction. Field observations showed the NPMLS to be much safer and to afford much easier control of steel members than the traditional method. In addition, the learning curve of NPMLS was found to be very short.
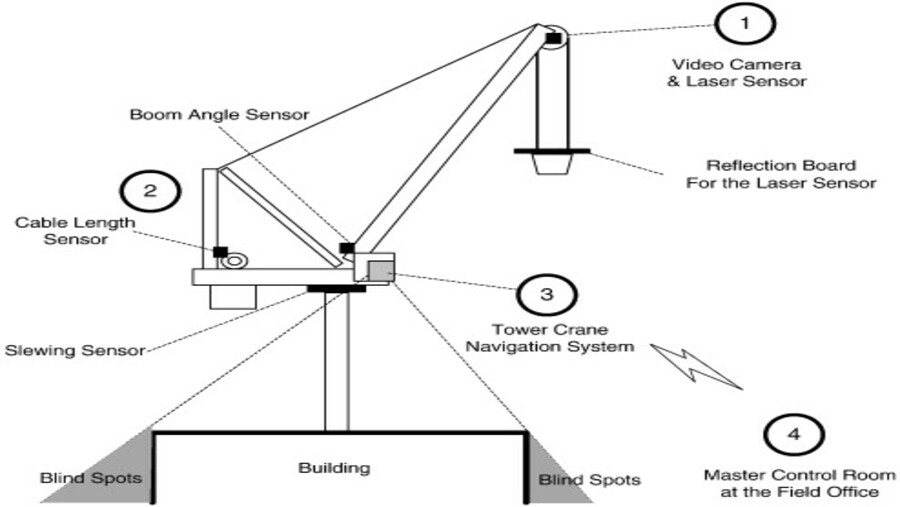
Tower crane operators often operate a tower crane with blind spots. To solve this problem, video camera systems and anti-collision systems are often deployed. However, the current video camera systems do not provide accurate distance and understanding of the crane's surroundings. A collision-detection system provides location information only as numerical data. This study introduces a newly developed tower crane navigation system that provides three-dimensional information about the building and surroundings and the position of the lifted object in real time using various sensors and a building information modeling (BIM) model. The system quality was evaluated in terms of two aspects, “ease of use” and “usefulness,” based on the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) theory. The perceived ease of use of the system was improved from the initial 3.2 to 4.4 through an iterative design process. The tower crane navigation system was deployed on an actual construction site for 71days, and the use patterns were video recorded. The results clearly indicated that the tower crane operators relied heavily on the tower crane navigation system during blind lifts (93.33%) compared to the text-based anti-collision system (6.67%).
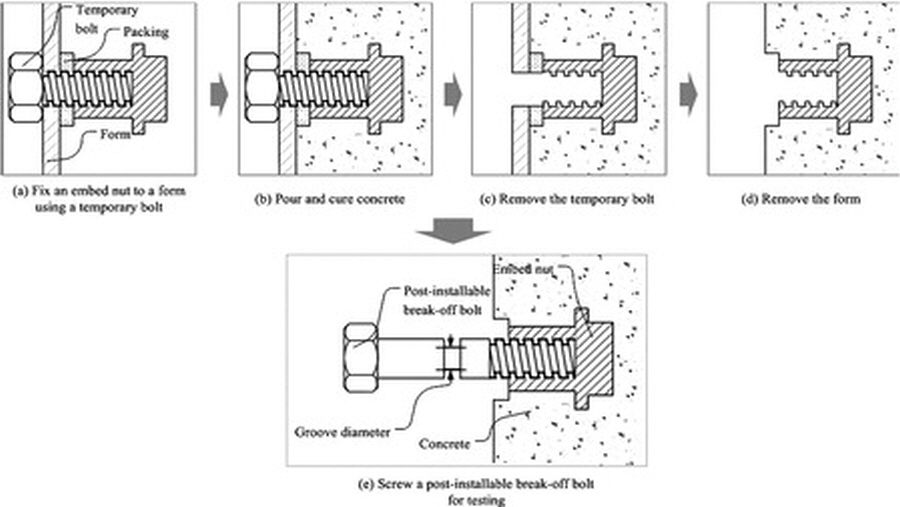
The pullout test is known to be more reliable for estimating the strength of concrete structures under construction than other nondestructive testing methods such as the Schmidt rebound hammer test, penetration resistance test, and ultrasonic pulse velocity method. However, existing pullout tests require several complex installation steps. Loading equipment that contains load cells is expensive. We propose a simplified pullout test using a post-installable break-off bolt, a standard bolt with a groove on the shaft, as an insert. The specific groove diameters of break-off bolts are designed to indicate concrete strength. However, the appropriate groove diameters for certain concrete strengths are not necessarily known. Regression models of groove diameter and the concrete strength were derived through a series of 188 experiments. The resulting equation showed 70.2% prediction accuracy for predicting concrete strength. The average difference between incorrect estimates and actual strengths was 0.13 mm, a magnitude that can easily be overcome if appropriate safety factors are studied and added to the prediction equations.
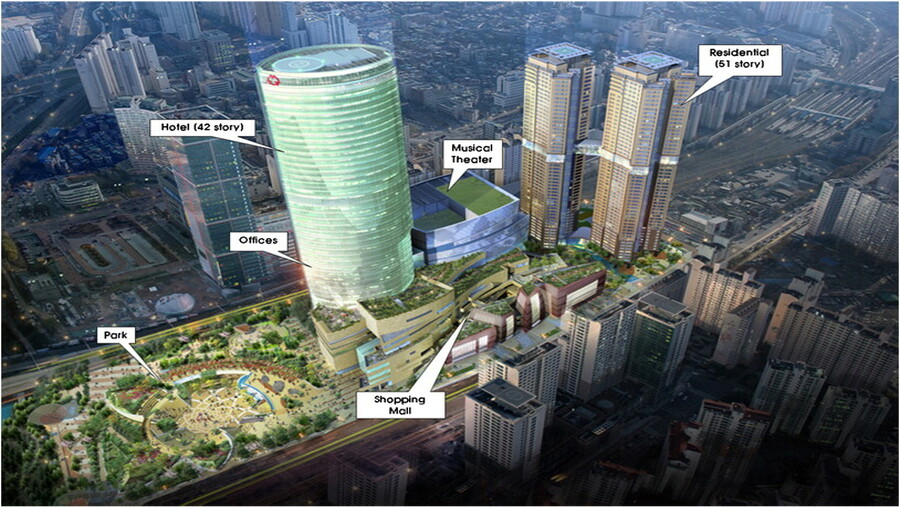

This paper reports a return-on-investment (ROI) case study of the use of building information modeling (BIM) in “design validation” based on the avoidance costs of rework due to design errors. The ROI was analyzed using the 709 individual design errors found during the BIM design validation of the six high- and medium-rise buildings in the D3 City project in Seoul, Korea. Each design error was categorized according to its cause and the likelihood of detecting it before construction. The likelihood of detecting errors in the ROI analysis made a large difference of a factor of four to fifteen. An additional analysis on the potential impact of design errors on the schedule shows that costs associated with schedule delays has a much larger economic impact than rework costs.
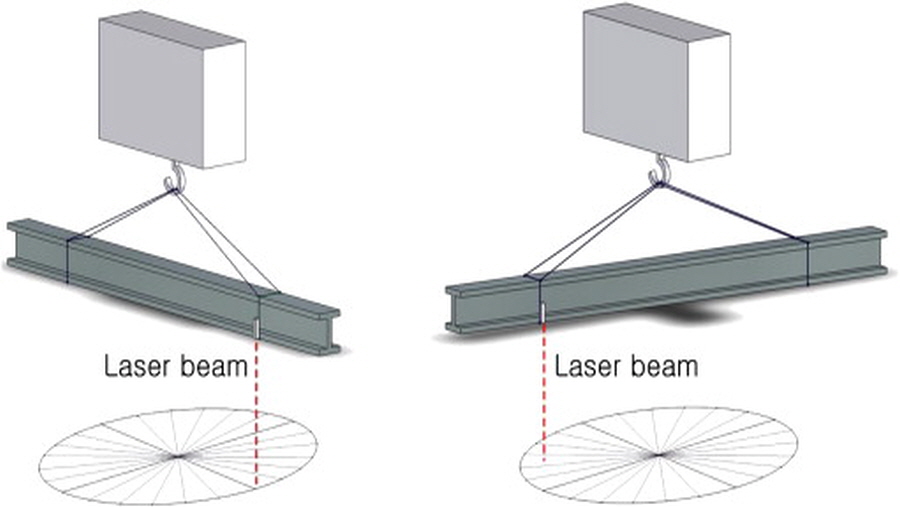
The rotation-controllable tower-crane hook block can control the horizontal rotation angle of a steel beam being lifted by a tower crane using a mechanical apparatus. It is expected that the mechanized hook block can relieve safety concerns; however, at the same time, there are several concerns: Is precise control of the rotation angle possible? Won't it be slower than rotating a beam by hand? If a mechanized system is faster, how fast is it? In order to test these, experiments were conducted. The precision of the rotating angle and the time for rotating and stopping the rotation controllable hook block were measured using an orientation sensor and a laser point. The results were compared to those of the conventional manual method. Since a steel beam usually has a symmetrical shape, π/2 rad (= 90°) is the maximum angle for placing a beam in the target location. The experiment results showed that a steel beam stopped after it moved 7π/600 rad (= 2.1°) and 9π/200 rad (= 8.1°) more, on average, due to inertia when the steel beam was rotated π/12 rad (= 15°) and π/2 rad (= 90°), respectively. However, it appeared that when an operator became used to the remote controller, the operator could reduce the rotation speed to stop a steel beam in the target location by reversing the motor direction. In terms of time, it took 5.80 s, 8.69 s, and 17.12 s, on average, to rotate a steel beam π/12 rad (= 15°), π/4 rad (= 45°), and π/2 rad (= 90°), respectively. The time for rotating steel beams using the conventional manual method at a construction site was also measured for comparison. The rotation time using the conventional manual method ranged from 11.96 s to 91.00 s depending on how easy it was for workers to reach and rotate a beam because workers rotate beams while hanging on a column. The results showed that the deviation could be reduced and work efficiency could be improved when a mechanized hook block is adopted on a construction site.
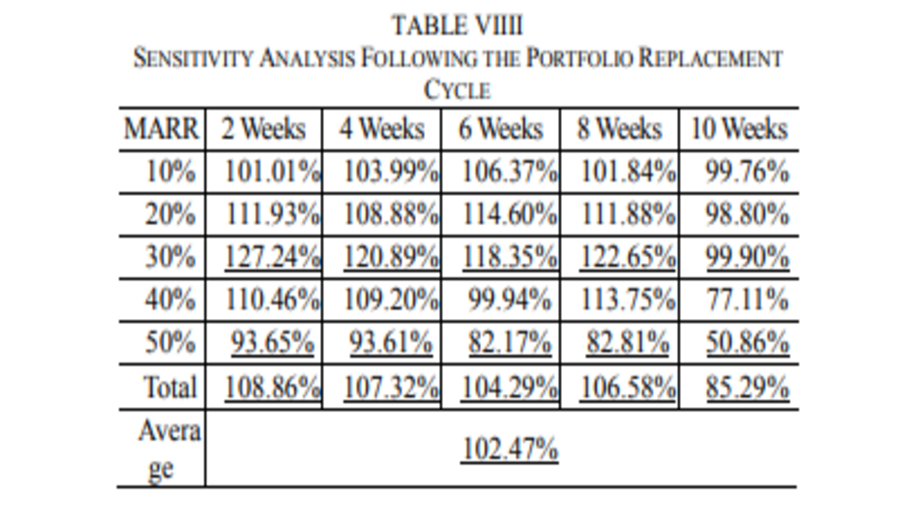
Domestic construction companies are suffering from financing difficulties in the wake of the economic slump in Korea and abroad. During this economic slump, real estate investment trusts (REITs), facilitators for improving financing and stimulating construction businesses, have increasingly expanded since their introduction in 2001. However, in terms of growth speed and marketing size, Korean REITs are falling behind those of other nations. The purpose of this study is to suggest a method for composing a portfolio using the Markowitz portfolio selection model to stimulate REITs. The main contents are as follows. First, a comparative analysis was conducted of increased REIT profit with the application of the Markowitz model and the average REIT profit rate from July 3, 2007, to July 21, 2008, during the investment analysis periods. The results showed that the total profit rate from the Markowitz model was about 10% higher than the average REIT profit rate. Second, the sensitivity was analyzed according to the portfolio's data-gathering and replacement cycle to measure the optimum cycle and yield. The six-mouth profit data collection period showed about 16% higher profits with the Markowitz model than with the REITs. The two-week portfolio change period resulted in about 11% higher profits with the Markowitz model than with the REITs.

This paper proposes improved architectural drawing representations and drafting methods for efficiently deploying building information modeling (BIM) in practice. The first BIM-mandated public project in Korea was announced in 2009. Over the course of several projects, the architectural firms learned that traditional drawing representations and drafting methods were ineffective and time-consuming and that drawings could be represented more efficiently and clearly when BIM tools were used. However BIM-mandated public projects still require traditional drawing representations and file formats. This study analyzed the limitations of current drawing practices in Korea by comparing them with drawing representations and drafting methods used in the US and discussed how the drawing representations and drafting methods could be improved when BIM tools are used. It was found that the readability of drawings could be improved by eliminating redundant information between drawings, effectively using cross-referencing functions between drawing files, and actively deploying perspective views that could easily be achieved from BIM model.
Although the number of projects applying Building Information Modeling (BIM) has increased, most construction industry groups that have adopted BIM are large construction corporations and architecture firms. BIM has had small effect because most of the application areas have been reviewed in part for construction error and clash detection. This study analyzed the necessity of original task improvement and the expected effect of BIM adoption in high-rise buildings in the increasing market size of Construction Management (CM) corporations. It also considered standards that have been suggested for BIM adoption. First, eight items were reclassified from the perspective of task-oriented action for the CM tasks of the Construction Management Association of America (CMAA), and high-priority tasks for improvement were derived from the perspective of productivity. Next, the expected effect of BIM adoption was investigated from previous studies and survey, and its applicability was analyzed in original tasks that need improvement. Although a detailed application method was not suggested for the potential improvement of tasks and lacked expert for survey, this study will provide standards to be considered by CM corporations that might investment in the adoption of BIM. Furthermore, the reclassified CM tasks could be used not only in the construction of high-rise buildings, but also that of other buildings.

The pullout test is a nondestructive testing method certified by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) and British Standards (BS). Research has shown that it is very reliable in terms of evaluating the concrete strength of reinforced concrete members. However, the pullout test is rarely performed on domestic construction sites due to the complex procedures and high costs involved. This study proposes a new pullout test composed of a post installable break-off bolt, an insert nut, and a pullout tester, which satisfy both economical and practical purposes on a construction site. Three different types of special fastening methods, a temporary fixed bolt, a plastic fixed panel, and a fixed bar, have been developed. A pullout tester is proposed that is driven by the circle force introduced into a handle composed of eight gears without a load cell and a hydraulic cylinder. The serviceability and reliability of these instruments were investigated through experiments at construction sites. Furthermore, the sample pullout test with a wall specimen was conducted to estimate the usefulness of the temporary fixed bolt type of fastening methods and pullout devices. Eventually, the developed instruments will be useful on construction sites if minor requirements are met.
The market competition among CM firms is rapidly increasing due to the rising demand of CM, large and complex construction products, and a limited domestic market for CM. The aim of this research is to offer useful data to CM firms on how to establish an effective marketing strategy by analyzing the characteristics of clients as factors in selecting CM. To study the characteristics and factors for selecting CM, this paper conducted a survey on 135 clients who have used CM services. CM selection factors are classified into brand image, management skills, ability of staffs, past performance and word-of-mouth marketing. This paper proposes certain patterns to apply in the CM selection factors according to the customers and projects, duration of service, and age of customers. Results of this study revealed that clients select CM based on their preferred patterns according to the type of customers and projects, duration of service, and age of customers. Also, clients prefer to look at past performance and the brand image in residential facilities and religion facilities. These results can be used to efficiently improve marketing strategy by first analyzing several factors that influence the selection of CM based on customer characteristics.

What information can or cannot be exchanged between different systems? Since the dawn of the computer-aided design and engineering era, interoperability has been an issue. The exchangeable set of information between different systems has been loosely defined as the intersection of information. Yet, as information flow has directionality, a general definition of “intersection” is inadequate to define an exchangeable set of information. This paper proposes a new directive set operation, semantic intersection, and discusses which information can or cannot be exchanged between different systems using the concept of semantic intersection. This opens up the possibility of predetermining or calculating the exchangeable set of information between two or more systems or the possibility of automated generation of a standard product model between different systems. This paper focuses on data exchange between systems, but the proposed theory is also applicable to data exchange between human beings.
This study suggest a selection method for exterior glass with regard to energy efficiency, CO₂ emissions, and economics. First, it set up a hierarchy of factors for the selection of exterior glass and analyze their importance. As a result of the importance analysis, insulation is the highest importance factor, followed in order by economic and technical state, lighting, view, and others. Second, exterior glasses were classified for application in apartment buildings and office buildings based on the importance of selection factors, and then some types of exterior glass were selected for energy efficiency analysis. Third, this study analyzed energy efficiency, CO₂ emissions, and LCC(life cycle cost) after the selected glasses had been applied to actual office and apartment buildings. In cases in which two types of glass were applied to office buildings, the break-even points were 4 years and 14 years respectively, while the economic profits over 40 years were 2,536,332,214 won and 146,972,379 won. In cases where two types of glass were applied to apartment buildings, the break-even point was 1 year, and the economic profits over 40 years were 1,416,321,266 won and 130,760,294,093 won.
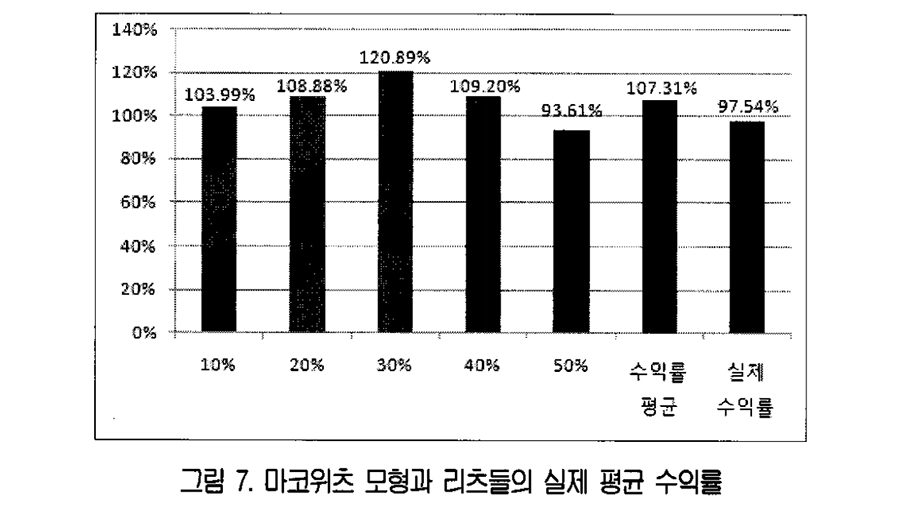
Domestic construction companies suffer from the difficulty in financing in the wake of economic slump at home and abroad. In the periods of this economic slump, which hit the nation, REITs, the facilitator of fluid financing and the stimulating of construction economic, has increasingly been expanded since its introduction in 2001. But, REITs relatively falls behinds any other nations, in terms of its growth speed and marketing volume. The purpose of this research thesis is to suggest the method for composing a portfolio using Markowitz portfolio selection models for stimulating REITs. Main contents are as follows. First, the thesis made the comparative analysis on profit increase in REITs’investment in application of models by Markowitz and REITs derivatives from 2007/07/03 to 2008/07/21 during investment analysis periods. The result showed that total profits by Markowitz model amounted to about 10 percent higher than average profits of REITs derivatives. Second, this thesis made the analysis on sensitivity of data-gathering and portfolio change periods of the existing profits, in order to measure the both periods and yield optimum profits. The six month data-collecting periods of profits accounted for some 16% higher profits than profits of REITs derivatives. In case when the two week periods of portfolio change accounted for some 11% higher profits than profits of REITs derivatives.
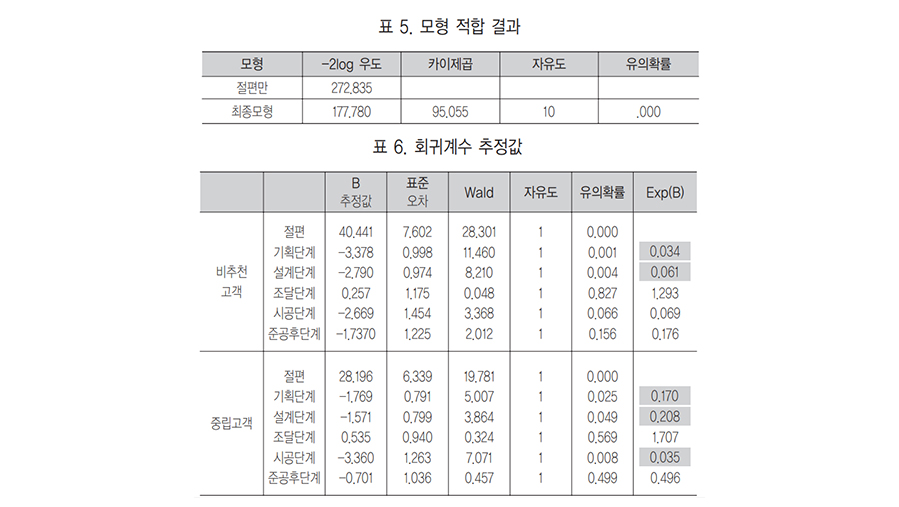
The main roots of CM service contracts include existing customer repurchases and those made by new customers by existing ones. The study on customers and loyalty can be factors to strengthen CM's competitiveness. However, there have been little attempt to study customer satisfaction and customer loyalty. Construction Management (CM), the advanced construction management method, was introduced 15 years ago in the mid 1990's in the domestic market. The aim of this research is to build a model that can predict customer loyalty based on how much customers are satisfied with CM service. To measure customer satisfaction and loyalty, this research surveyed 135 decision-makers who have experienced CM services. Customer satisfaction was tested and analyzed according to different phases: planning, designing, procurement, construction, and post construction. Referral intention was tested based on NPS theory. Customer types were divided into detractors, passively satisfied and promoters according to the tested measurement and multinomial logistic regression between the satisfaction by construction phases and customer types. This research resulted to a model that can predict customer types: detractors, passively satisfied and promoters, which were determined according to satisfaction level. The initial planning phase also revealed which factor is most influential for a customer to become promoter. These results can be used to acquire customer loyalty by managing the satisfaction of customers through a project under an Internet-based environment. Such can provide the needed information in quickly exploring positive and negative word-of-mouth feedbacks.
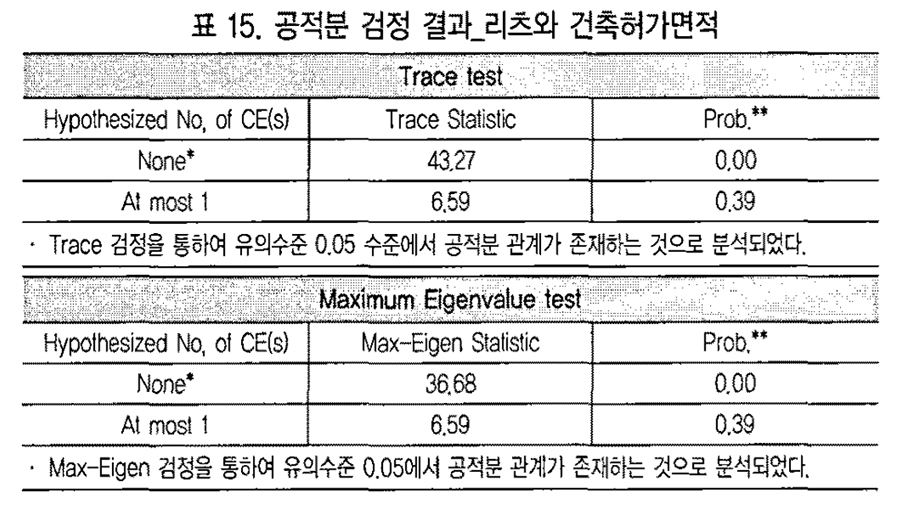
Even though REITs (Real Estate Investment Trusts) are listed on the stock market, REITs have characteristics that allow them to invest in real estate and financing for real estate development. Therefore REITs is related with stock market and construction business and real estate business. Using time-series analysis, this study analyzed REITs in relation to construction businesses, real estate businesses, and the stock market, and derived influence factor of REITs. We used the VAR (vector auto-regression) and the VECM (vector error correction model) for the time-series analysis. This study classified three steps in the analysis. First, we performed the time-series analysis between REITs and construction KOSPI(The Korea composite stock price index) and the result showed that construction KOSPI influenced REITs. Second, we analyzed the relationship between REITs and construction commencement area of the coincident construction composite index, office index and housing price index in real estate business indexes. REITs and the housing price index influence each other, although there is no causal relationship between them. Third, we analyzed the relationship between REITs and the construction permit area of the leading construction composite index. The construction permit area is influenced by REITs, although there is no causal relationship between these two indexes, REITs influenced the stock market and housing price indexes and the construction permit area of the leading composite index in construction businesses, but exerted a relatively small influence in construction starts coincident with the composite office indexes in this study.
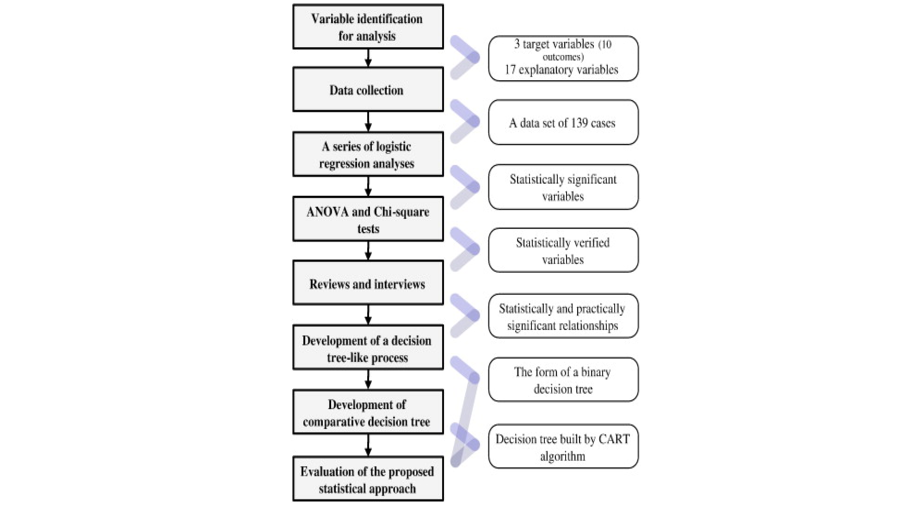
Machine learning techniques generally require thousands of cases to derive a reliable conclusion, but such a large number of excavation cases are very difficult to acquire in the construction domain. There have been efforts to develop retaining wall selection systems using machine learning techniques but based only on a couple of hundred cases of excavation work. The resultant rules were inconsistent and unreliable. This paper proposes an improved decision tree for selecting retaining wall systems. After retaining wall systems were divided into three components, i.e., the retaining wall, the lateral support, and optional grouting, a series of logistic regression analyses, analysis of variance (ANOVA), and chi-square tests were used to derive the variables and a decision tree for selecting retaining wall systems. The prediction accuracy rates for the retaining walls, lateral supports, and grouting were 82.6%, 80.4%, and 76.9%, respectively. These values were higher than the prediction accuracy rate (58.7%) of the decision tree built by an automated machine learning algorithm, Classification and Regression Trees (CART), with the same data set.
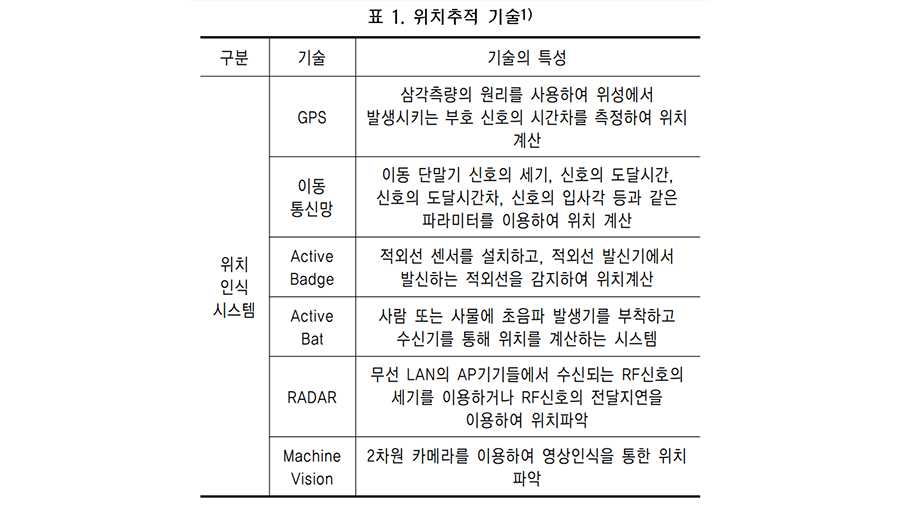
Steel frame construction in high places entails many risk factors. In order to improve the safety and productivity of steel frame construction, a project to develop a robotic tower-crane has been undertaken. As the first step, a real-time lifting-path tracking system is being developed. In a previous study, a laser-based tracking system was proposed. While a laser-based tracking system requires at least three laser sensors to detect the x, y, z coordinates of a lifted steel member, a GPS-based system has an advantage over the laser-based system, in that the x, y, z coordinates of a lifted steel member can be detected by a single GPS sensor. To improve the accuracy, a relative positioning method using two GPS sensors was proposed in a previous study. This paper reports an improved GPS-based lifting-path tracking system of a tower crane based on an integrated RF modem and GPS system. The results showed that the RF modem could successfully send the identifier information to a server a maximum distance of 1 km away from the lifted steel beam, and the lifting path information of each beam captured by the GPS-based tracking system was successfully saved together. Also, by using an improved algorithm for the GPS relative positioning method, the deviation was reduced to 0.61 m on average.
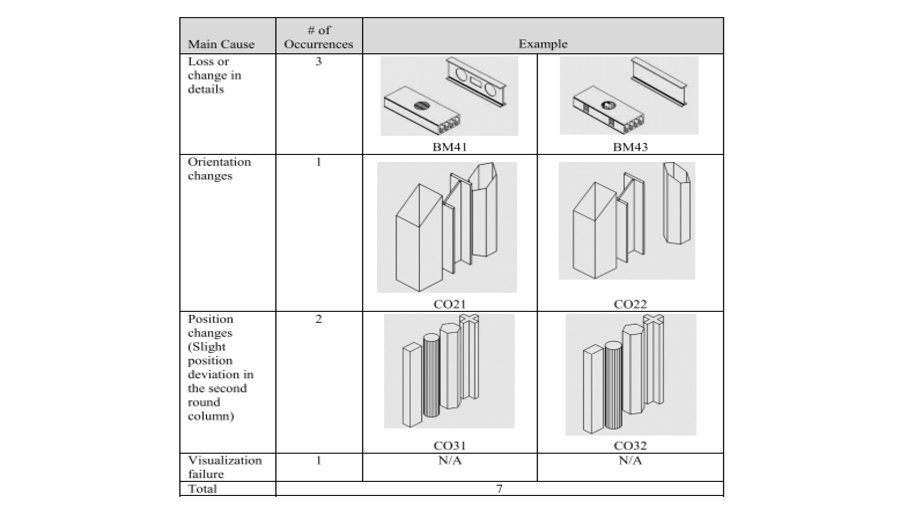
Recently, several papers reported problems in data exchange using industry foundation classes (IFC). However, most comparisons were made based on a visual check, a manual count, and observation of properties that were selectively chosen. This study proposes a set of metrics for quantifying the similarities and differences between IFC files. The proposed metrics include the similarity rate, the matching rate, the globally unique identifier (GUID) preservation rate, the missing rate, and the addition rate. A long-term goal of this study is to develop a set of metrics for quantifying the information exchange rate between two IFC files. Automated identification of modified information versus newly generated information is an unsolved challenge. The proposed metrics were used in analyzing 88 IFC files generated from different systems to demonstrate the potential use of the proposed metrics.
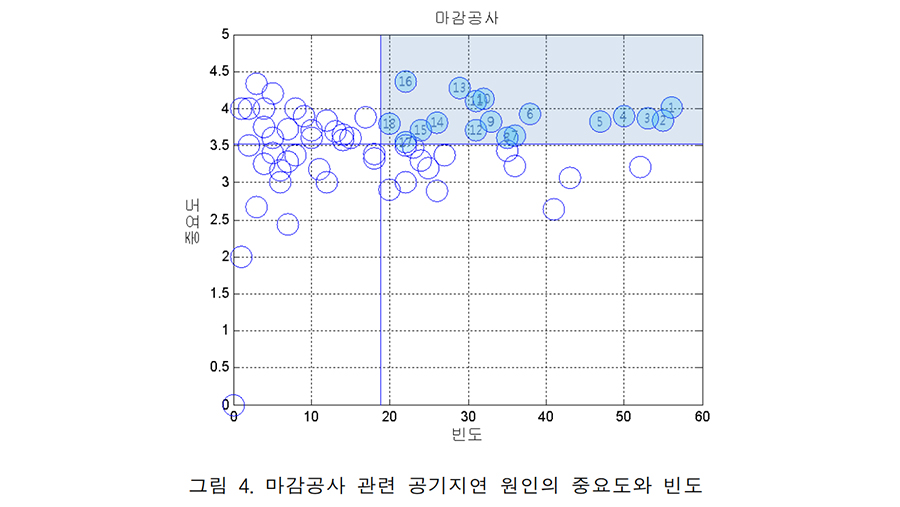
Reduction of construction duration is very important factor in construction productivity and have a strong influence on the reduction of material cost, labor cost, and financial cost. Thus, many technologies for reduction of construction duration have been developed. Many of them, however, cannot be applied in construction practice because of the difficulties and construction delays which arise from the legal or customary aspects other than the technological aspects. In this study, we conducted a survey of 122 engineers of construction companies to identify these legal or customary factors for difficulty and delay in detail which disturb the application of the developed technologies. Then we analyzed the importance and priority of the factors of difficulty and delay factors quantitatively and, finally, identified the appropriate countermeasures for them.
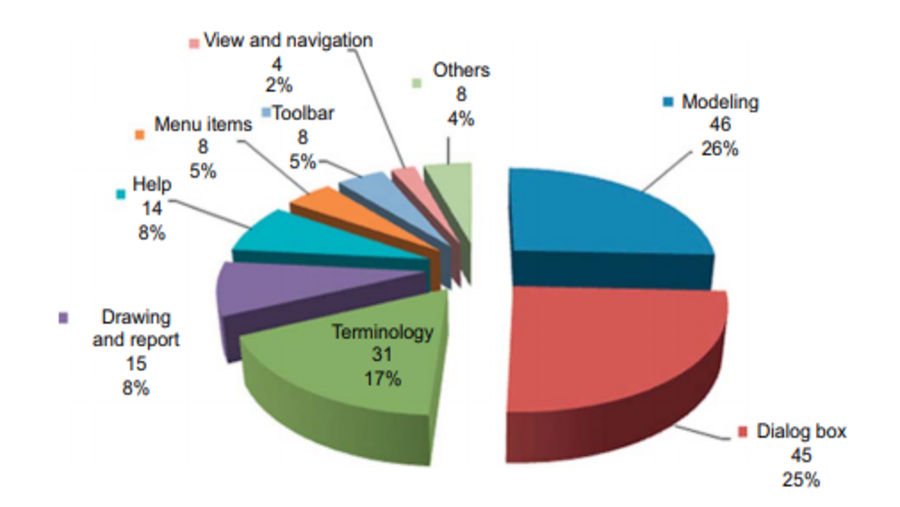
This study proposes usability principles for the user interfaces (UI) design of complex 3D parametric architectural design and engineering tools. Numerous usability principles have been developed for generic desktop or web applications. The authors tried to apply existing usability principles as guidelines for evaluating complex 3D design and engineering applications. However, the principles were too generic and high-level to be useful as design or evaluation guidelines. The authors, all with more than 10 or 30 years of experience with various CAD systems, selected and reviewed 10 state-of-the-art 3D parametric design and engineering applications and captured what they thought were best practices, as screenshots and videos. The collected best practices were reviewed through a series of discussion sessions. During the discussion sessions, UI design principles underlying the collected best practices were characterized in the line of existing UI principles. Based on the best practices and the derived common UI principles, a new set of refined and detailed UI principles were proposed for improving and evaluating 3D parametric engineering design tools in the future.
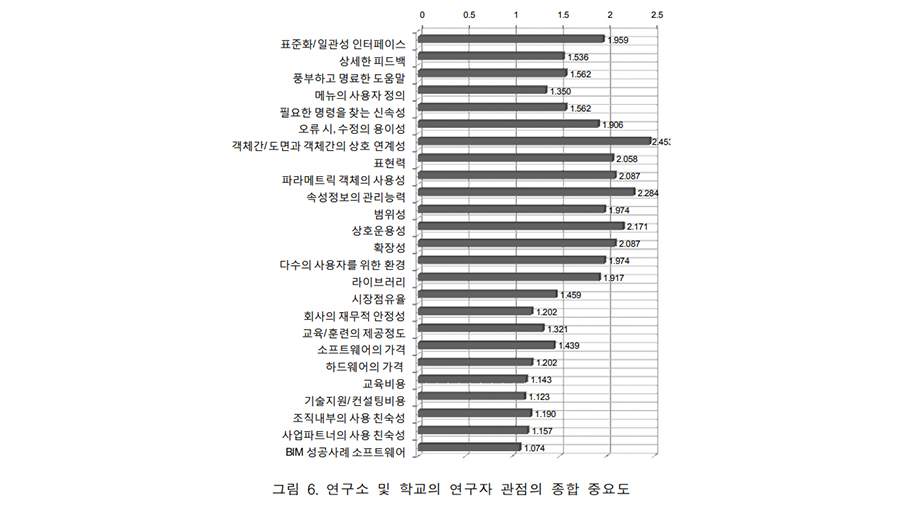
In this study, degree of support of main BIM functions was analyzed and relative importance and priority were analyzed by drawing out selection factors for selecting proper BIM software per business process. Main contents are as follows. First of all, BIM functions introduced in overseas construction related companies were analyzed in order to analyze main functions and limits of the current main BIM software. In addition, BIM functions required in domestic construction companies were drawn out and level of support at present was analyzed. Next, after drawing out selection factors for selecting BIM software, level of importance and priority were analyzed. Selection factors were drawn out in layers of upper level factors and lower level factors. In case of errors in degree of importance in integration of upper level factors and lower level factors, easiness of modification and mutual connectivity between objects and between drawings and objects were turned out as the highest. Finally, subjects of BIM introduction were classified in aspects of construction companies, design companies, research institutes, and schools and degree of importance was analyzed. Construction companies and design companies showed importance of factors of usability aspect as the highest and factors of business issues aspect were shown as the lowest. In viewpoints of researchers of research institutes and schools, it was found out in sequence of functionality and usability aspects and importance of business issues aspects was shown relatively higher than construction companies and design companies.
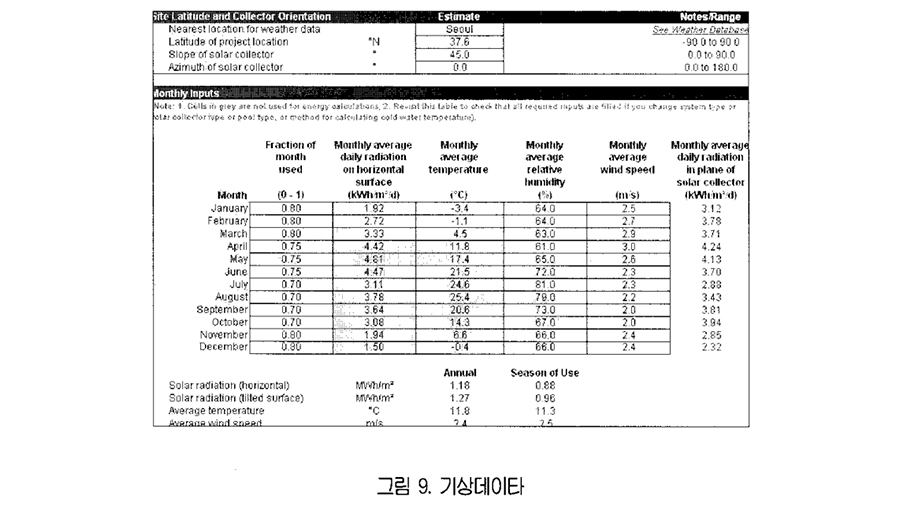
This study is to analyze the performance of SWH(Solar Water Heating) and GSHP(Ground Source Heat Pump) systems by evaluating their energy efficiency and LCC(Life Cycle Cost) as being applied to the OO hall as a selected building in the Army. The OO hall, used as bathrooms, dining rooms, accommodations and offices, has reinforced concrete structure system with three floors above the ground and one underground, and its total floor area is approximately 2,917 m2 . Two energy simulations are conducted to predict the yearly cooling and heating energy of the selected building: One is for analysis of an air-conditioning energy consumption using the e-Quest program, and another is for two new-renewable energy facilities as a water heating source using the RETScreen. The installed capacity of two new-renewable energy facilities is determined according to the 5% level of total standard construction cost. As a briefly result, SWH system is more energy-effective than GSHP system. Considering the break-even point, it is expected that SWH can take only 3 years 11 months to pay for itself in savings while the investment of GSHP can be recovered in more than 16 years 6 months.
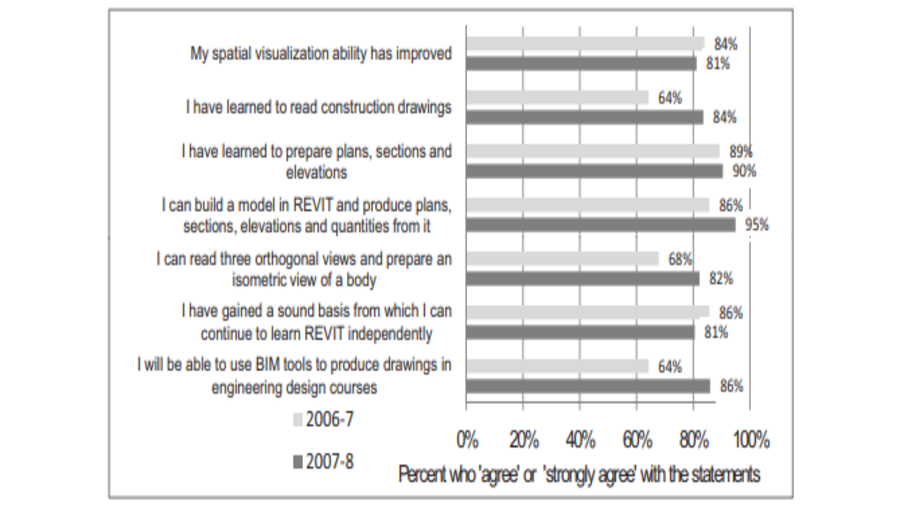
Lack of personnel with Building Information Modeling (BIM) skills is a significant constraint retarding use of the technology in the architecture, engineering, and construction industry. Unless BIM is introduced into undergraduate civil engineering curricula in a fundamental way, graduate civil engineers will lack the skills needed to serve a construction industry in which three-dimensional models are the main medium for expression and communication of design intent and the basis for engineering analysis. A mandatory freshman year course titled “Communicating Engineering Information,” which teaches both theoretical and practical aspects of BIM, has been developed to replace the traditional engineering graphics course at the Technion. The main lesson learned through four semesters of teaching the class is that students find BIM tools intuitive and therefore relatively easy to learn; the majority of lecture hours are now devoted to the conceptual aspects of BIM and the principles for preparing models that can be analyzed in multiple ways. BIM can and should be taught in its own right, and not as an extension to computer-aided drawing. The skills students have been able to bring to bear in design courses later in their university education indicate that the approach is sound and will enable graduates to meet the needs of the civil engineering profession in the “BIM age.”
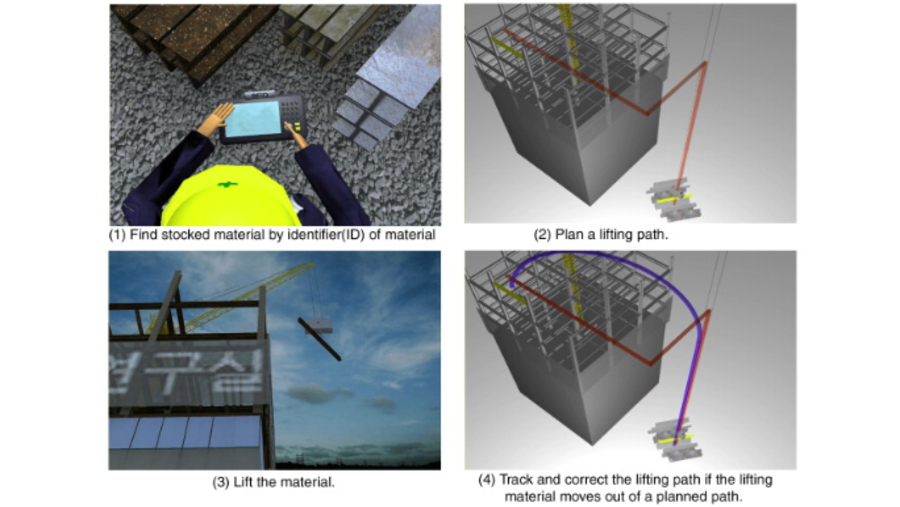
As the number of high-rise buildings increases, so does the use of tower cranes, the number of which now tops 3000 per year in Korea. Accordingly, the safety issues of high workspaces and efficiency issues of repeated work arise in the process of lifting materials to high places. As an alternative to traditional tower cranes, we are developing a robotic tower-crane system. By developing a robotic crane system, we expect the productivity to improve by 9.9%–50% based on the results of previous studies. In this study, we examine the feasibility of a laser-technology-based lifting-path tracking system for a robotic tower-crane system. There have been efforts to develop a robotic tower crane but they could travel only through preplanned paths or had blind stop problems. We proposed a robotic tower-crane system with a laser device, an encoder, and an accelerometer, and tested the feasibility of the system under indoor, outdoor, and swinging conditions. In the process, we developed a software application to receive and record data from the laser device. The test results showed the feasibility of a proposed lifting-path tracking system for a robotic tower crane under various outdoor conditions. Several limitations have been also recognized.
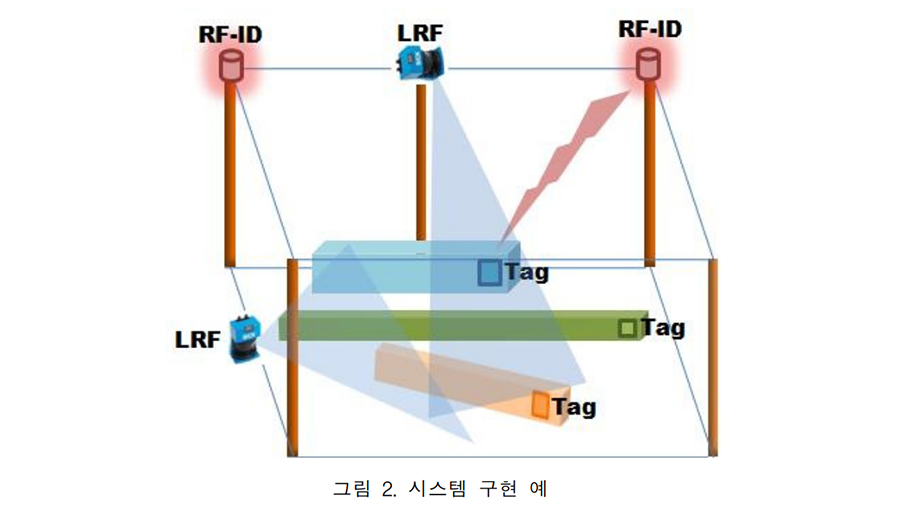
Automation and robotization has been required in construction for several decades to reduce the cost and time and to increase the productivity and safety. Especially for steel construction in high-rise building, the needs for automation is emphasized because this is inherently a very dangerous and difficult job. As one procedure of automation, the equipment like robotic crane should carry steel frames from staging area to the installed spot automatically. To do this, the position and pose of steel frames should be known to robotic crane. This paper presents a recognition and localization method for steel frame materials to remedy this problem. In the proposed method, the shape model is acquired by RF-ID technology and the loading shape of steel frame materials in staging area is recognized by laser range finder (LRF) sensors. After clustering the scanned data into several objects, scan matching method is applied to recognize each object. Experimental results are included to verify the performance of the proposed method.
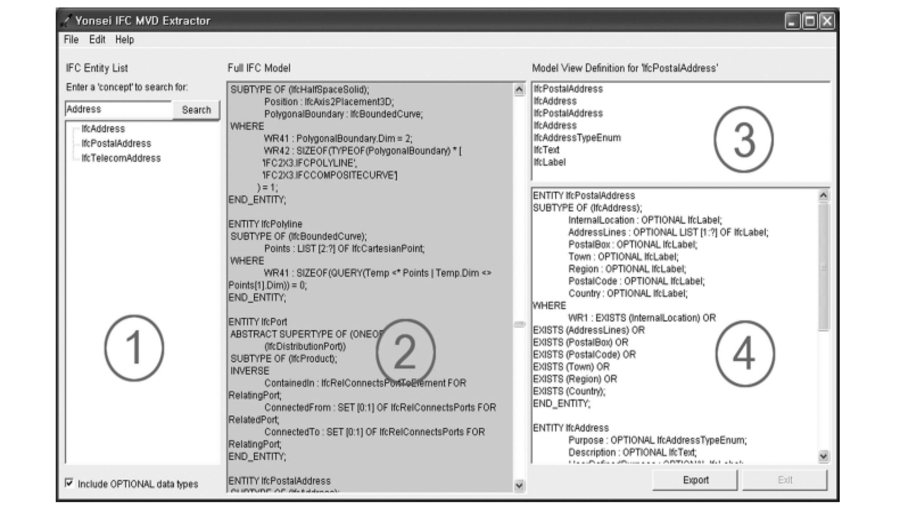
An EXPRESS schema is a data schema defined in EXPRESS, an international standard language for defining product data schemas. This technical paper proposes and formally defines a set of conditions for generating a minimum valid subset of an EXPRESS schema corresponding to a concept, where a concept is a general idea and a subset is a partial model of a data schema. We introduce a notion of “minimal set” to define the relationships between a subset and other subsets, and also between a subset and concepts. A minimal set is the smallest complete subset of a schema that corresponds to a concept. Using IFC, an international standard data model for the architecture, engineering, and construction industry, the proposed conditions have been implemented in a software application developed for extracting subsets from the IFC schema matching the concepts. A number of examples are demonstrated.
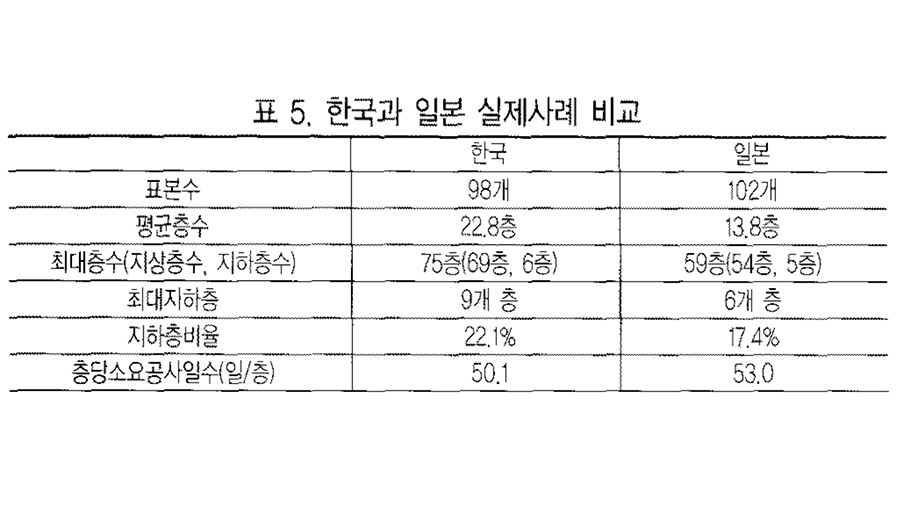
In the previous comparative studies of international competitiveness conducted before 2003, Korean construction productivity had been estimated to be lower (or poor) than that of developed countries such as US, UK, and Japan. However, the amount of international contracts Korean has won increased substantially, and Korean construction has progressed with creating two skyscrapers such as Petronas Tower and Burj Dubai. At this point we need to reevaluate what we are capable of. In this paper, we evaluated international competitiveness of our construction industry comparing to advanced countries by analyzing labor productivity. For evaluating construction competitiveness we measured labor productivity using the value of construction work in US dollar per hour based on domestic and foreign statistical data and analyzing completion days per a story and the ratio of underground floors to ground floors of buildings in Korea and Japan. As a result, although our construction productivity is not yet competitive with the US and Japan yet, we excel the UK.
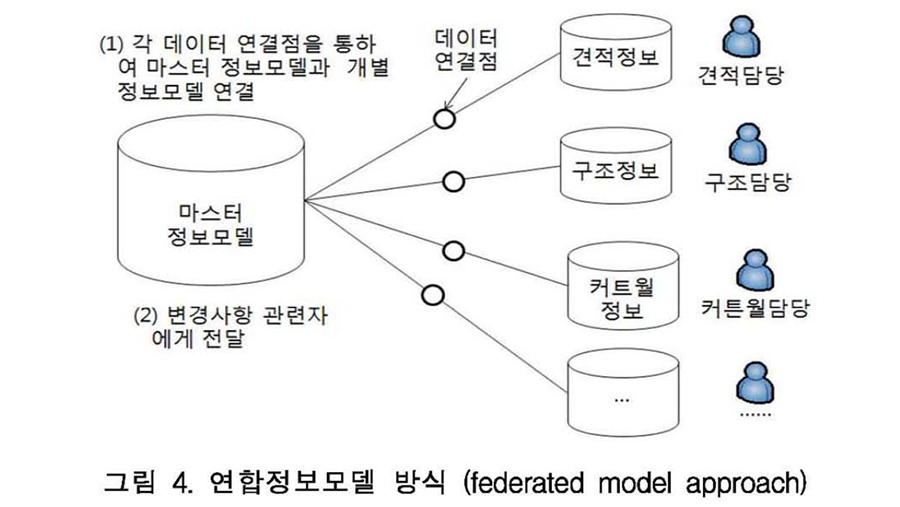
As information technology and the skills of communication rapidly advance, the number of BIM implementations in the field is also increasing. Collaboration and communication among project participants are important factors of BIM implementation. In this paper, we discussed collaboration and information management in BIM implementation based on case studies we conducted of successful international projects implementing BIM. The size of the project is more extensive than the previous one, so legal liability among the participants was higher. Because reuse and sharing of information are important in the BIM process, the minimizing of conflicts is a key factor for success. The master BIM model centers on information exchange and coordination of BIM collaboration. Successful projects require the efficient management of the master BIM model. Project managers must therefore make information mangers like Digital Design Director (DDD)or organizations that are in charge of information exchange, coordination, and changed models. Also, project mangers introduced the integrated project delivery method to help consultants and construction companies participate in the design phase. The integrated project delivery method can boost the efficient progress of projects. BIM implementation in Korea is at an early stage compared to other developed countries. As BIM spreads rapidly in Korea, we expect that difficulties in collaboration among participants will also increase, as it did in the international projects we examined. For future construction projects to go smoothly without any communication difficulties, I believe the Korean construction industry needs to accept management of the master BIM model, information exchange, and coordination of the BIM process, each of which is discussed in the case study of this paper.

The objective of this paper is to propose a conceptual framework of a BIM based collaboration supporting System, called Construction Project Life Cycle Management (CPLM). The framework of CPLM is proposed by reflecting the characteristic of AEC industry such as delivery methods, process, fragmentation, etc.. And it is a system intended to help project participants make better decisions and to facilitate coordination between various stakeholders in a project by providing virtual collaboration environment.
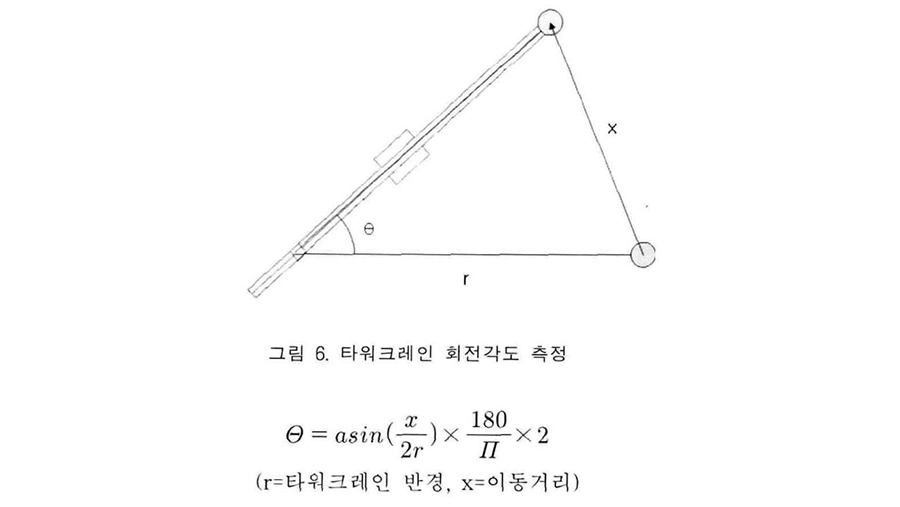
As buildings are becoming bigger, higher, and more complex, skilled workers are needed more than ever. But the number of skilled workers is decreasing. The automation of construction processes was suggested as a possible solution. For the construction of high-rise buildings, tower cranes, in particular, are the most important equipment. Our long-term goal is to develop a robotic tower crane. In this paper, as the first step towards the development of a robotic crane development, we tested a possibility of adopting the Global Positioning System (GPS) combing with the Building Information Modeling (BIM) technology in tracking the lifting paths of a rower crane. In order to support the management of lifting processes of construction materials, especially steel frame members, a tower crane simulation system is developed using the GPS and BIM technologies. For the rower crane simulation system, a lifting path tracking system and an object model for a tower crane are developed. We proposed a variation of the relative measurement method in GPS, which uses a pair of regular GPS, and tested the precision of the proposed system in various situations.
To be contrast past which supply ahead of demand and institutional entry barrier built present which uncertainty and instability is raised, for achieving business result it is necessary with differentiation resources and grasping who is competitor who is customer. Especially small and medium-sized firms in trouble with funding have to be faithful to customer satisfaction and managing customer to attain the constant market demand. But problem related with row-price order and worse profit causes deficient investment in managing customer. Who confront with this uncertain construct market small and medium-sized firms have to set up self-strategy with analyzing customer/orderer relationship and possibly outbreakable scenario. This research adopting scenario planning technique and design of experiment is looking through core-issues raised connected with managing customer of small and medium-sized construct firms and analyzing the effect cause, after submitting scenario for highly probable future situation in vision of customer, estimated and evaluated through the design of experiment. And presenting the strategy direction to confront with scenario situation it can be use to be a database for analyzing of customer/orderer/building-owner for small and medium-sized firms.
Occasionally an owner of public construction work pays financial costs in addition to progress payments. However, the overall scale of financial costs are not known. This research examines, based on a case study, the financial cost incurred in public construction works and the following issues: the overall scale of financial costs, the impact on financial costs on the owner, and the impact of timing on the overall sum of the financial costs. Annually, more than 2.3 trillion KRW are paid as progress payments for public construction work; yet, there is no research data showing the scale of financial costs thus incurred. The purpose of this research is to illustrate the scale of financial costs incurred due to progress payments for public construction works, and to suggest alternatives that would improve relevant regulations.

도심지 지가가 높아짐에 따라 건축물의 공간 활용도에 대한 기대치가 높아지게 되었고, 건축물은 더 크고, 더 깊고, 더 높게 지어지는 방향으로 나아가고 있다. 이에 따라, 공사의 첫 단계이자 전체 건물의 기초가 되는 지하 공사는 그 중요성이 날로 더해가고 있다. 최소한의 비용으로 최단기간에 터파기 공사를 완료해야 하는 도심지 공사의 특성상 공사 관계자들은 지하 공사를 계획, 설계, 시공, 설계하는 과정에서 심혈을 기울이고 있다. 그럼에도 불구하고 지하 공사 전반에 걸쳐 있는 불확실성과 위험 요소 때문에 공사 실패 사례가 발생하고 있다. 더욱이 이런 사고가 어느 정도의 경제적 피해를 끼쳤는지에 대한 보고나 연구 없이 사고 사례만 알려지기 때문에 지하 공사의 위험성에 대한 경각심이 부족한 것이 우리나라 건축의 현실이다. 이런 사고를 타산지석으로 삼아 터파기 공사 공법을 선정하고 지하 공사를 이행하는데 있어서 하나의 지침이 되기를 바라면서 지하 공사 실패 사례가 과연 어느 정도의 경제적 피해를 발생시키는지를 개산견적 기법을 도입하여 추정해 보았다.

In many studies, the labor productivity of the construction industry was measured without distinguishing general contractors from specialty contractors. While the productivity of general contractors reflects the ability to build a building. This study evaluates the ability of the Korean construction industry in comparison to the productivity of the US construction industry after the dividing the construction industry into general contractors and specialty contractors. The results indicate that the labor productivity of the Korean construction industry is lower than that of the US for both general contractors and specialty contractors. The difference of labor productivity between the Korean general contractors and the US general contractors highly affected the result. This paper discusses the possible reasons for the results.
As buildings become higher, larger, and more complex, safety issues for construction workers working at such environments become more important. We analyzed 83 critical accident cases reported to the KOSHA(Korea Occupational Safety & Health Agency) for construction cranes by types of cranes and by patterns of accidents and causes. There are more number of accidents related to mobile cranes than that related to tower cranes, but the numbers of dead were similar in both cases. The most dominant cause of crane accidents was “fall of materials”. We also analyzed the cases of crane accidents using the FMEA(Failure Mode and Effect Analysis) in order to set up a priority for safety management and also to prioritize research and development items relating tower cranes. In the process, we tried to eliminate subjective indexes such as an expert group survey and use objective and quantitative indexes. As a result, it was found that critical crane accidents occurs most during the “lifting and translating” activity.

As the proportion of underground construction increases, the impact of inappropriate selection of a underground construction method for a construction size increases. The purpose of this study is to develop an objective way of selecting an excavation method. There have been several attempts to achieve the same goal using various data mining methods such as the artificial neural network, the support vector machine, and the case-based reasoning. However, they focused only on the selection of a retaining wall construction method out of six types of retaining walls. When we categorized an underground construction work into four groups and added more number of independent variables (i.e., more number of construction methods), the predictability decreased. As an alternative, we developed a decision tree by analyzing 25 earthwork cases with detailed information. We implemented the developed decision tree as a computer-supported program called Dr. underground and are still in the process of validating and revising the decision tree. This study is still in a preliminary stage and will be improved by collecting and analyzing more cases.

As buildings become higher, larger, and more complex, safety issues for construction workers working at such environments become more important. We analyzed 140 critical accident cases reported to the KOSHA(Korea Occupational Safety & Health Agency) for construction cranes and lifts by types of cranes and by patterns of accidents and causes. By finding out the accident`s types and causes, we expect to develop an efficient measure for preventing similar accidents in the near future. The cases will be studied further and reexamined using the FMEA(Failure Mode and Effect Analysis) as a quantitative analysis method.

As a demand for underground structure is increasing with more parking and retail spaces required. Various construction methods are reviewed and selected for each specific site for economical and fast construction. In this study, factors for selecting construction methods were categorized for substructure construction. Construction processes of substructure are consisted of methods for excavation, earth retaining systems, and placement of slabs. Factors for the selection of substructure construction method are the condition of surrounding, geotechnical, information and constraint by comfortness for others nearby. After survey for the construction data of 5 different sites, analysis about reliable substructure construction selection method was suggested.
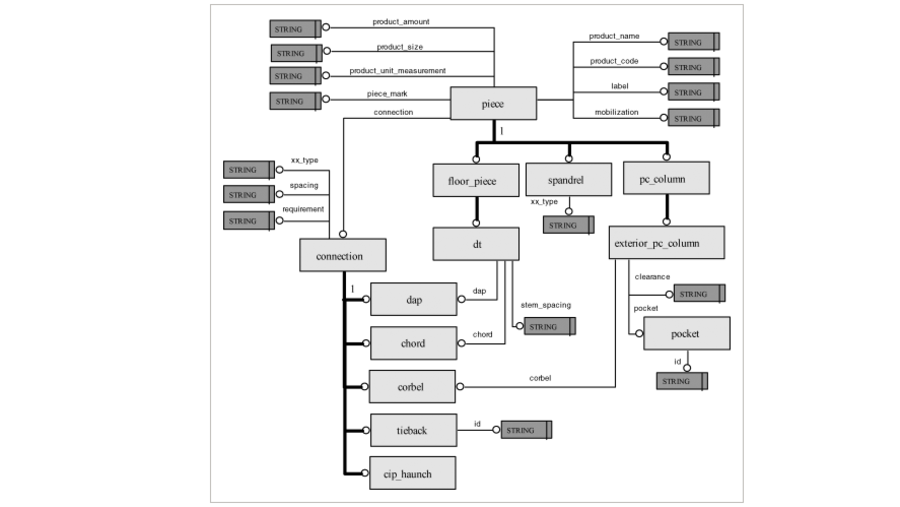
This article reviews a method for generating a product model from user data and introduces 12 design patterns for resolving conflicts that may occur in the integration and normalization process. The generating method and design patterns were evaluated during a project to integrate the product models collected from three different precast concrete companies in the United States, testing the new method of product model generation. The application results indicate that the 12 design patterns are effective and sufficient for resolving most known schema conflicts and for integrating and normalizing multiple product models into a single well‐formed product model.
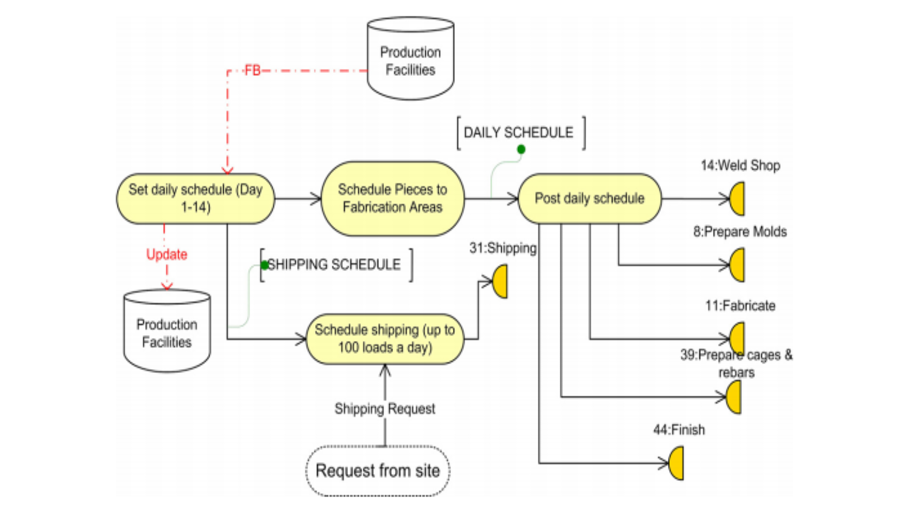
A product model is a formal and structured definition of product information. The most common procedure for defining a product data model is to first describe the business and/or engineering process in a formal process model, then to create a product data model based on the process model. However, there is a logical gap between process modeling and product modeling methods in the current ISO 10303 standard product modeling process. We propose a new formal approach, called Process to Product Modeling (PPM) in which process and product modeling can be logically linked. This paper focuses on the semantics and syntax for the Requirements Collection and Modeling (RCM) of PPM. The new RCM method aims to model heterogeneous business processes and their information flows. The major difference between the proposed method and traditional requirements collection methods is that it provides a theoretical linkage to integrate process models and a set of specific information items used in them. This theoretical linkage enables modelers to capture the contents, scope, granularity, and semantics of information used in activities, which are depicted in process models. A PPM method, called Georgia Tech Process to Product Modeling (GTPPM), has been developed and was deployed for the North American Precast Concrete Software Consortium; examples from this effort are presented. Experience to date indicates that the new RCM method and the GTPPM tool hold the potential to improve and expedite elicitation of information for product model development.

The top-down construction method is an excavation and substructure construction method by excavating earth and building slabs from the ground level to the bottom of a building. The top-down method can be categorized into several types by its process and other technical details. Some of commonly used top-down methods in Korea today are S.O.G., N.S.T.D., and S.P.S. Among these, one method is chosen depending on construction field conditions, cost, construction time and so on. This study explores several factors that may affect the selection of a top-down method. This paper reports preliminary survey results with 54 top-down construction experts and comparison results of 5 top-down construction sites.
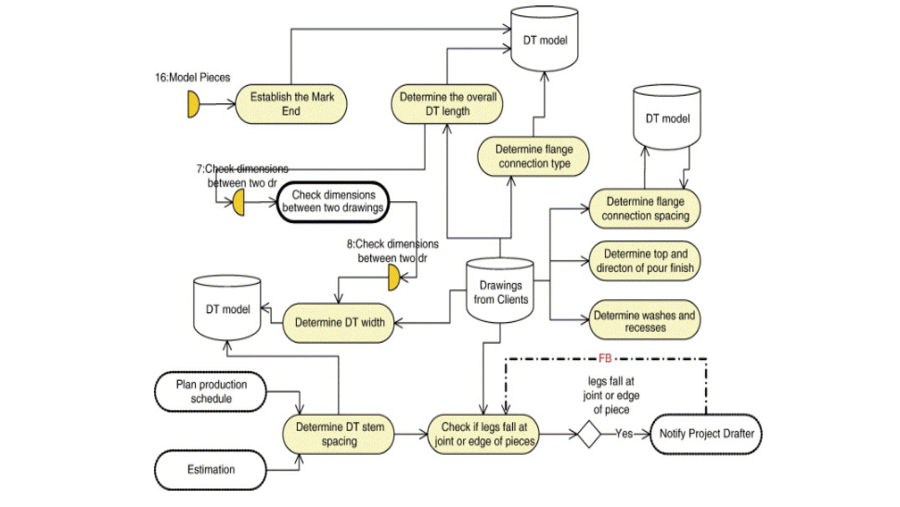
The Georgia Tech Process to Product Modeling (GTPPM) is a formal process-centric product modeling method. It enables capture of domain-specific information and work processes through process modeling. The method was initially developed in response to the need to integrate multiple use-cases with differing data definitions from different companies. It automates and applies formal methods to aspects of process and product modeling that have traditionally been negotiated by committees. It has been deployed in several research projects, in addition, as an information flow analysis method rather than as a product modeling method. This paper reports a case of deploying GTPPM as a product modeling method, using a purpose-built software tool for its implementation. The case study in the domain of precast concrete construction demonstrates that it is possible to semi-automatically derive a product data model from the collected information through normalization, information integration, and conflict resolution processes.
Parametric modeling has been proposed as an effective means to embed domain expertise in models of buildings. As information technology becomes more powerful in terms of the ability to manipulate large parametric models, the potential grows to build increasingly sophisticated functional systems for designing, modeling and fabricating buildings. Implementing more powerful systems implies greater functional specificity, which requires elicitation and capture of increasingly detailed and complex domain-specific semantics and knowledge. This paper explores the extent to which design and engineering knowledge can be practically embedded in production software for building information modeling (BIM). It focuses on a building object behavior (BOB) description notation and method, developed as a shorthand protocol for designing, validating and sharing the design intent of parametric objects. Examples are drawn from an advanced BIM system development project for precast concrete.
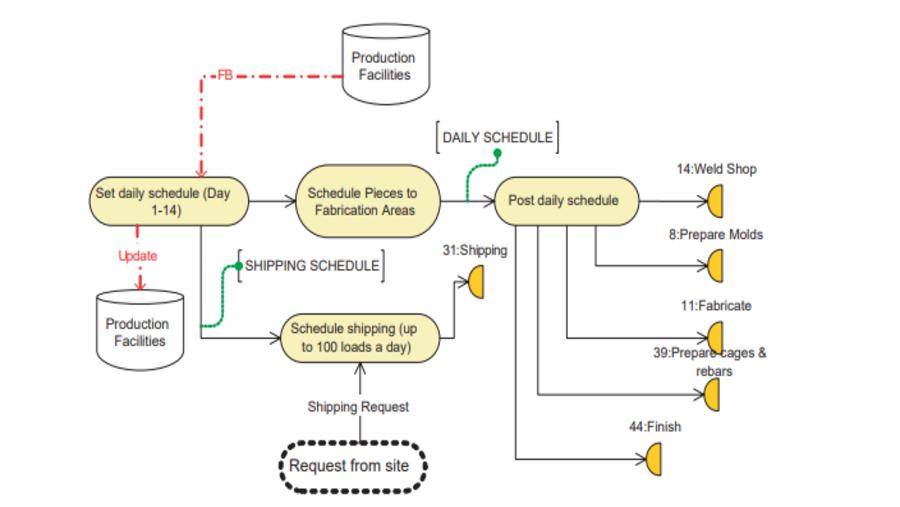
This paper presents a linguistic framework for developing a formal knowledge acquisition method. The framework is intended to empower domain experts to specify information required by activities in design, engineering, manufacturing, and maintenance processes. The longer-term goal of the framework is to (semi-)automatically derive a data model from product information specified by domain experts. The framework for information specification is named the Product Information Specification (PIS) framework. The linguistic framework categorizes terms (‘tokens’) required to define product information into six constituents, similar to the parts of speech in grammar, based on abstraction concepts of Knowledge Representation. Syntactic rules for combining these six constituents guarantee the consistency and the analyzability (computability) of the specified product information. A Context-Free Grammar (CFG) has been adopted for analyzing and defining the rules. The applicability and feasibility of the PIS framework has been demonstrated through a research project with the North American precast concrete industry. Examples in this paper are drawn from this project. The major contribution of the PIS framework is that it provides a basis for a knowledge acquisition method that can facilitate domain experts' direct participation in product modeling, can potentially increase the quality of the resultant model and decrease the product modeling time.
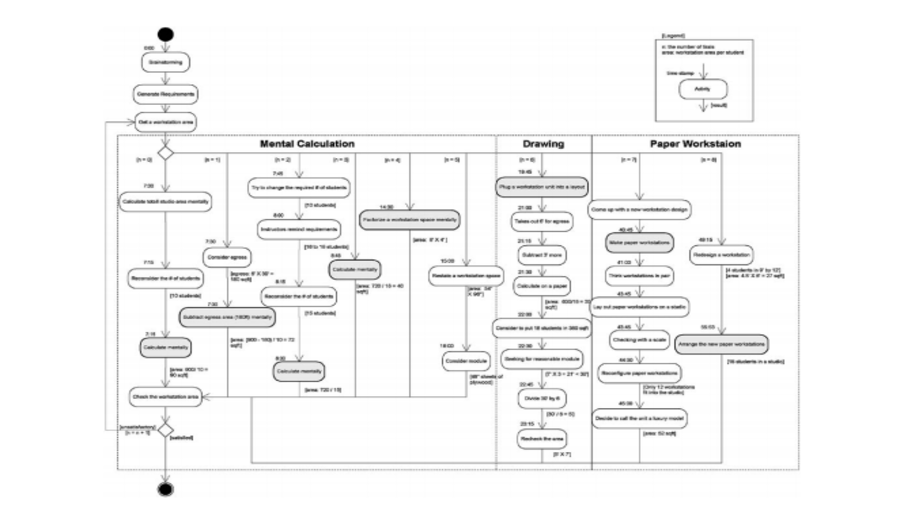
Most design problems have multiple interacting constraints and levels of analysis. Some designers are able to reduce errors by developing heuristics and rules of thumb that lighten the cognitive load that such design problems impose. In this study we explore these heuristics by studying three groups of experienced architects solving a one-hour design problem that involves issues of multiple levels of spatial organization. Only one group was able to solve the problem. A special coding scheme was developed to explore the use of several kinds of heuristics such as problem decomposition into design units, rules of thumb from domain knowledge and strategic design moves. The differences in heuristics were examined to identify possible causes for these errors.
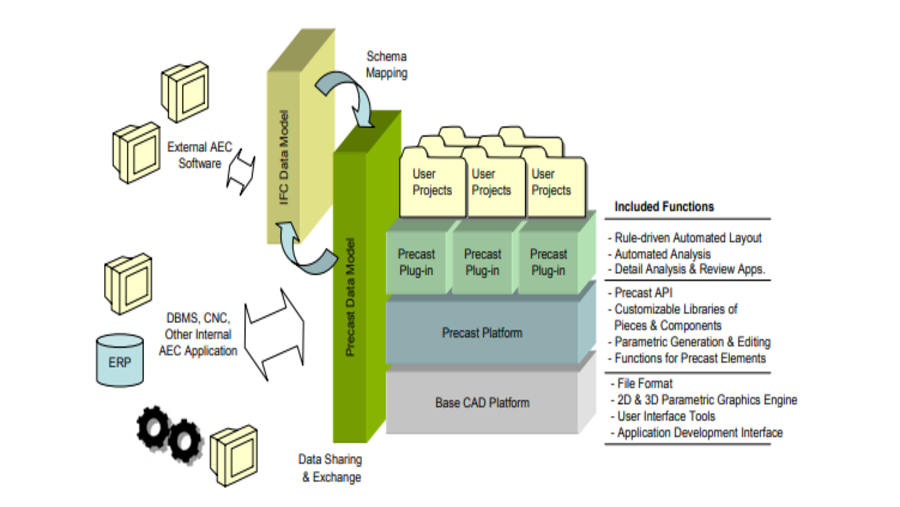
We report on a large-scale effort to integrate advanced design and engineering information technologies (IT) in the North American precast/prestressed concrete industry. The effort has been undertaken by a consortium of precast producer companies formed specifically for the task The effort involved significant process modeling work, using a unique method and set of tools. It led to the development of a specification for an advanced precast concrete design and engineering parametric application platform, which is currently being implemented by a major building modeling software company. The problems and lessons learned are reported. The project reported is on-going. With the first phase now well established and underway, the groundwork for the second phase - development of a Precast Building Product Data Model - will soon begin.
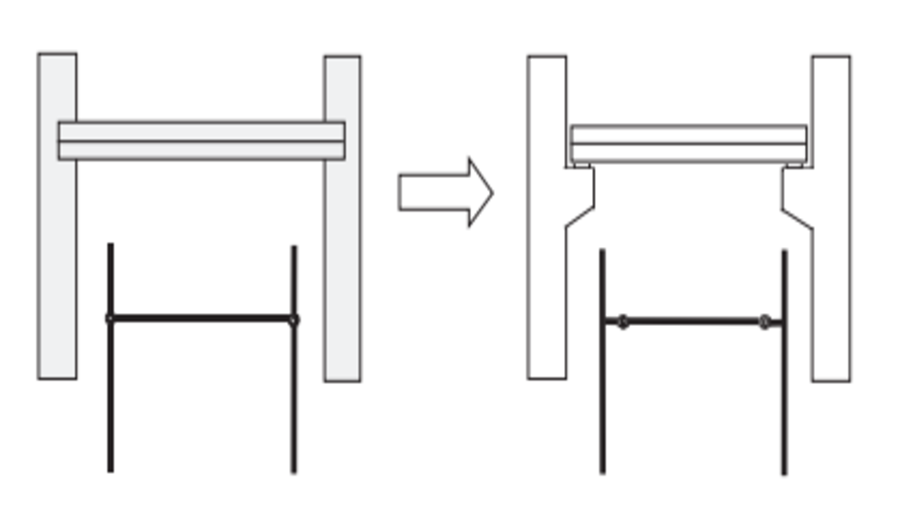
Buildings are complex products containing relatively large numbers of distinct parts that are collected in multiple assemblies for different design, analysis and production purposes. Modeling buildings in fully parametric 3D computer-aided design (CAD) systems offers numerous benefits in terms of productivity, the ability to rapidly generate design alternatives at different levels and elimination of errors that result from the disparity between different drawings in current practice. However, full realization of these benefits requires specialized functionality, including top-down modeling, objects with functional behavior, the ability to embed contextual design intent, automation of layout and detailing and appropriate management of similar objects. An effective system must provide such functionality while maintaining adequate response times. The requirements, features and performance have been examined as part of specification of a new 3D parametric CAD platform for the North American Precast Concrete Software Consortium (PCSC). They are described and discussed after a review of solid and parametric modeling, with examples from the domain of precast concrete construction.
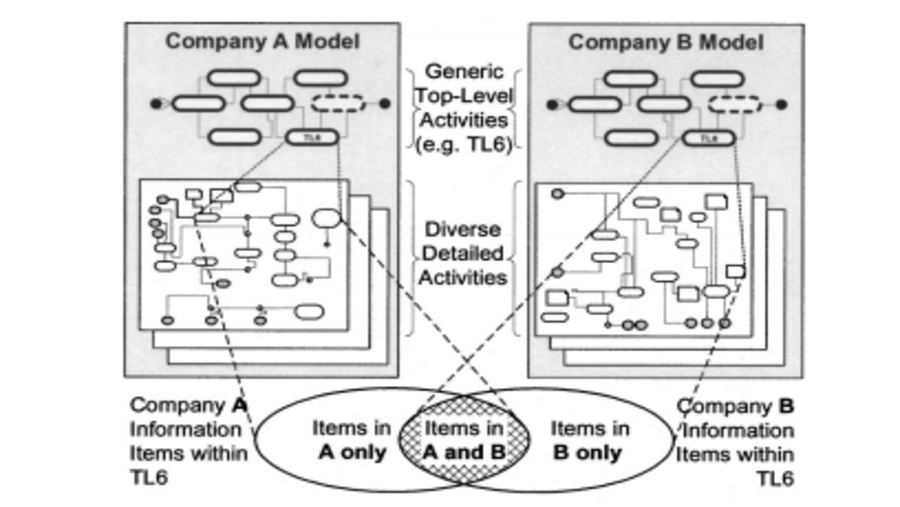
The preparation of detailed models of information and process flow by 14 member companies of the North American Precast Concrete Software Consortium has provided a unique window into the current management, engineering design, and production operations in this industry. The modeling was performed using the authors’ Georgia Tech Process for Product Modeling tool, within the framework of the consortium’s effort to develop a precast concrete product model and to specify new integrated three dimensional modeling software. The paper opens with a comparative economic review of precast construction internationally and in North America, which reveals that the market share of precast construction in North American is relatively low. The models are analyzed and aspects of the underlying management procedures that they reveal are discussed, such as types of contracting arrangements, cost estimating, design outsourcing, engineering design communication, mold design, product diversity, and quality control. The results highlight aspects of precast management processes that may be re-engineered through appropriate application of information technology.
Design professionals worldwide have applied the technology of computer-aided design and drafting (CAD) on a broad scale, primarily to increase the efficiency of manual design and drafting methods and to promote standards, rather than to improve the process itself. Even with improvements in the technology, however, errors in design and drafting remain common. Taking the 2-D CAD technology further, the application of three-dimensional integrated parametric modeling of precast buildings at the assembly and piece levels may enable producers to greatly reduce design errors, resulting in significant improvements in project quality, cost, and schedule. An examination of a number of case studies of precast/prestressed concrete projects has revealed that the common causes of construction problems are design, detailing, and drafting errors, a lack of coordination between different disciplines, and inadequate management of changes. An analysis of the cases presented in this paper indicates that the application of 3-D top-down modeling and automated production of shop drawings holds the potential to eliminate most of the sources of error.

Because of the depression of construction market, the competition in domestic construction market has become higher recently Therefore, m order to take a leading edge m construction market, the scientific marketing based on reliable data is required. Among those, the construction site and its surroundings are the most important data to the construction companies To satisfy these needs, the construction Achievement Management System was developed The objective of this system is to provide rapid and exact construction site information to the marketers This system uses GIS(Geographic Information System) concept to provide the GUI(Geographic User Interface) for the users who are not accustomed to the computer In spite of its huge size, the raster type graphic data was used to support a good print quality and easy data-up-date in this system.
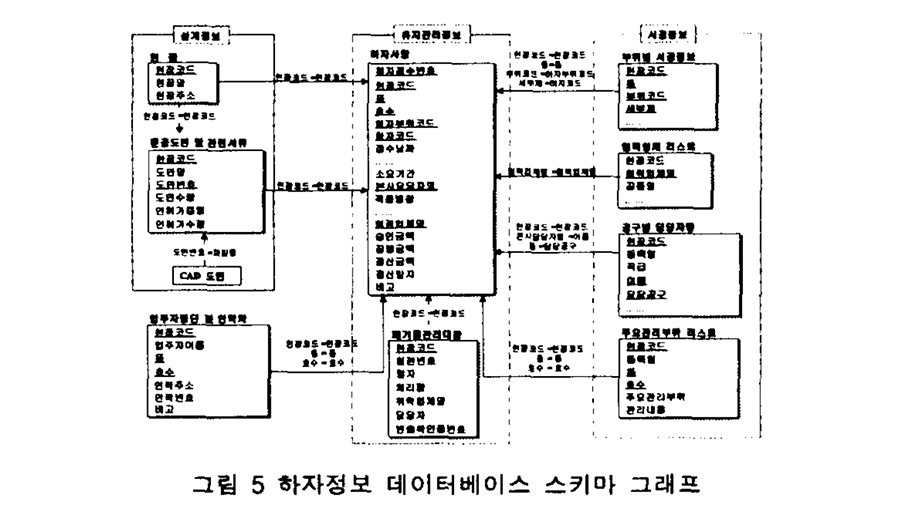
건축물의 하자보수에 있어서 신속하고 정확한 대응은 매우 중요한 일이다. 그러나, 지금까지의 하자정보가 서류상으로 관리되고, 다른 건설단계와 연 결이 유연하지 않아 그 관리의 효율성이 떨어졌던 것이 사실이다. 이를 개선하기 위하여 국내 건설업체 중 선두주자인 4개업체의 하자정보 내용과 업무흐름을 분석하여 파일설계도를 작성하였다. 또한, 데이터베이스 의 작성시 각 건설단계와의 연계가 원활할 수 있도록 최대한 고려하여 스 키마그래프를 작성하였다. 끝으로 이렇게 작성된 파일설계도와 스키마그래 프를 토대로 컴퓨터와 전산망을 이용한 하자정보관리시스템의 샘플을 개발 하였다.
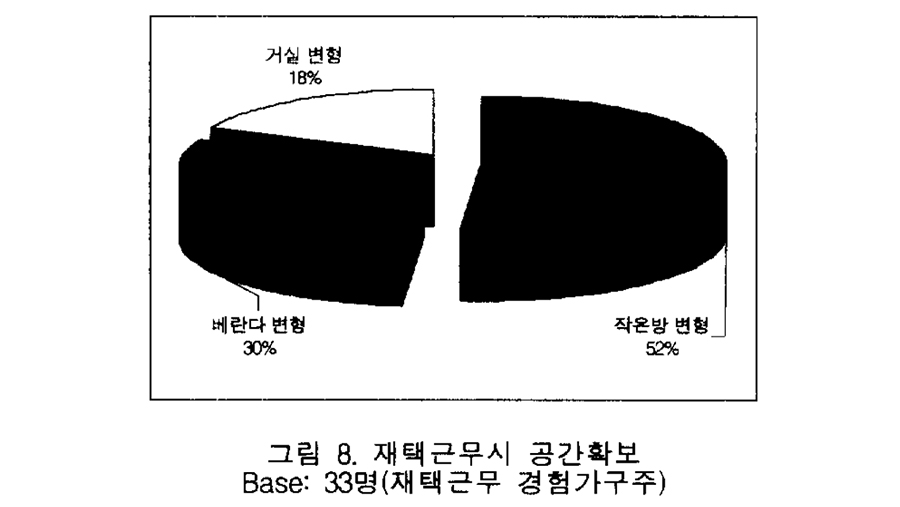
The modern marketing strategy is changing its way from the producer to the consumer. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a new apartment design that meets the needs of both the residents and the construction companies. The major target of this study is to find out needs of apartment residents by analyzing the residential behavior of the residents who live in apartment complex located in Incheon. Though this study we could find out; how much are the residents satisfied with the apartments where they live in; the relationship between rooms by analyzing residential behavior of each room; the types of the apartment which they prefer to move in; and kinds of space and facilities needed for the telecommutor.

We developed an AHSIS(Apartment Housing Sales Information System) which can help managers and apartment-housing-sales-related departments to make an appropriate decision efficiently in a diverse and fast-changing housing-sales environment. 1) This system enhances the visual effects of text data and also supports decision-making database system. 2) AHSIS helps the decision-makers with quick information gathering and immediate problem extraction. This system will be extended to support the management of apartment housing sales by a higher quality information, and tele-conference system using internet.
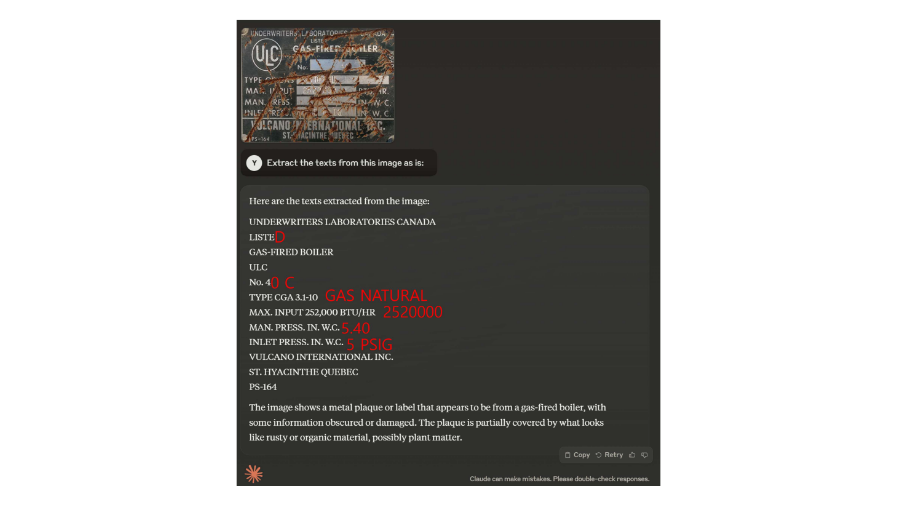
플랜트 장비 명판(Plant Equipment Nameplate)은 장비의 주요 사양, 제조 정보, 운영 조건 등과 같은 정보를 포함한 플랜트 자산 관리의 핵심 요소이다. 그러나 시간이 지남에 따라 부식, 긁힘, 오염 또는 기타 물리적 손상으로 인해 정보가 손실될 수 있으며, 이로 인해 장비의 식별과 유지보수를 위해 필요한 데이터를 확인하는데 어려움이 발생한다. 이러한 정보 손실은 자산 관리, 장비 교체, 그리고 플랜트 안전 관리 측면에서 심각한 문제를 초래할 수 있다. 광학 문자 인식(Optical Character Recognition, OCR) 기술은 명판의 텍스트를 인식하는데 탁월한 성능을 보이지만, 명판이 손상된 경우 성능이 급격히 저하되어 정확한 텍스트를 인식하는데 한계가 있다. 반면, 최근 멀티모달 언어 모델(Multimodal Large Language Model, MLM) 기술의 발전으로 텍스트뿐만 아니라 이미지와 같은 다양한 유형의 데이터를 종합적으로 이해하고, 예측할 수 있는 능력으로 인해 손상된 명판 정보를 보다 효과적으로 복구할 수 있는 가능성이 제시되었다. 그러나 여전히 플랜트 장비 명판에서의 손상된 정보 인식 및 추론 능력은 충분히 탐구되지 못하고 있다. 이에 본 연구는 OCR 알고리즘과 MLLM의 성능이 손상된 플랜트 장비 명판에서의 정보 인식 및 복구 성능 관점에서 어떤 차이가 있는지를 평가함으로 기술의 활용 가능성을 탐구하고자 하였다. 이를 통해 플랜트 자산 관리에서 발생할 수 있는 정보 손실 문제를 완화하고, 효과적인 복구 방법론을 제시하는데 기여하고자 한다.
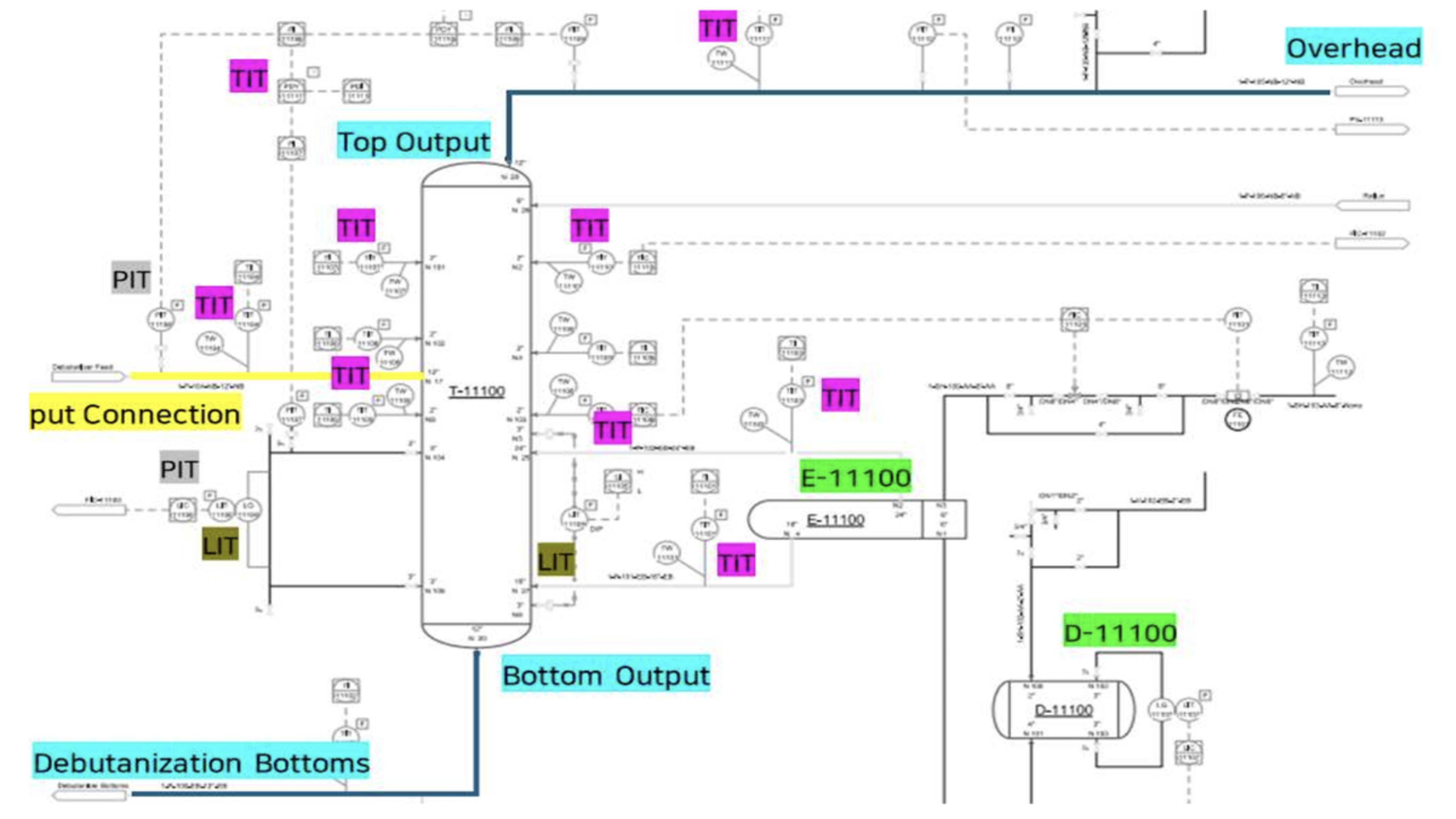
공정 배관 계장도 (Pipe and Instrumentation Diagram, P&ID)는 프로세스 흐름도(Process Flow Diagram, PFD)를 기반으로, 장비 간 연결 상태와 배관, 계측기의 배치를 시각적으로 표현한 공정 설계의 핵심 문서이다. P&ID에 표현된 장비들의 논리적 연결성을 검토하는 것은 단순히 기계적 결함을 넘어서, 공정 설계의 타당성과 안전성을 평가하는 중요한 과정이다. 기존의 P&ID 설계와 검토는 주로 숙련된 엔지니어에 의해 수행되어 왔다. 그러나, 이러한 P&ID 논리 검토 방식은 세 가지 주요 한계가 있다. 첫째, 오류를 검토하고 수정하는 과정에서 많은 시간과 비용이 소요되며, 설계 오류를 완벽히 탐지하지 못한다. 둘째, P&ID 도면은 주로 심볼과 기호로 구성되어 있어, 발주처와 다른 프로젝트 참여자들과의 도면 검토 과정에서 소통의 어려움이 발생할 수 있다. 셋째, 플랜트 산업의 보안 요구로 인해 P&ID 도면은 PDF 공유되는 경우가 많다. 이는 정보의 충분한 제공과 해석에 있어 한계를 초래해, 도면 검토의 효율성을 저해할 수 있다. 이러한 한계를 극복할 수 있는 기술로 거대 멀티모달 모델(Large Multimodal Models, LMMs)이 주목받고 있다. 그러나, 일반적인 지식에 강점을 가진 LMMS을 특정 산업에 적용하기 위해서는 해당 산업에 특화된 도메인 지식을 추가하는 작업이 필요하다. 이러한 한계는 외부 데이터베이스로부터 추가 정보를 검색하여 분석의 정확성과 신뢰성을 높이는 검색 기반 증강 생성(Retrieval-Augnented Generation, RAG)기법을 통해 해결할 수 있다. 이와 같은 기술적 잠재력에도 불구하고 P&ID에서 LMM-RAG의 적용 가능성에 대한 연구는 아직 부족한 상황이다. 이에 본 연구는 LMM-RAG을 활용하여 P&D 도면의 장비, 배관, 계측기 간의 논리적 연결성을 자동으로 검토할 수 있는 방법을 제안하고자 한다. 이를 통해 기존 수동 검토 방식의 한계를 극복하고 공정 설계의 신뢰성과 효율성을 향상시키는데 기여하고자 한다.
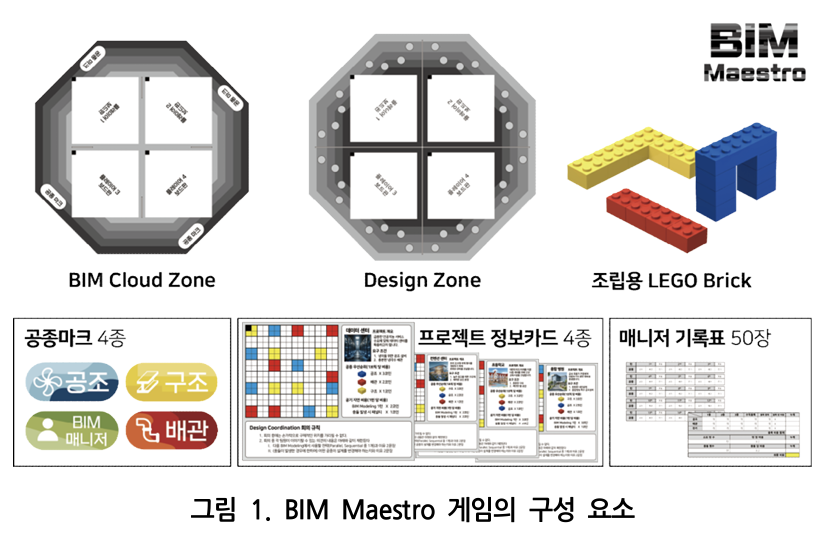
Building Information Modeling(BIM)의 이해관계자 간 의사소통 증진 및 통합적 정보 관리 등의 장점에도 불구하고, 국내외 건설 산업에서의 BIM 기술 도입 수준은 상승하지 못하고 있다. 기존 연구에서는 훈련된 전문가의 부족을 BIM 도입의 장애물로 지적하고 있으며, 특히 고등교육기관에서 BIM 기반의 협업과 같은 개념적 차원의 교육 과정이 부족한 것으로 나타났다. 따라서 본 연구는 설계 단계에서 구조, 공조, 배관 등 다양한 공종 사이의 협업 프로세스인 BIM 기반 설계 조정(BIM-based design coordination) 과정을 학습할 수 있는 레고 시리어스 게임인 ‘BIM Maestro’를 개발 및 배포하였다. 게임의 학습 효과 검증을 위해 20명의 건축공학 및 건축학 전공 학부/대학원 과정 학생을 대상으로 사전 및 사후 BIM 지식 평가를 진행하였다. 평가 결과, 사전 평가에 비해 사후 평가에서 평균 25.6%의 성적 향상을 보였다. 또한, 사전 평가에 비해 사후 평가의 표준편차가 33.5% 감소하는 등 해당 게임이 학습자의 과거 학습 경험에 관계없이 교육에 효과적이었다. 본 연구를 통해 고등교육기관에서 BIM을 교육하는 데 있어 게임을 활용한 인터랙티브 학습 경험이 짧은 시간 안으로도 BIM의 실무적 활용 방법을 학습하는 데 효과적임을 확인하였다.
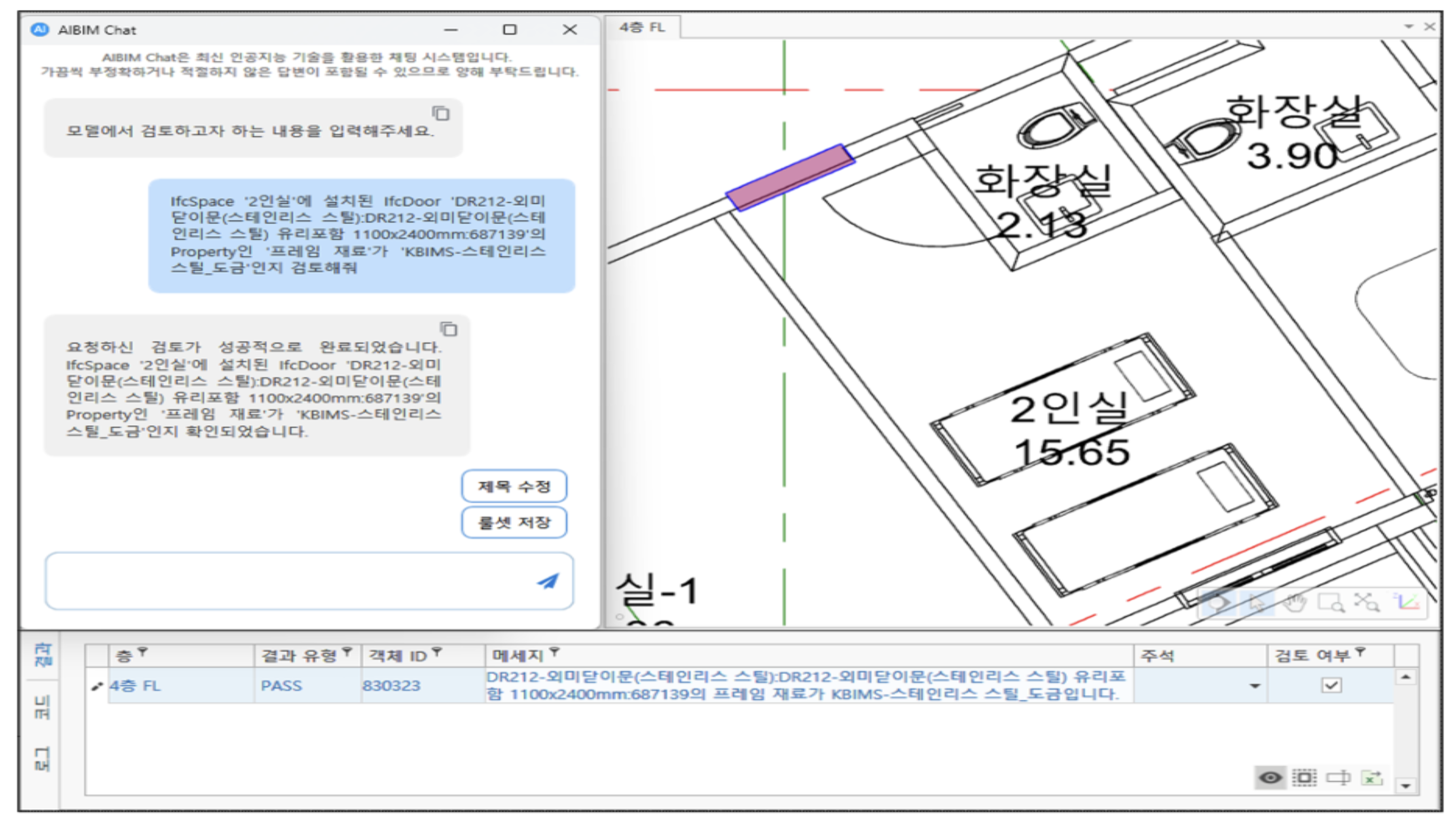
디자인 요구 사항 검토는 건축 설계 단계에서 발주자의 요구나 건축 법규 등의 반영 여부를 확인하는 중요한 과정이다. 그러나 건축 정보 모델링(building information modeling, BIM)의 등장으로 설계자가 직접 디자인 요구 사항을 분석하고 검토하던 기존 방식이 아닌, 컴퓨터 환경에서 디자인 요구 사항을 검토하는 환경적 변화를 경험하고 있다. 실제로 거대 언어 모델(large language models, LLMs)을 활용하여 자연어로 표현된 건축 법규 및 디자인 요구사항을 프로그램 언어로 자동 변환하는 것이 가능하게 되었다(Lee et al., 2023). 하지만 LLMs는 사용자가 제공하는 프롬프트에 따라 결과물이 달라진다는 한계가 있다. 이에 본 연구는 LLMs을 활용한 BIM 모델의 디자인 요구 사항 검토를 위한 컴퓨터 프로그램 언어 자동 변환에서의 효과적인 프롬프트 설계 방법을 제안하고자 한다.
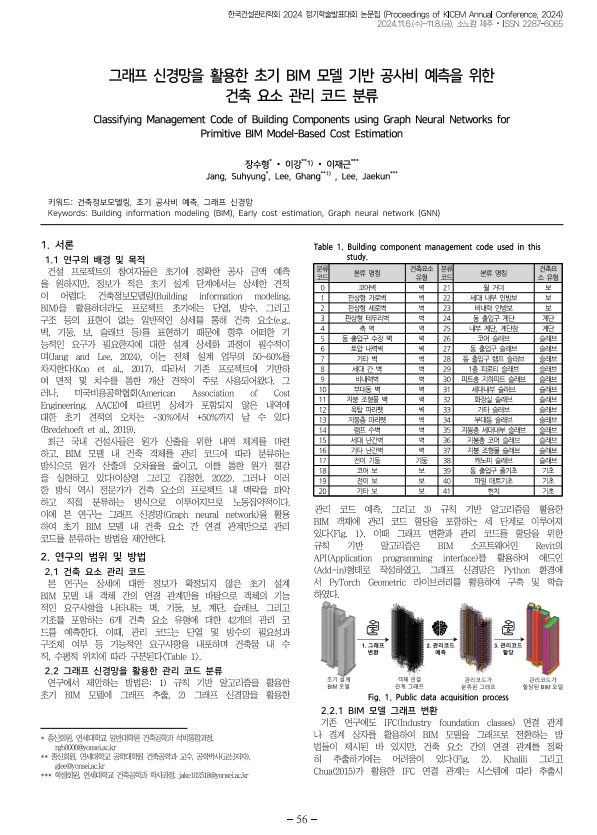
건설 프로젝트의 참여자들은 초기에 정확한 공사 금액 예측을 원하지만, 정보가 적은 초기 설계 단계에서는 상세한 견적이 어렵다. 건축정보모델링(Building information modeling, BIM)을 활용하더라도 프로젝트 초기에는 단열, 방수, 그리고 구조 등의 표현이 없는 일반적인 상세를 통해 건축 요소(e.g,, 벽, 기둥, 보, 슬래브 등)를 표현하기 때문에 향후 어떠한 기능적인 요구가 필요한 지에 대한 설계 상세화 과정이 필수적이며(ang and Lec, 2024), 이는 전체 설계 업무의 50~60%를 차지한다(Koo et al, 2017). 따라서 기존 프로젝트에 기반하여 면적 및 치수를 통한 개산 견적이 주로 사용되어왔다. 그러나, 미국비용공학협회(American Association of Cost Engineering, AACE)에 따르면 상세가 포함되지 않은 내역에 대한 초기 견적의 오차는 30%에서 +50%까지 날 수 있다 (Bredehoeit et a., 2019). 최근 국내 건설사들은 원가 산출을 위한 내역 체계를 마련 하고, BIM 모델 내 건축 객체를 관리 코드에 따라 분류하는 방식으로 원가 산출의 오차율을 줄이고, 이를 통한 원가 절감 을 실현하고 있다(이상영 그리고 김정헌, 2022). 그러나 이러한 방식 역시 전문가가 건축 요소의 프로젝트 내 맥락을 파악하고 직접 분류하는 방식으로 이루어지므로 노동집약적이다. 이에 본 연구는 그래프 신경망(Graph neural network)을 활용하여 초기 BIM 모델 내 건축 요소 간 연결 관계만으로 관리 코드를 분류하는 방법을 제안한다.
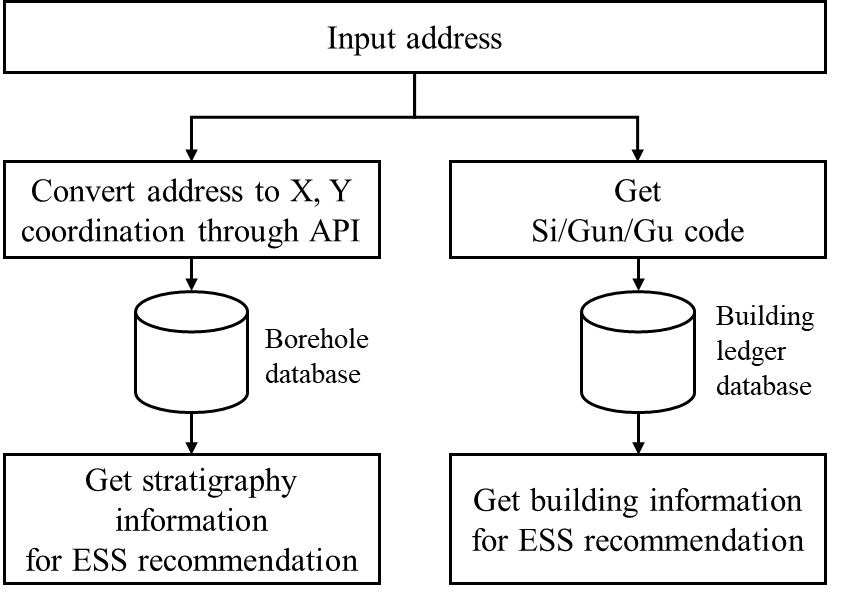
본 연구는 흙막이 공법 및 설계 상세를 추천하는 과정에서 공공데이터를 활용하여 데이터 수집의 효율성을 높이는 것을 목표로 한다. 기존에는 흙막이 시스템 추천을 위해 시추 검사 및 현장조사를 통해 흙막이 추천을 위한 정보를 획득해야 하는 한계가 있다. 또한, 설계 초기 단계에서 다양한 출처의 정보를 모두 수집하고 검토하는 데 어려움이 있다. 이를 해결하기 위해 본 연구는 주소지 입력만으로 건물정보와 지반정보를 자동으로 수집하고, 최소한의 사용자 입력 정보를 통해 흙막이 공법과 설계 상세를 추천하는 알고리즘을 제안한다. 이를 위해 공공데이터 내의 건축물대장, 시추공, 지층정보 등을 전처리하고, 데이터베이스를 활용하여 해당 주소지의 정보들을 통합적으로 수집하였다. 수집된 정보 항목들을 통해 흙막이 시스템을 추천하고, 설계 저작도구에서 시각화 및 모델링을 할 수 있게 하였다. 이를 통해 설계 초기 단계에서 복잡한 정보 수집 과정을 간소화하고, 신속하게 흙막이 설계 초안을 작성할 수 있게 하였으며, 설계의 품질과 효율성을 향상시키는 데 기여할 것으로 기대된다.본 연구는 공공데이터와 자동 추천 알고리즘을 결합하여 흙막이 설계에서 발생하는 시간적·경제적 비용을 줄일 수 있는 새로운 접근법을 제시하고, 공공데이터 활용의 가능성을 확장할 것으로 기대된다.

This study aims to identify potential root causes of defects using retrieval augmented generation (RAG) by chaining knowledge graphs (KGs) with a large language model (LLM). Complex defects refer to defects caused by multiple influencing factors or other defects, which tend to recur if the root causes, such as mold or leakage, are unresolved. In the defect management process, unveiling the root causes significantly prevents recurring defects and can reduce the time and effort required for defect repair. However, identifying the root cause from past complaint data is challenging because most complaints only describe superficial defect phenomena without causal relationship information. Although recent LLMs can provide plausible causes of defects using their extensive knowledge, LLMs can provide neither context-specific nor fact-based causes considering similar historical cases. To fill these gaps, this study incorporates LLMs with KGs that represent causal relationships derived from past defect cases and defect management documents by using RAG. In a graph database, the most relevant information was retrieved using a vector index and then transferred to enable LLM to respond to the initial question of a user through the chaining process. The proposed method has been validated by inferring water-related defects and achieved 73.47% answer accuracy based on cosine similarity between the generated answer by the LLM and the ground truth. This study highlights the importance of domain-knowledge structuring and demonstrates the potential use of RAG and generative AI applications in construction.
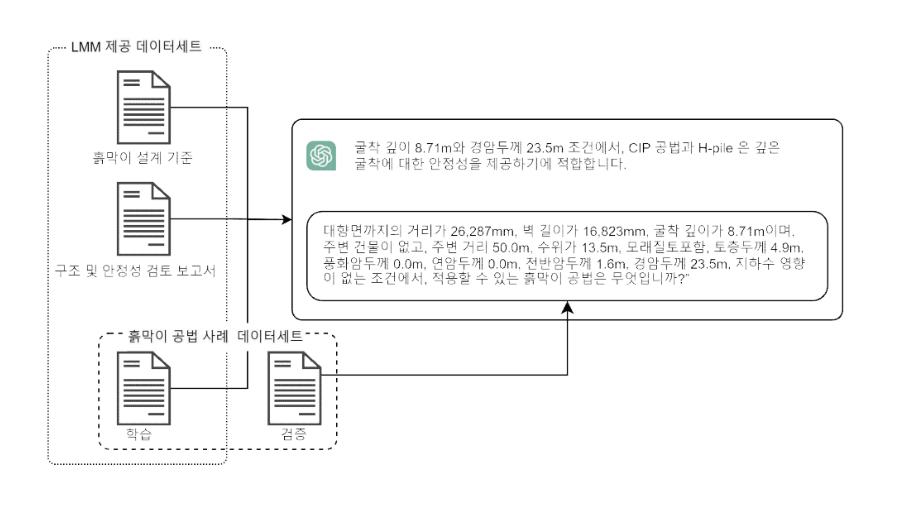
The purpose of this study is to develop an explainable dataset for the validation of an Al-enhanced Excavation Support System (ESS). To achieve this, data required for ESS design were collected from the Korean Design Standards (KDS), excavation projects, and four sets of ESS calculation reports. These data were then processed using Large Multimodal Models (LMM) to create 2,874 data sets. Each dataset consists of a triple of a response (a selected ESS component), a reason for selection (drawn from design standards, design calculation processes, and real design cases), and a reference list (the source of the reason). The study emphasizes the feasibility of the proposed explainable dataset structure, which can lead to explainable Al (XAI) for an intelligent ESS recommendation system
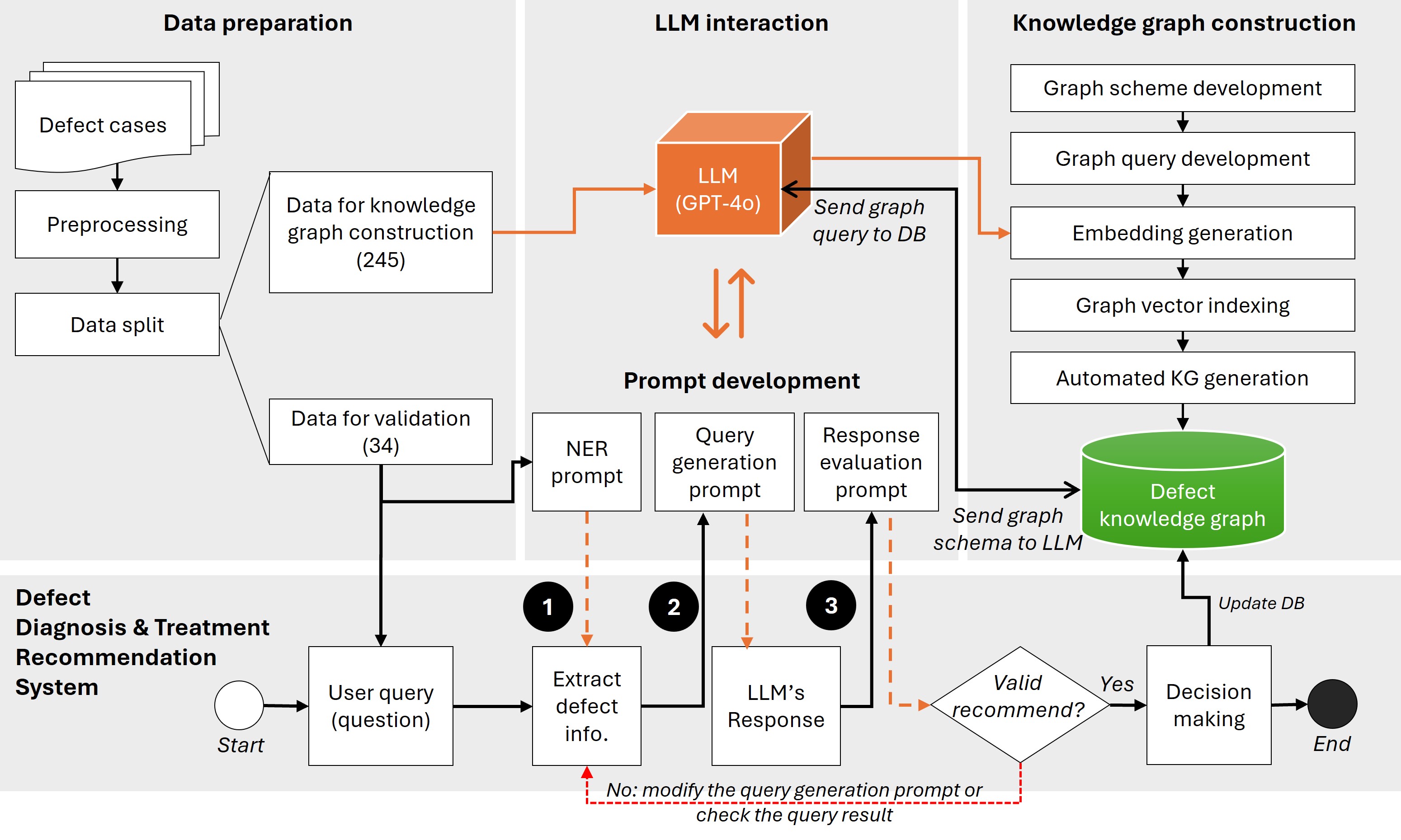
Defect complaint texts from residents typically contain partial information on the defect location, affected parts, and observed phenomena (Jeon et al., 2022). Due to a lack of context information, repair works have traditionally relied on the implicit knowledge and experiences of a few skilled workers. However, unstructured information makes it difficult to accumulate, explore, and share historical data on defect causes, repair methods, and preventive measures (Liu et al., 2020), Shooshtarian et al., 2023). To infer the causes of defects from historical data, this study deploys a knowledge graph that can represent relationships among defect data and relevant properties, and causal mechanisms. Integrating this knowledge into a graph database allows for queries and inferences, enabling the identification of root causes and appropriate countermeasures. With advances in large language models (LLMs) and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) technology, external domain knowledge can be seamlessly incorporated into LLMs (Lewis et al., 2021). Graph-RAG (G-RAG) combines graph databases with LLMs (Jin et al., 2024), retrieving relevant data from the knowledge graph to generate contextually accurate responses. To establish effective defect prevention measures, it is essential to consider the complex relationships between various factors contributing to defects in historical cases. This study proposes a G-RAG-based defect diagnosis and treatment recommendation system using LLMs, transforming unstructured defect-related text data into a structured knowledge graph for accurate diagnosis and treatment recommendations.
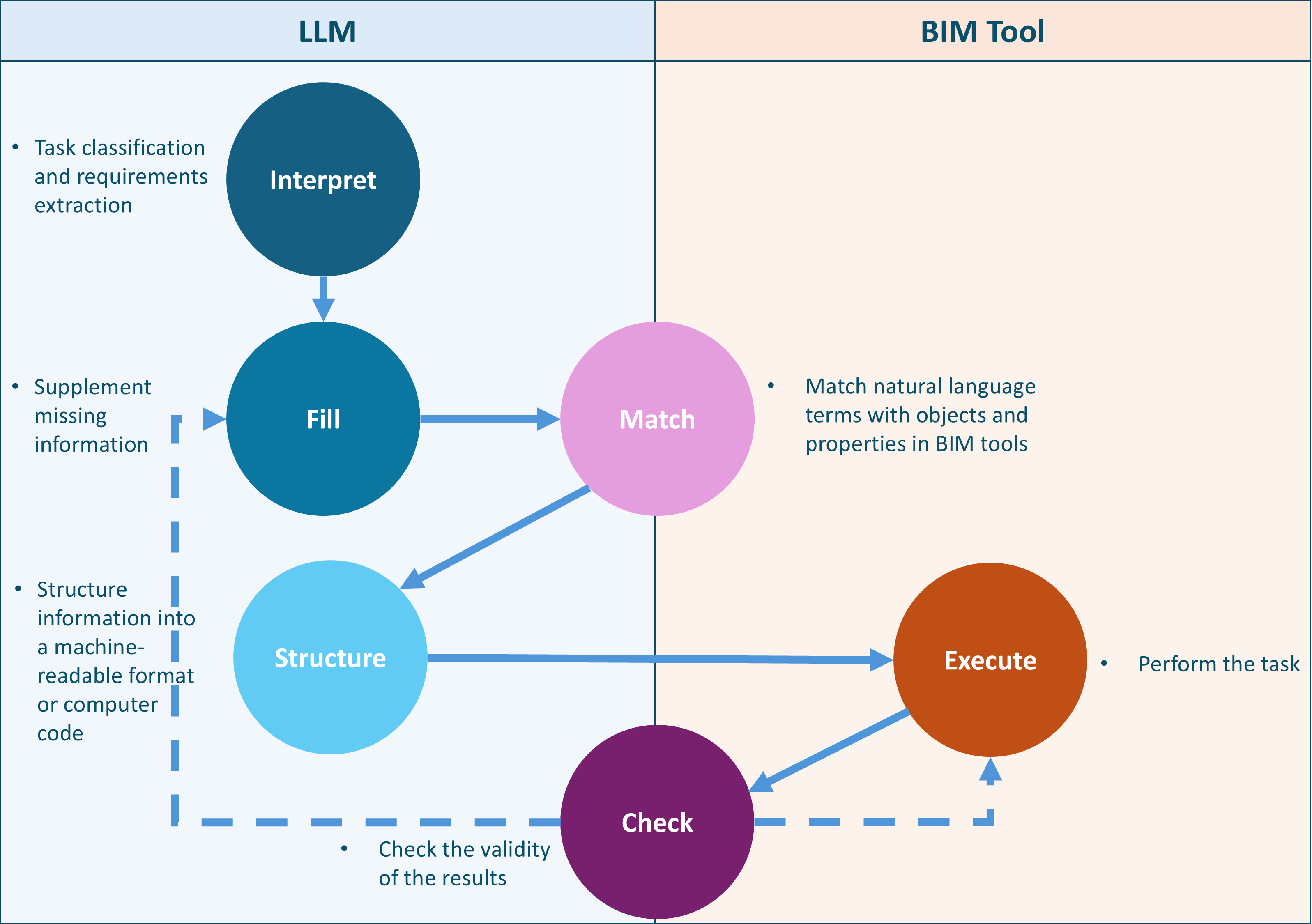
Performing building information modeling (BIM) tasks is a complex process that imposes a steep learning curve and a heavy cognitive load due to the necessity of remembering sequences of numerous commands. With the rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs), it is foreseeable that BIM tasks—including querying and managing BIM data, 4D and 5D BIM, design compliance checking, or authoring a design, using written or spoken natural language (i.e., text-to-BIM or speech-to-BIM)—will soon supplant traditional graphical user interfaces. This paper proposes a generalized LLM-augmented BIM framework to expedite the development of LLM-enhanced BIM applications by providing a step-by-step development process. The proposed framework consists of six steps: interpret-Lill-match-structure-execute-check. The paper demonstrates the applicability of the proposed framework through implementing a speech-to-BIM application—NADIA-S (Natural-language-based Architectural Detailing through Interaction with Artificial Intelligence via Speech)—using exterior wall detailing as an example.
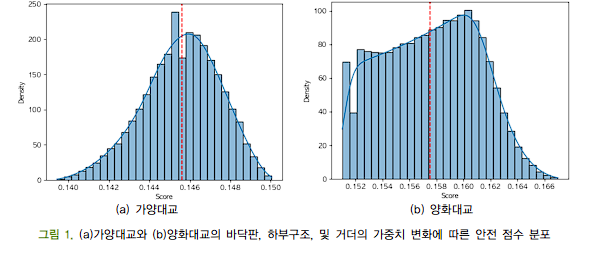
Currently, the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport in South Korea calculates the overall safety of bridges by applying weights, which reflect the impact on safety, to the safety inspection scores of individual components. Notably, the highest weights are assigned to the bridge's key elements: the deck (20%) and girder (19%) of the superstructure, and the substructure (20%). This study analyzed the bridge safety inspection reports from Seoul to understand how changes in the weights of these three components affect the inspection results. The analysis found that statistically significant changes in the inspection outcomes occurred when the weights of these components were altered by more than 20% from the current standards. Specifically, a decrease in the weights of these components by 20%, an increase in the deck's weight to 120%, and the substructure's weight to over 140%, showed noticeable differences in the inspection outcomes. However, increasing the girder's weight by up to 150% did not result in significant changes in the inspection outcomes. The findings of this research are expected to contribute important evidence for improving bridge safety inspection and management methods.
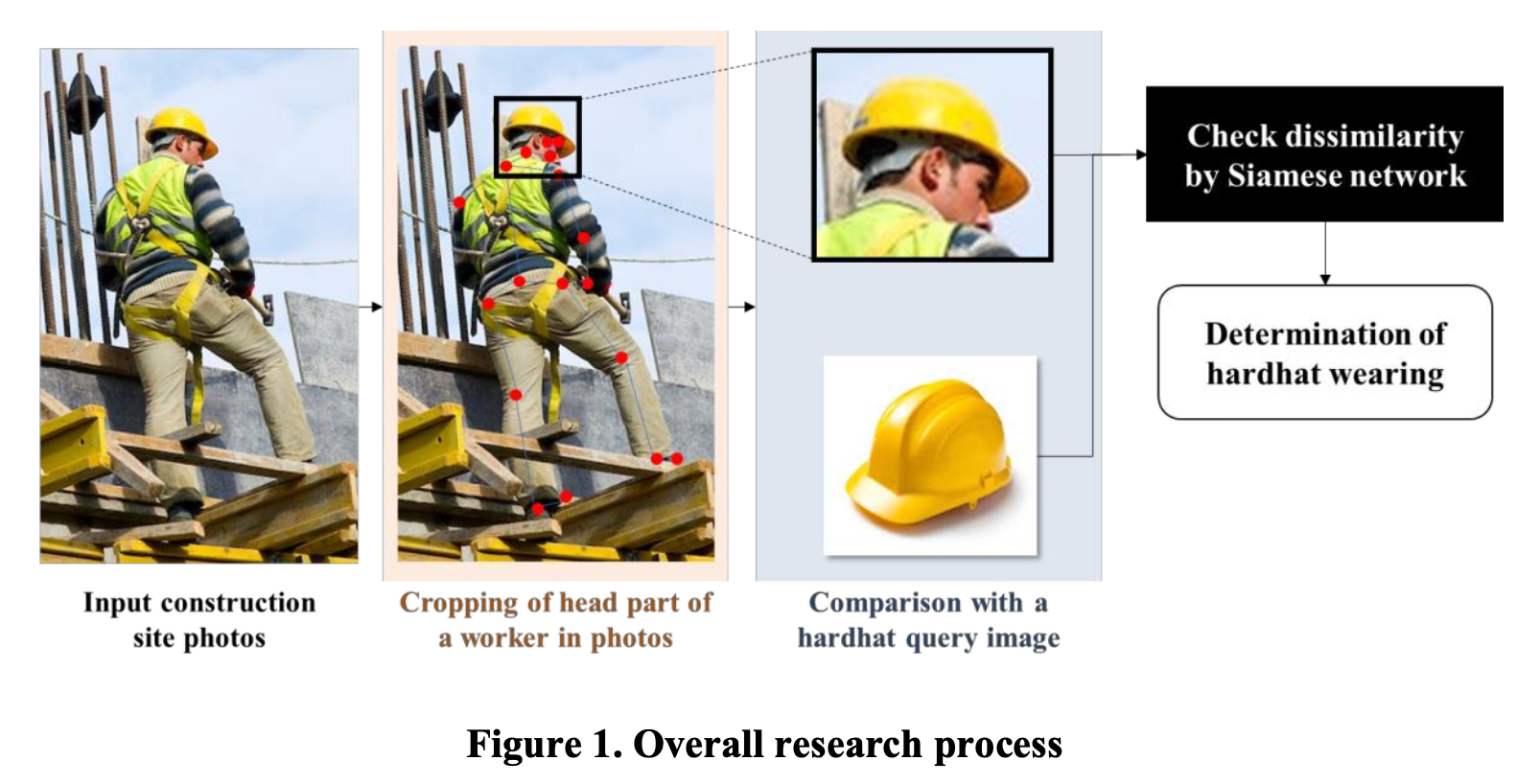
This study proposes a method to monitor workers’ personal protective equipment, particularly hardhats, at construction sites with a single query image. Prior studies on this subject required a large dataset for training, which can be time-consuming and labor-intensive since many of them utilize object detection models based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs). The proposed approach involves two steps. First, workers are detected, and their body key points are extracted through human-pose recognition used to crop head images. Second, the cropped head images are compared to a hardhat image using a Siamese network to determine whether a worker complied with the hardhat requirement. The proposed one-shot method showed 69.25% F1-score when validated against 2,000 photos of each worker wearing and not wearing a hardhat. The result indicates that the proposed approach has the potential to reduce the effort required for dataset construction while maintaining performance.
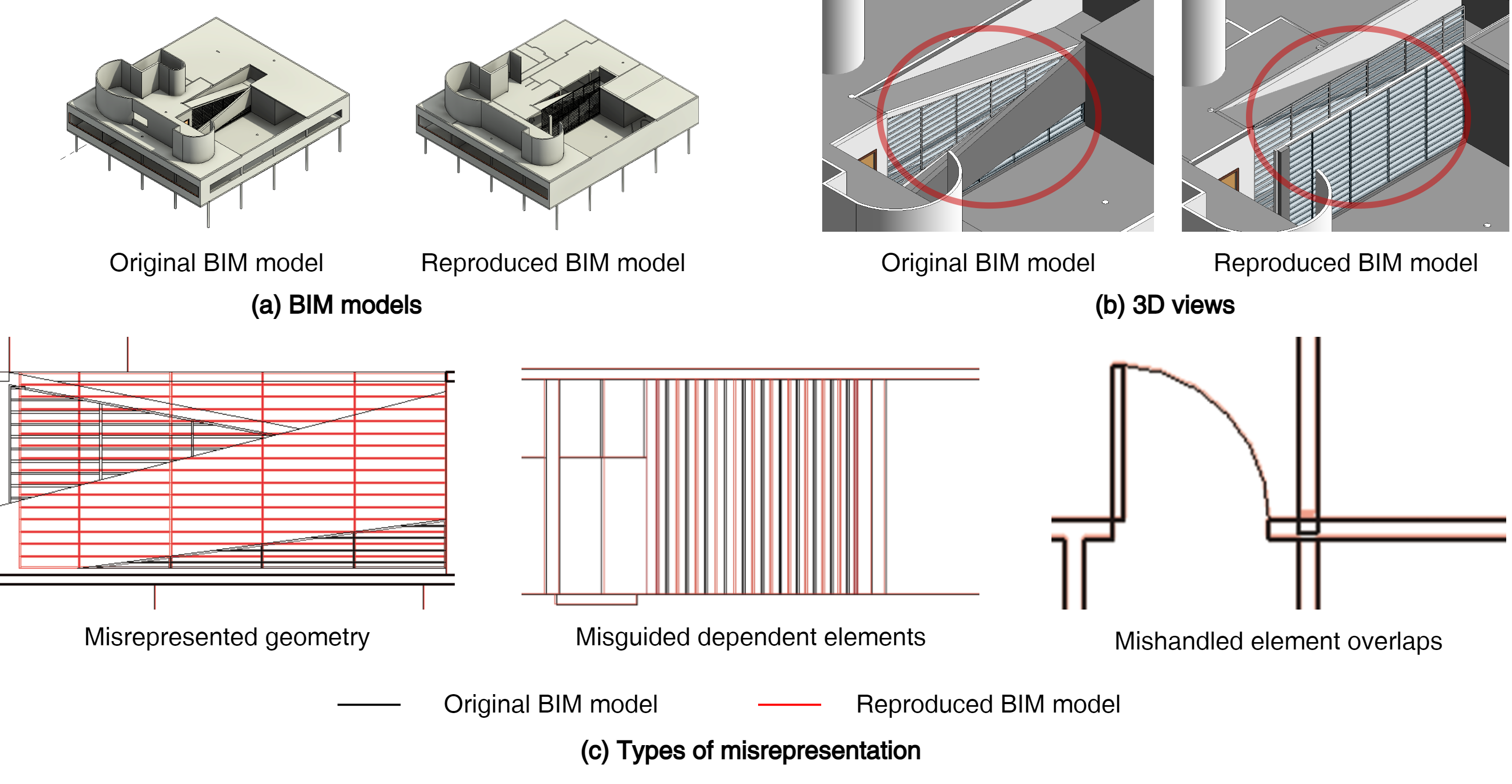
This paper presents an enhanced building information modeling (BIM) logger that captures building element geometry and attributes to accurately represent the BIM authoring process. The authors developed the logger and reproducing algorithm using the Revit C# API based on the analysis of information required to define building elements and associated attributes. The enhanced BIM log was evaluated through a case study of Villa Savoye designed by Le Corbusier, and the results show that it can accurately represent the BIM authoring process to a substantial level of reproducibility. The study provides a tool for capturing and reproducing the BIM authoring process. Future research can focus on improving the accuracy of the logging and reproducing algorithm and exploring further applications to automate the BIM authoring process using enhanced BIM logs.
Building information modeling (BIM) is widely used to generate indoor images for indoor localization. However, changes in camera angles and indoor conditions mean that photos are much more changeable than BIM images. This makes any attempt at localization based on the similarity between real photos and BIM images challenging. To overcome this limitation, we propose a reasoning-based approach for determining the location of a photo by detecting the cue objects in the photo and the relationships between them. The aim of this preliminary study was to determine the optimal number of cue objects required for an indoor image. If there are too few cue objects in an indoor image, it results in an excessive number of location candidates. Conversely, if there are too many cue objects, the accuracy of object detection in an image decreases. Theoretically, a larger number of cue objects would improve the reasoning process; however, too many cue objects could lead to declining object detection performance. The experimental results demonstrated that of two to five cue objects, three cue objects is most likely to yield optimal performance.
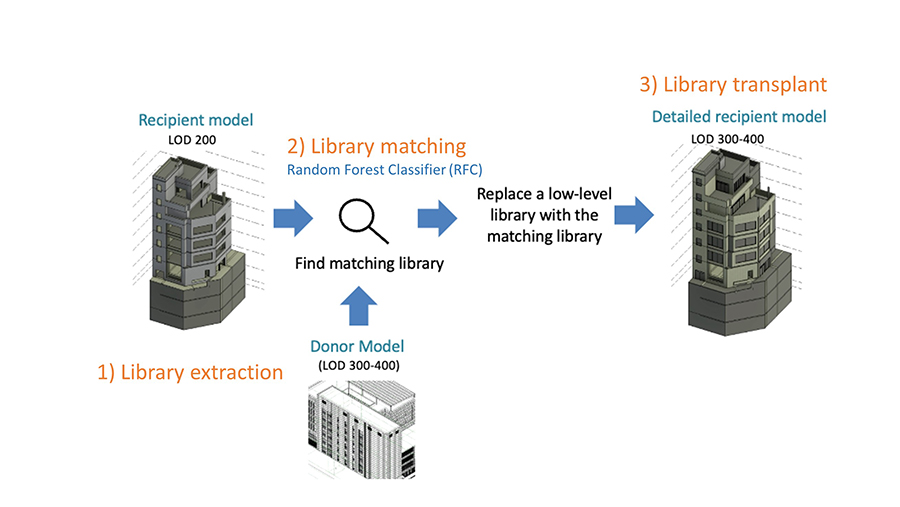
Building information modeling (BIM) library transplant is a framework proposed by the building informatics group at Yonsei University as a way to develop the details of a BIM model by automatically finding and replacing a low-level BIM library object with a match-ing high-level BIM library object in a donor BIM model. This paper introduces three BIM library transplant approaches: namely, attribute matching, semantic elaboration, and natu-ral language-based architectural detailing through interaction with artificial intelligence (NADIA).KEYWORDS: building information modeling (BIM), library transplant, graph neural net-work (GNN), semantic enrichment, semantic annotation, semantic elaboration, natural lan-guage-model-based architectural detailing through interaction with artificial intelligence (NADIA).
An omnidirectional (i.e., 360°) camera is an efficient device that can capture the status of a room with a single shot. To detect objects in a spherical image captured by a 360° camera, the image should be flattened and divided into patches reflecting normal fields of view (NFoV). However, detecting indoor defects in omnidirectional camera images is difficult because they are relatively small and span multiple patches. Another challenge is to set the appropriate size for an NFoV patch. To overcome these challenges, this paper proposes a method to locate possible regions of indoor defects using building information modeling (BIM). The core idea is to subtract a 360° camera image from a photorealistically rendered BIM model image of the same location. Bounding boxes are generated around the areas where differences are detected. The proposed method was tested in a single room with artificially implanted cracks. In the experiments, two different omnidirectional cameras were used. The image classification algorithm was trained on open crack datasets. The results showed that the proposed method improved the F1-score from 0.15 to 0.39 and recall from 0.16 to 0.87. The proposed method could detect more cracks while reducing the number of patches needed for indoor crack inspection compared to the traditional method.
In domain-specific named entity recognition (NER), the out-of-vocabulary (OOV) problem arises due to linguistic features and rare vocabulary. OOV problem is particularly challenging in agglutinative languages such as Korean. The irregular decomposition of morphemes makes it difficult to represent all of them in language model dictionaries, resulting in poor NER performance. Subword tokenization which segments a word into atomic tokens that are no longer divided can be one of the possible solutions. In the construction industry, existing NER methods do not effective on housing defect complaints which contain many rare words, including jargon, slang, and typos. To address this challenge, we propose subword tokenization algorithms that can mitigate OOV problems based on considering linguistic features and pre-trained language models (PLMs). The primary objective of this study is to identify the optimal NER performance by comparing different subword tokenization methods depending on the language models used. For domain-specific NER, we defined and used 23 defectspecific named entity tags for dataset labelling. We then experimented with a total of three state-of-theart language models: one SentencePiece-based and two WordPiece-based subword tokenization models. The results demonstrate that the SentencePiece-based Korean Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (KoBERT) outperformed the two WordPiece-based language models (multilingualBERT and Korean Efficiently Learning an Encoder that Classifies Token Replacements Accurately (KoELECTRA)) with an F1 score of 84.7%. The proposed method is expected to improve not only NER but also other downstream tasks that involve using Korean documents in the construction industry.
This paper provides an overview of South Korea's 20-year journey in adopting building information modeling (BIM) and future direction. It first discusses the six phases of BIM adoption in South Korea, starting from the use of BIM as a marketing tool to its current intelligent BIM phase. The government's support for BIM-related research and development projects is also highlighted, with a focus on the artificail intelligence (AI)-based architectural design automation project. As the future direction, it explores the integration of AI with BIM in both local and global contexts. The paper presents AI-powered architectural design methods, including AI-powered early architectural design generation and architectural detailing. Compared to AI-based early architectural design generation, architectural detailing is an unexplored research topic. This paper introduces two AI- and BIM-based architectural detailing methods, being developed at Yonsei University: namely, BIM library transplant and Natural language-based Architectural Detailing through Interaction with AI (NADIA). These methods demonstrate how AI-enhanced BIM can enable architects to interactively develop building details using a language model as a conversational AI and a knowledge base, and a BIM authoring tool as a design platform, in the near future.

This study proposes a method to monitor workers’ personal protective equipment, particularly hardhats, at construction sites with a single query image. Prior studies on this subject required a large dataset for training, which can be time-consuming and labor-intensive since many of them utilize object detection models based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs). The proposed approach involves two steps. First, workers are detected, and their body key points are extracted through human-pose recognition used to crop head images. Second, the cropped head images are compared to a hardhat image using a Siamese network to determine whether a worker complied with the hardhat requirement. The proposed one-shot method showed 69.25% F1-score when validated against 2000 photos of each worker wearing and not wearing a hardhat. The result indicates that the proposed approach has the potential to reduce the effort required for dataset construction while maintaining performance.
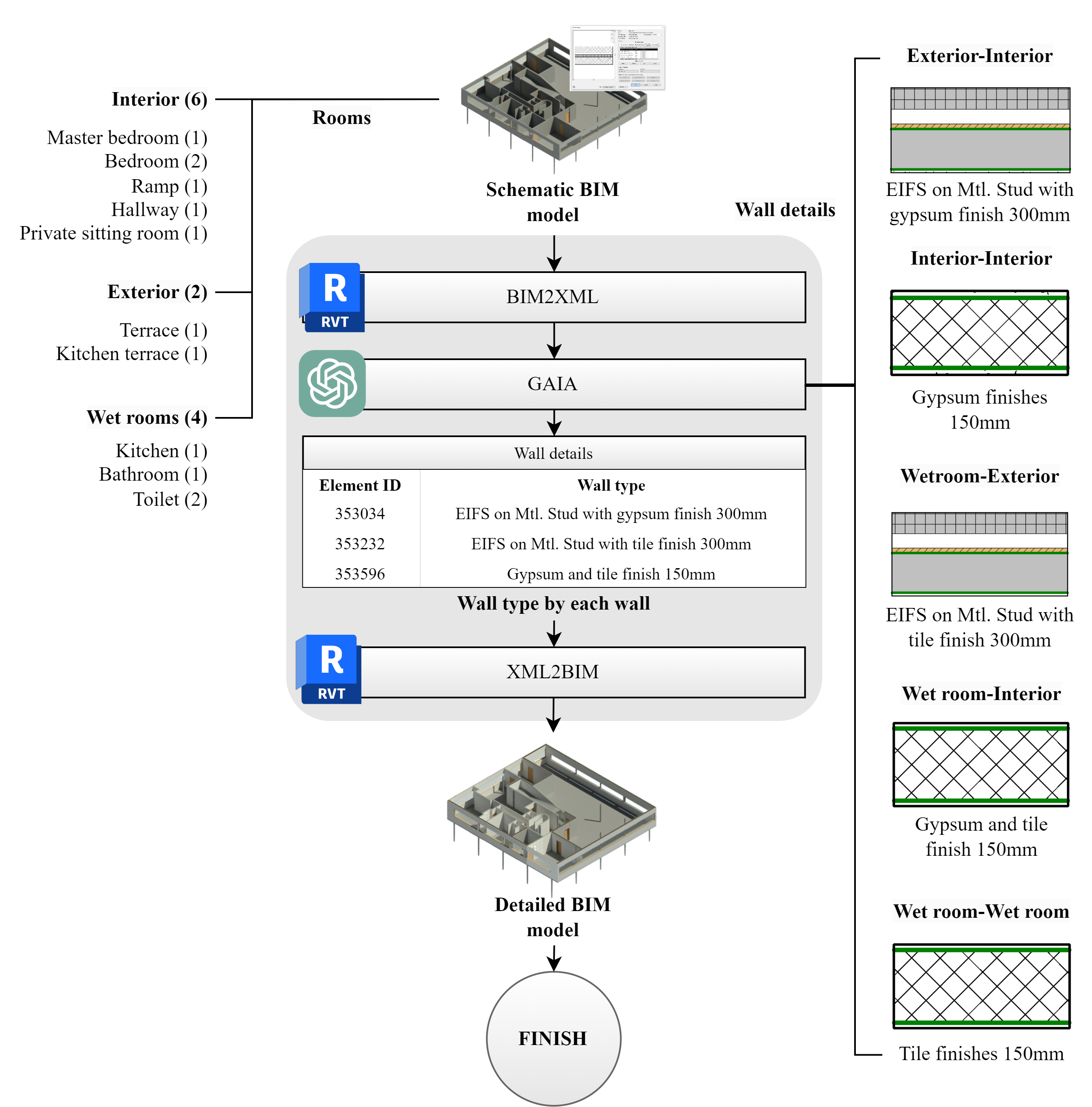
This study explores the potential of generative artificial intelligence (AI) models, specifically OpenAI's generative pre-trained transformer (GPT) series, when integrated with building information modeling (BIM) tools as an interactive design assistant for architectural design. The research involves the development and implementation of three key components: 1) BIM2XML, a component that translates BIM data into extensible markup language (XML) format; 2) Generative AI-enabled Interactive Architectural design (GAIA), a component that refines the input design in XML by identifying designer intent, relevant objects, and their attributes, using pre-trained language models; and 3) XML2BIM, a component that converts AI-generated XML data back into a BIM tool. This study validated the proposed approach through a case study involving design detailing, using the GPT series and Revit. Our findings demonstrate the effectiveness of state-of-the-art language models in facilitating dynamic collaboration between architects and AI systems, highlighting the potential for further advancements.
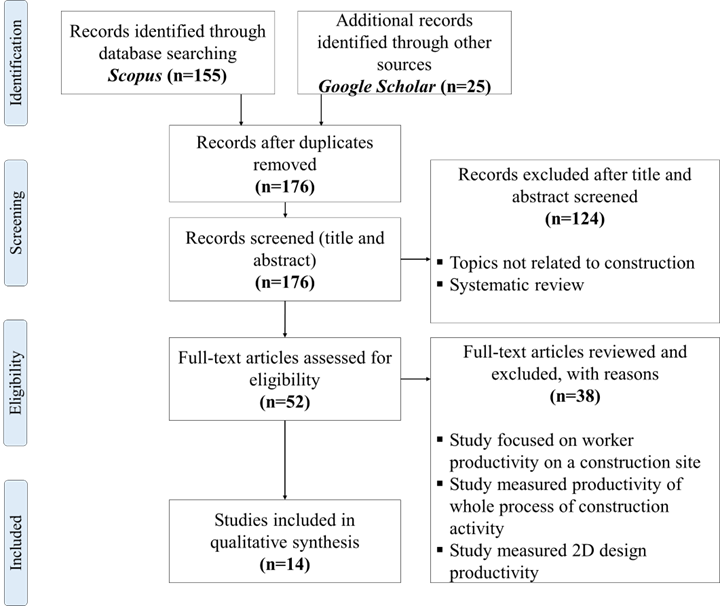
The purpose of this paper is to identify indicators for quantifying the modeling productivity of building information modeling (BIM) through a critical literature review of the factors considered in productivity analysis. Measuring BIM productivity, to which end quite a few efforts have been made, is important for efficient workforce management. The authors reviewed a total of 16 papers col-lated from Scopus and Google Scholar. The examples of topics included the productivity factors related to 2D/3D design modeling. The indicators of BIM productivity analysis can be classified into three types: Work hours as an input, work hours as output, and quantity as input or output. Among the 16 papers, the most frequently used productivity measurement indicator was workhours, and in other papers, different indicators were used according to the purpose of the study. Among the factors affecting BIM productivity, scale was the one most commonly considered. Other factors included quality, complexity and economic. Through the analysis of BIM productivity indicators and factors, it is possible to improve the project team’s efficiency and each modeler’s assigned task flexibility with high productivity.
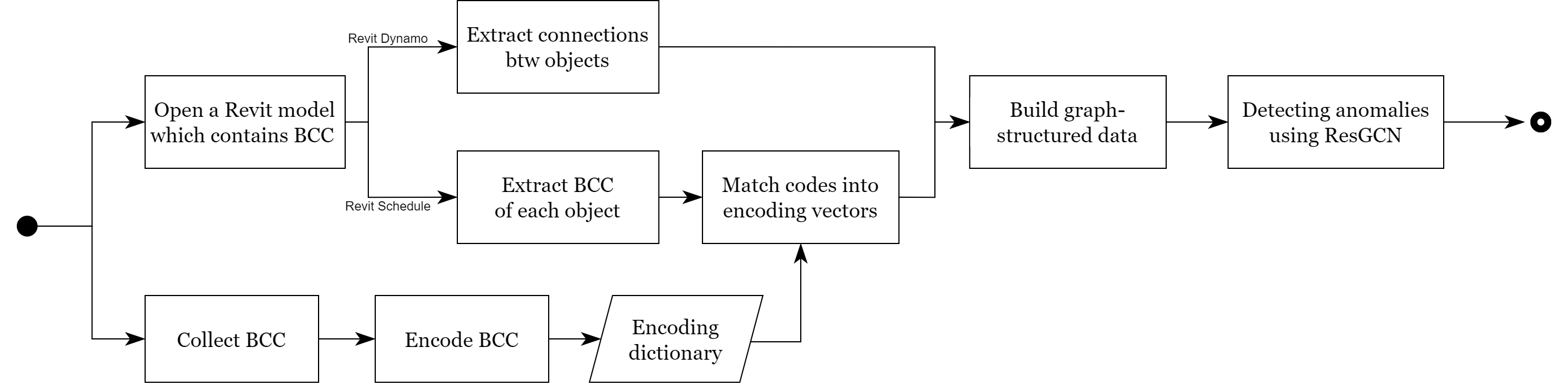
This paper introduces a framework for detecting abnormal objects in structural building information models (BIMs) based on the graph neural network (GNN). An abnormal object is a BIM object such as a wall, slab, or beam containing one or more incorrectly defined properties. Examples include incorrectly defined object types, names, and reference levels. These errors are difficult to detect using a ruleset, because the error patterns are irregular, and different companies have different modeling guidelines. To overcome these limitations, a few studies have deployed machine learning in anomaly detection, focusing primarily on the geometric features of objects. Geometric features, however, are not sufficient for detecting various cases of abnormal objects, particularly those related to property values. This study applied the residual graph convolutional network (ResGCN) model to detect anomalies in a BIM. As the first step, various types of building objects in a BIM model and their spatial relationships were translated into an attributed graph. Intentionally created anomalies were then inserted into the graph to train ResGCN. As a result, the trained ResGCN detects the abnormal BIM model objects using the properties of objects and the physical connections between objects. The proposed method contributes to the quality improvement of BIMs, which can be repurposed.
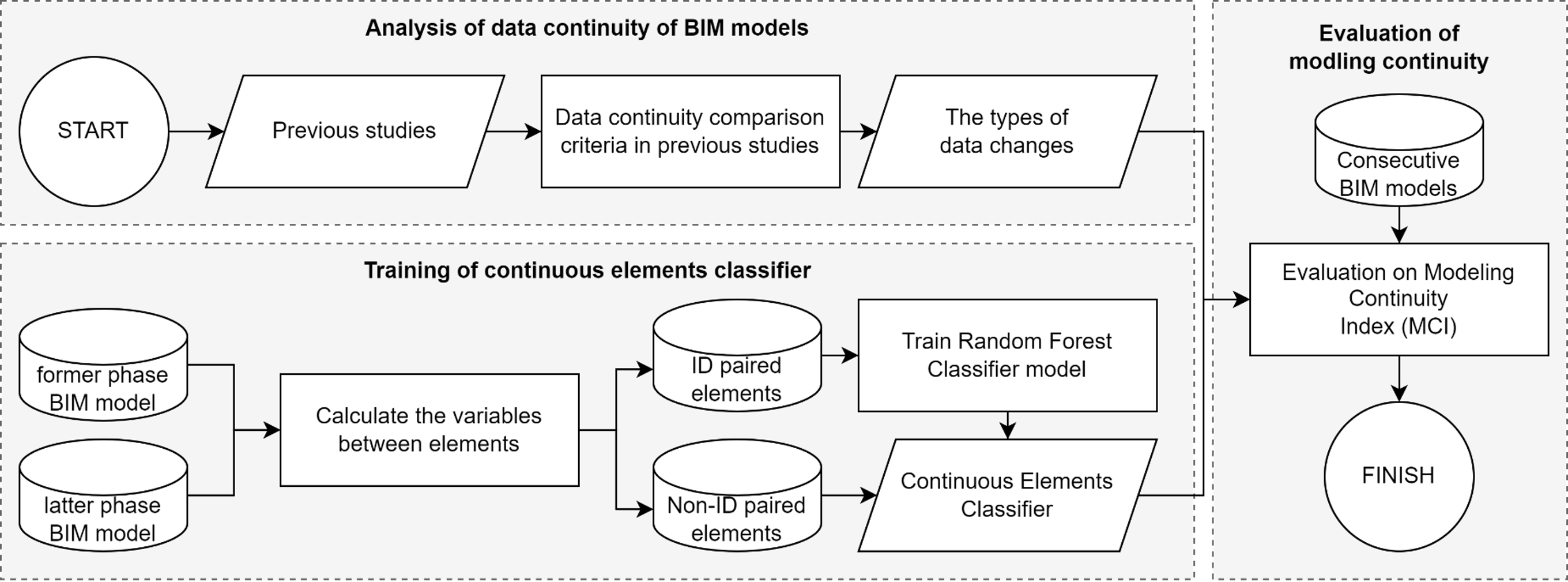
This study was aimed at quantifying the data continuity between building information models throughout the life cycle of a design project. By data continuity, this study refers to the degree of data updates and losses between consecutive phases of a single process. The benefits of building information modeling (BIM) adoption come from the reuse of information across multiple project phases and participants. In this regard, efforts have been expended to improve the interoperability of BIM data, but data continuity between BIM models across multiple project phases has been minimally explored. This research first defined the types of data changes occurring at the model, element, and property levels, after which the metrics for measuring data continuity were developed on the basis of the quantities and types of changed data. The applicability of the metrics was tested on BIM models that were created and developed throughout the schematic design, design development, and construction documentation phases of a design project. From the case, it was identified that data continuity can be differentiated by the element categories within a project. Data continuity patterns can be identified to develop an optimization strategy for design process management.
This paper aims to identify factors influencing the selection of retaining wall systems (retaining walls, lateral supports, and water-retarding methods). Choosing an appropriate retaining wall system is critical for successful excavation work in terms of safety, construction duration, and cost. Several studies have proposed the use of statistical analyses and machine learning algorithms for improving the selection process of a retaining wall system. However, each study proposed a different set of influence factors and the common influence factors were defined differently in each study. Thus, it is necessary to re-review the influence factors and their statistical significance in selecting a retaining wall system. This study collected 29 potential factors used in previous studies related to the selection of a retaining wall system. Potential factors were then filtered to shortlist candidate factors by considering whether the factors were objectively quantifiable without subject interpretation. Examples of potential factors that required subject interpretation include resident safety and site shape. Among the candidate factors, the ones that were highly correlated with the retaining wall systems were finalized and the definitions of factors were refined. Finally, 12 factors were selected, which will be used for a big data-based algorithm for recommending retaining wall systems.
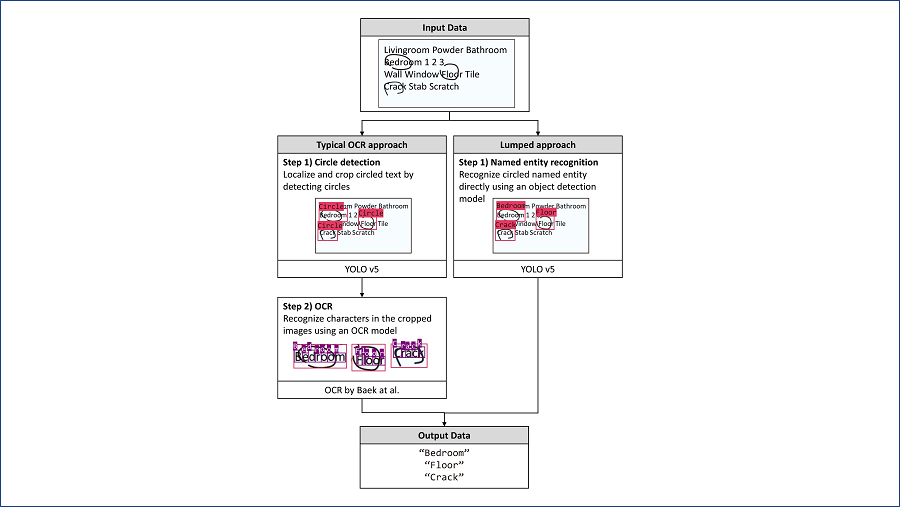
This study aims to improve the performance of optical character recognition (OCR), particularly in identifying printed Korean text marked by hand-drawn circles from images of construction defect tags. Despite advancements in mobile technologies, marking text on paper remains a prevalent practice. The typical approach for recognition in this context is to first detect the circles from the images and then identify the text entity within the region using OCR. Numerous OCR models have been developed to automatically identify various text types, but even a competition-winning multilingual model by Baek et al. does not perform well in recognizing circled Korean text, yielding a weighted F1 score of just 69%. The core idea of the lumped approach proposed in this study is to recognize circles and named entities as one instance. For this purpose, the YOLOv5 is fine-tuned to detect 65 types of named entity overlapped with hand-drawn circles and yields a weighted F1 score of 94%, 25% higher than a typical approach using YOLOv5 for circle detection and a model by Baek et al. for subsequent OCR. This work thereby introduces a novel approach for developing advanced text information extraction methods and processing paper-based marked text in the construction industry.
This study aims to review the use of graph databases in construction research. Based on the diagnosis of the current research status, a future research direction is proposed. The use of graph databases in construction research has been increasing because of the efficiency in expressing complex relations between entities in construction big data. However, no study has been conducted to review systematically the status quo of graph databases. This study analyzes 42 papers in total that deployed a graph model and graph database in construction research, both quantitatively and qualitatively. A keyword analysis, topic modeling, and qualitative content analysis were conducted. The review identified the research topics, types of data sources that compose a graph, and the graph database application methods and algorithms. Although the current research is still in a nascent stage, the graph database research has great potential to develop into an advanced stage, fused with artificial intelligence (AI) in the future, based on the active usage trends this study revealed.
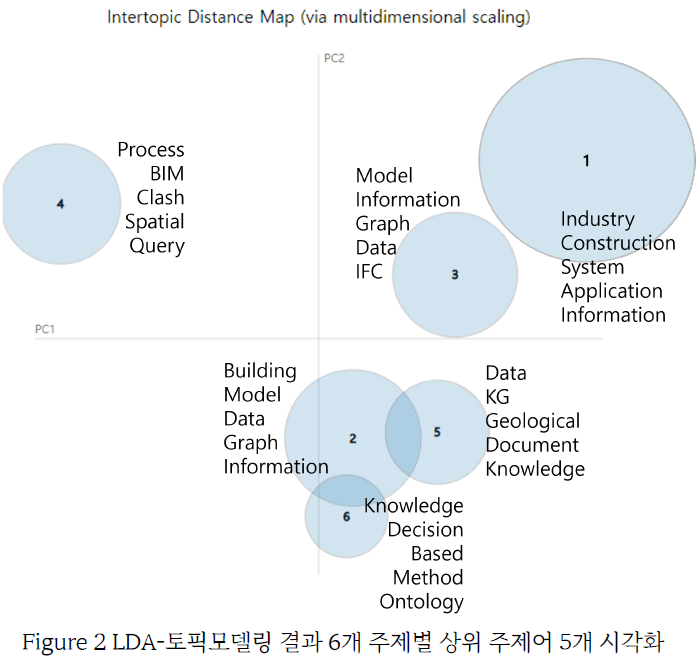
건설 프로젝트는 건축, 토목, 전기, 기계 등 다양한 분야의 전문 지식의 상호작용을 통해 완성된다. 건설 생애주기동안 발생하는 여러 현상과 문제들은 이 수많은 지식과 정보들이 서로 영향을 주고 받는 복잡한 관계를 통해 추론하고 해결할 수 있다. 건설 정보들의 네트워크로 구성된 건설지식그래프는 최근 화두가 되고있는 설명 가능한 인공지능(eXplainable AI, XAI)의 핵심 요소이기도 하다. 따라서, 지식그래프는 기존 딥러닝 연구의 블랙박스 한계를 극복할 수 있는 솔루션이라는 측면에서도 필요성과 중요성이 크다. 지금까지의 건설정보관리 관련 연구들은 Building Information Model(BIM), Industry Foundation Classes(IFC) 등을 중심으로 정 보의 교환과 재사용에 초점을 두었다. 최근에는 단편적으로 집약된 정보들간에 관계망(network)을 구축하고 이로부터 새로운 지식을 추론하는 건설지식관리로 인식의 전환이 일어나고 있다. 그러나 건 설 빅데이터의 복잡한 상호관계를 표현하고 처리하기에 기존의 관계형 데이터베이스(RDBMS)는 구조적, 비용적 측면에서 매우 비효율적이다. 반면, 그래프 데이터베이스는 복잡한 관계구조를 가지는 데이터를 유연하게 표현할 수 있고 유기적인 추론이 가능하다는 점에서 건설지식체계의 표상에 더 적합하다고 할 수 있다. 그러므로 본 연구에서는 그래프 데이터베이스 관련 주요 개념과 특징을 살펴보고, 건설지식관련 연구들을 텍스트마이닝 기반으로 분석하여 연구 동향을 파악하고 향후 발전 방향을 모색한다.
An automated keyword-based trend analysis service, such as Google Trends, is helpful for quickly grasping changes in interest in a particular topic over time. However, the current keyword-based search sometimes returns a nonsensical result due to homonym issues. This study proposes a method that analyzes construction trends using the semantic search function of the Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3 (GPT-3). The performance of GTP-3 as a construction-trend analysis method was analyzed by selecting top-ranked countries associated with building information modeling using a keyword, synonyms, and acronyms. The results demonstrate the possibility of using the proposed method as an alternative to the traditional bibliographic analysis, the scientometric analysis, and a Google Trends-based analysis.
This study proposes a novel approach to detect the verticality defects of installed objects through monocular depth estimation. Previous studies for automated defect identification so far have focused on defect detection such as cracks, mold, stains, etc., however, automated methods for examining the vertical alignment of installed objects have not been studied. This study explores methods for automatically checking the vertical alignment of installed objects through monocular depth estimation. The proposed method showed an accuracy of 82%. However, as close to 100% accuracy is required in practice, further research is expected to put the proposed technology to practical use.
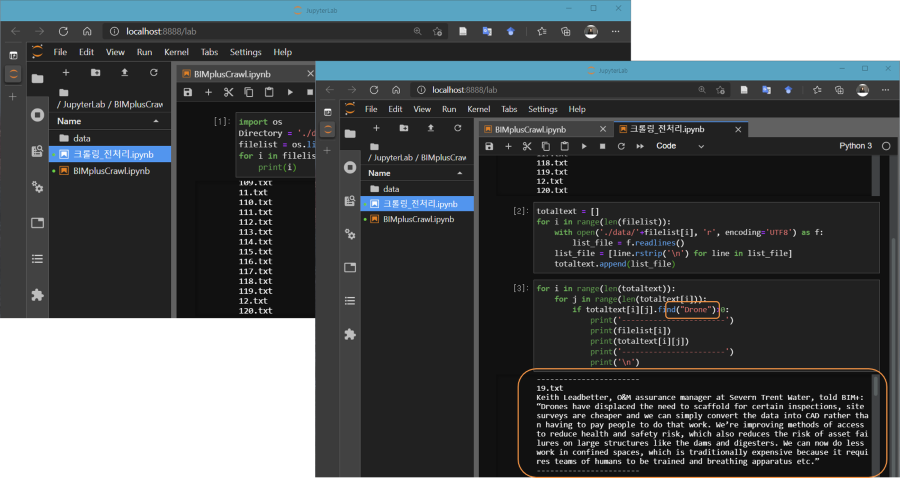
The purpose of this study was to develop a method that could automatically scrape and extract construction project information from the web. The manual collection of construction project information begins with the search for websites containing the target information using keywords, which is time consuming. Moreover, it requires visits to at least four websites to collect all the target information. To improve this process, we collected construction project information by web scraping using Python 3.8.5. In additionally, we extracted paragraphs containing keywords to consider the context.
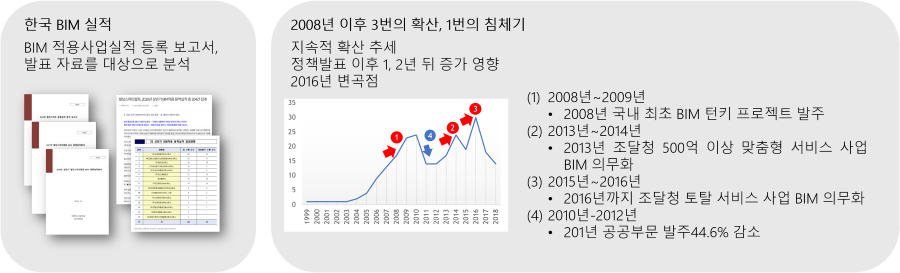
본 연구는 지난 10여 년 동안의 한국 BIM 정책과 다른 나라의 정책에서 정의하는 BIM 도입의 목적을 비교해보고 실제 프로젝트에서 BIM 채택에 미친 영향을 분석하였다. 연구에 사용된 데이터는 2008년부터 발표된 정부의 BIM 정책과 BIM 실적조사결과 등을 포함하였다. 분석 결과 지난 10여 년 동안 BIM 사용이 눈에 띄게 증가한 세 번의 주요 시점이 있었다. (1) 정부에서 관련 정책을 발표할 때마다 BIM 채택이 증가 되었다. (2) 정책 발표기관은 정부 부처, 공기업, 지방행정부 등이 주도적이었다. 국토교통부가 주도적인 역할을 하였다. (3) BIM 채택은 국토교통부 산하 건축 부문에서 토목 및 도로, 철도와 같은 인프라 부문으로 확장되었다.
This paper introduces a method for managing daily construction tasks using a text messenger and a tool to support the method. Many construction field management tools have been developed and used in practice. In addition, each company has developed its own construction task management tools. Nevertheless, due to the number of various tools available, contractors and subcontractors suffer from installing at least three or four applications on mobile devices to support different projects. To resolve this issue, the authors developed ProjectHub-CL (Construction Listener), a method and tool to manage daily construction tasks using a popular text messenger that doesn’t require the installation of an additional mobile app. It helps field engineers and subcontractors to exchange and manage field tasks using text messages and additional features on a text messenger and can automatically produce a construction daily report at the end of the day as a result. The system was implemented on top of KakaoTalk, the most popular text messenger in South Korea. Its applicability and usability in the field were validated with contractors and subcontractors in four different projects (conducted by different general contractors).
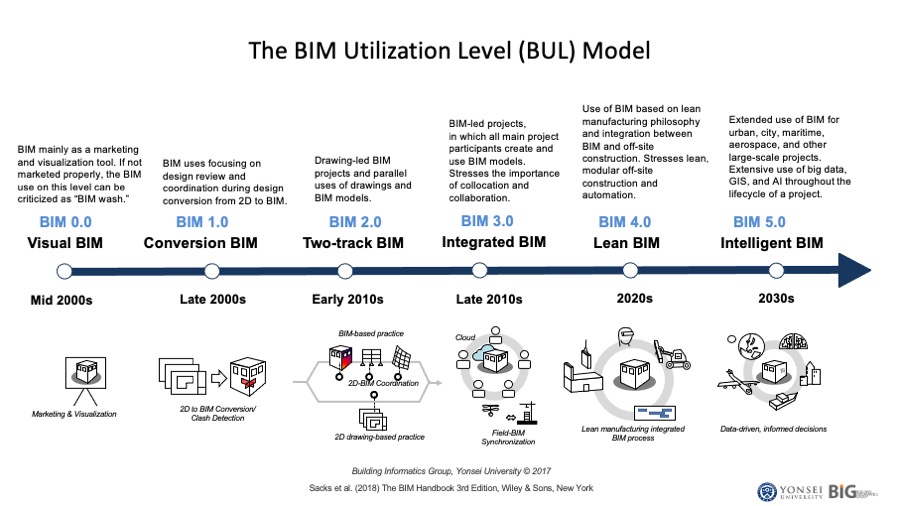
This presentation describes the BIM Implementation in South Korea from 2008 to 2020.
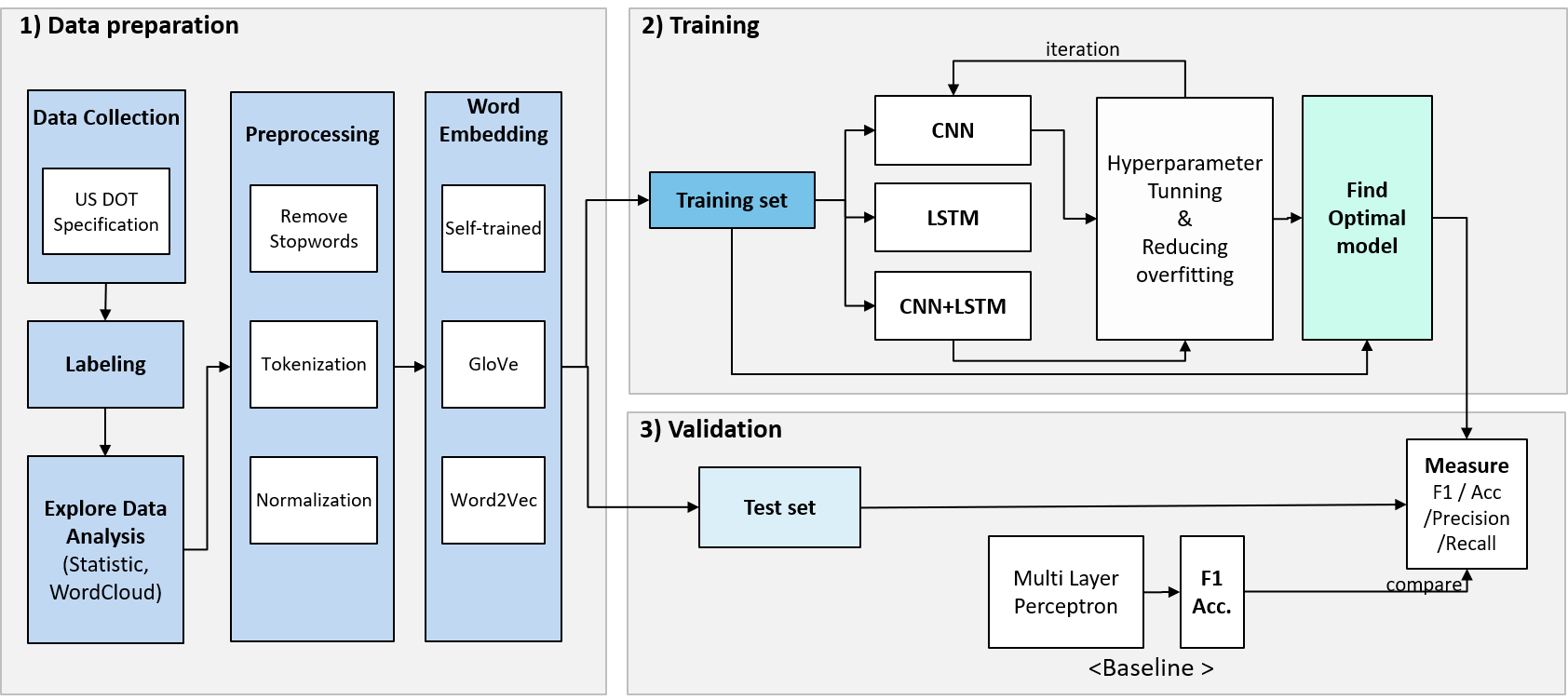
This aim of this study is to classify requirement sentences from the specifications of US DOT using natural language processing (NLP) and a deep neural network. At the contract phase of the project, the requirements analysis of contract documents is a significant task to prevent claims or disputes caused by ambiguous or missing clauses, but it is highly human-intensive and difficult to identify requirements within a given short period. In this article, the requirement sentences identification model was proposed based on deep-learning algorithms. First, the critical terms that define what the requirement sentence is were identified, and then all sentences were labeled using the pre-defined critical terms. Second, three vectorizing methods were used, including two pre-trained methods—GloVe and Word2Vec—and a self-trained method to produce word embedding. Third, the automated classification of requirements sentences was experimented using three deep-learning models: the convolutional neural network (CNN), the long-short-term memory (LSTM), and the combination of CNN+LSTM. In the evaluation of nine total experiments, the results showed that the F1 scores of the CNN model were the highest at 92.9% and 92.4% for both the Word2Vec model and the Glove model. This study provided a way to achieve a high level of classification accuracy with simple deep-learning models and pre-trained embedding models.
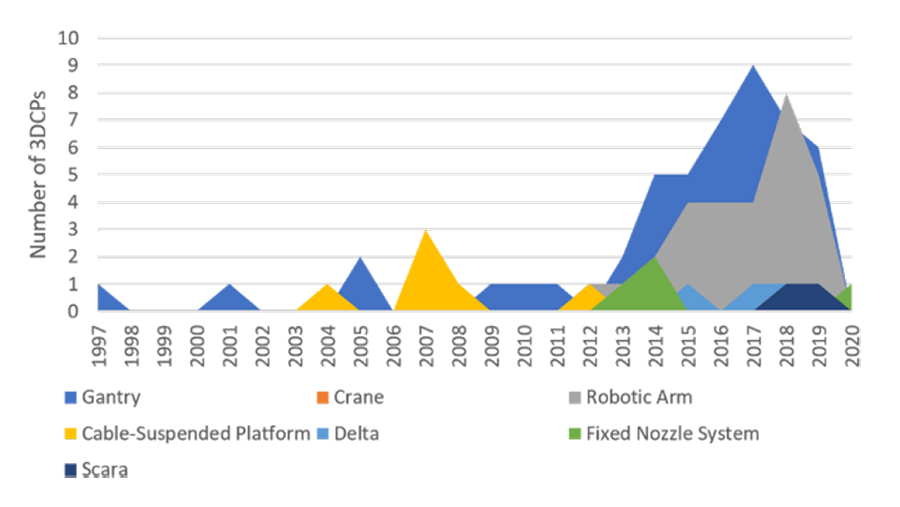
Although several previous studies have reviewed 3DCPs, they have been based on few cases and do not include the latest 3DCPs. This study analyzed 139 academic papers and 98 types of three-dimensional concrete printers (3DCPs) developed from 1997 to 2020 through a systematic literature review. A chronological distribution analysis showed that the number of papers and printers suddenly increased after 2012. Most papers (89%) and 3DCPs (86%) were produced from 2012 to 2020. A geographic distribution analysis showed that while Switzerland published more papers than the US, the latter developed more than twice as many 3DCPs than Switzerland. The difference is attributed to who led the development: the industry (US) or academia (Switzerland). Among nozzle-traveling 3DCPs, gantry and cable-suspended platforms were the most common types for some time, but the robotic arm type has spread considerably in the last five years. Since 2013, mobile and collaborative 3DCPs have also increased.
본 연구는 현장시공품질기반의 건설기능인의 숙련도 평가항목의 중요성과 적정성 검토를 위한 사전연구이다. 기존 기능인자격제도는 다양한 현장상황을 반영하지 못하는 평가방법으로 기능인의 숙련도를 제대로 평가하지 못하는 한계가 있고 이는 곧 시공품질저하로 이어져 공동주택의 하자급증의 주요 원인으로 대두되었다. 시공품질 확보와 하자 저감을 위해 현장시공품질기반의 기능인 숙련도 평가제도가 도입되고 시범 운영 되었다. 본 연구는 하자발생율이 높은 도배공종으로 연구 범위를 한정하여 시범 운영에 활용된 도배기능인 숙련도 평가항목의 중요성과 적정성을 검토하였다. 현장시공품질기반 관점에서 도배 표준시방서와 품질체크리스트 항목에 모든 평가항목이 포함되어 현장기반평가항목으로의 적정성을 검증했으며 전문가 설문조사와 AHP 분석 결과 22개 평가항목 모두 도배품질에 영향이 큰 중요 평가항목으로 도출되었다. 향후 연구방향으로는 평가제도의 확대를 위한 평가체계의 신뢰도와 타당성 검증 및 평가방법의 개선 방향을 제시하였다.
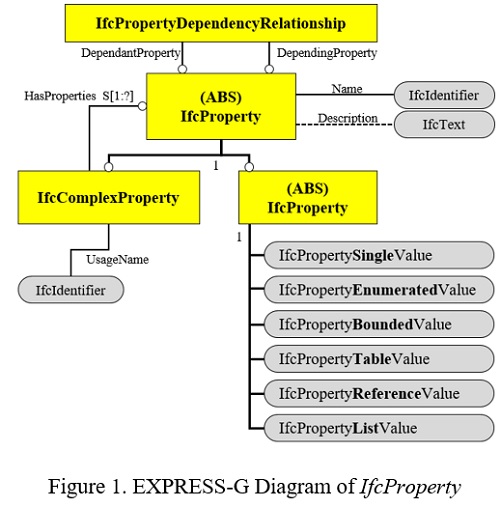
This study compares methods of defining property sets for industry foundation classes (IFC) in information delivery manuals (IDMs) and building information modeling (BIM) tools. Since their inception, IFC has been extended to support various domains and use-cases. However, it is common to find information items from a project that are not supported even by the latest version of IFC. IfcPropertySet (Pset) is the IFC element that allows users to temporarily add such missing information items to IFC data. Many commercial BIM tools support a function to define Psets, but in different ways. This paper compares each tool from five aspects: term definition, IFC element search and mapping, data type and cardinality, and usability. The analysis results show that there is a great deal of room for improvement, although the current IDM and major BIM tools provide functions to define user-defined information drawn from these five review criteria.
This study is a review of a variety of methodologies for defining information delivery manuals (IDMs), focusing particularly on exchange requirements (ERs). The notion of a reusing predefined ERs in information delivery manual (IDM) has existed for decades. Over that time, studies have been conducted assuming the reuse of IDMs. However, it is still difficult to find IDM/MVD documents that have been reused because no standardized method for exchanging IDMs exists. As a preliminary study for developing a standard for exchanging IDMs, this paper reviews five studies centered on methodologies for defining ERs, based on the ISO 29481-1:2016 IDM standard. This comparison revealed differences that can be used as a strategic basis for developing IDMs.
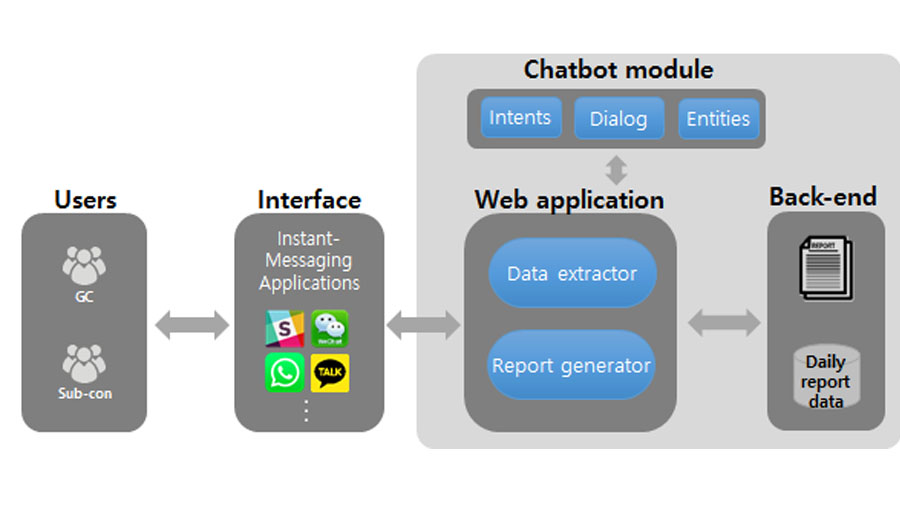
Consistently updating, analyzing, and managing construction-related information is one of the key success factors in project management. Quite a few construction projects have recently started to utilize instant messaging (IM) applications such as Slack, WhatsApp, and WeChat as a communication channel among project participants to share daily construction information due to easy accessibility. However, general contractors are still required to manually extract and integrate the data from instant messages to compose daily reports. This is because the data inputted by subcontractors through IM applications are usually in an unstructured form and the IM application is not normally interoperable with the systems database especially developed for construction management. To solve this problem, this study proposes a chatbot-assisted construction daily report data management system. The chatbot in the proposed system collects and processes the required information through conversations with subcontractors, and automatically generates and shares a daily report for general contractors. A prototype system has been designed and implemented to prove the concept.
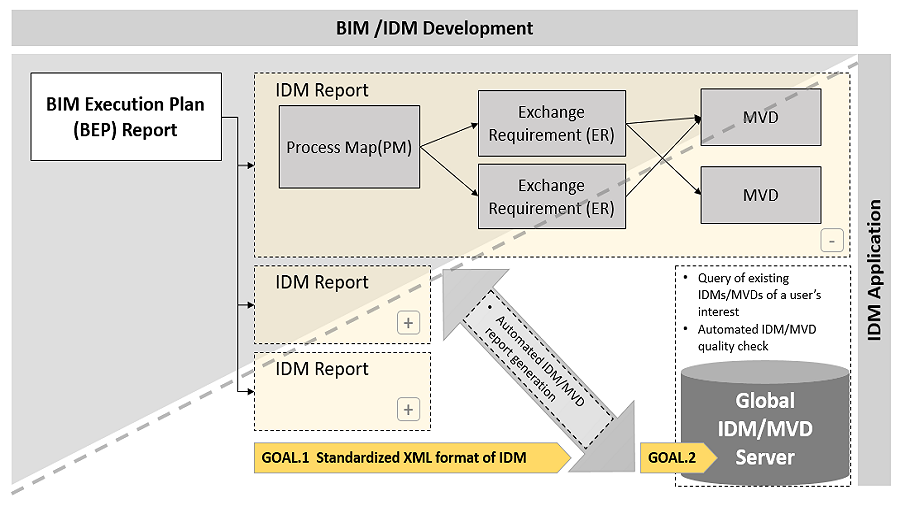
This study reviews a variety of previous efforts to support the development of the information delivery manual (IDM) configurator to satisfy a digital construction environment. Due to requirements for submitting a BIM execution plan (BEP), including employer’s information requirements (EIRs) by the UK government, the need to develop an updated IDM and model view definition (MVD) is increasing. However, currently developed IDMs and MVDs are hard to share and modify for reuse. Moreover, neither a system nor a standard exists to globally share and manage IDMs and MVDs. In this paper, this study reviews significant previous efforts that can potentially be part of an IDM configurator or a global IDM server. These efforts can be categorized into three groups: (1) software development, (2) IDM framework development, and (3) MVD development. To conclude, we identify current challenges and future work to fill the gaps between the present status and goals of the IDM configurator. The existing efforts discussed in this paper will serve as a fundamental basis for realizing the IDM configurator
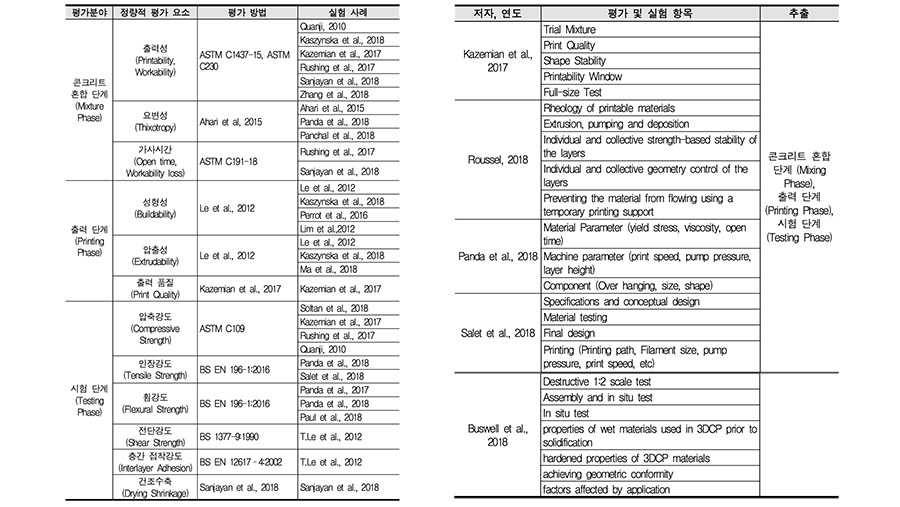
본 연구의 목적은 건축물 3D 프린팅 성능평가의 표준 개발을 위한 기초연구 자료를 제공하는 것이다. 본 연구는 건축물 3D 프린터 기술과 관련된 기존의 연구들을 검토하고, 3D 프린팅 성능평가 분야를 도출한다. 그리고 도출된 평가분야를 중심으로 관련 실험들을 종합하여 공통적으로 진행되고 있는 실험들을 선정하고 표준화될 수 있는 실험방법을 제시하고자 한다. 3D 프린팅용 콘크리트 배합물과 그를 통한 출력물이 건설현장에서 적절한지 판단기준을 정의하는 것은 건축물 3D 프린팅 기술 상용화의 초석이 된다는 것에 의의가 있다.
본 연구는 챗봇 기반 시공 이슈관리 시스템의 모델을 개발하였다. 최근 건설산업은 건설정보모델링 기술을 기반으로 현장관리를 지원하는 시스템 시장의 규모가 증가하고 있다. 하지만 강력한 기능을 제공하고, 적용에 따른 성공사례가 증가하고 있음에도, 기술 수용에 대한 저항감 등으로 인해 아직까지도 문자나 채팅 어플리케이션을 활용하여 건설 관리를 수행하는 관계자들이 다수 존재한다. 한편 채팅 어플리케이션은 챗봇 기술의 발달로 인해 그 활용이 업무영역으로 확대되는 추세이다. 때문에 본 연구에서는 기존의 시공관리 시스템을 분석하여 주요기능을 도출하고, 챗봇에 관한 기존 연구 고찰을 하였다. 이를 기반으로 시곤관리에서 발생하는 이슈를 대화내용을 자동분석하여 관리하는 챗봇 기반의 시스템 모델을 제시하였다. 개발한 시스템 모델은 시공관리 전문가와의 인터뷰를 통하여 기대되는 표율성을 평가하였다.
null
Classifying pictures of construction sites is very time-consuming when done manually. This study proposes a method to automate the classification of construction pictures using a deep-learning algorithm. In this study, the classifier was trained using images of construction sites, categorized by work program to distribute the input images into correct categories. The validation process included three categories for the construction process, which were repeated several times using different training times and images. The results showed that deep learning has potential for classifying site images and that the system becomes more accurate as the number of images accumulates.
This study proposed an early prototype of a real-time 3D visualization system for structural health monitoring data using BIM. Since structural health monitoring (SHM) data from sensors are in the numerical form, it is hard to intuitively understand the status of a structure. Currently this problem is solved through a costly process of developing a custom-built application for visualizing the SHM data. However, as the BIM and interoperability technologies advanced, integration between SHM sensor data and an existing BIM model became much more than accessible than ever. This study demonstrates this possibility through two experiments: 1) using an Arduino chip set, a force-sensor resistor (FSR), Dynamo and a BIM model; 2) and using a SHM data set of an actual beam collected from a laboratory. The result shows a potential for repurposing a BIM model developed during the design and construction phase for real-time structural health monitoring at an affordable cost.
This study collected and analyzed BIM strategies of nine countries. The BIM roadmaps of 9 countries could be classified into 3 types depening on how the milestones were set up. Each milestone of some BIM roadmaps were defined by collaboration level, method of data exchange, and level of BIM uses. This paper also identified 6 areas of strategies, namely education, policy, leadership, .... Among them, education, policity and leadership are the most frequently discussed topics.
The purpose of this study was to develop a BIM (Building Information Modeling) project information–classification system to collect and analyze BIM project data. To develop the classification system, previous studies on construction project classification systems were reviewed first. In parallel, the project factors that were studied in 128 BIM case studies were analyzed. An early version of a BIM project information classification was quantitatively and qualitatively reviewed in five categories by a total of five practitioners with BIM experience. The five categories were importance, appropriateness, urgency, specificity, and collectability. The classification has been modified based on the review results.
Some people claim that they are not users of building information modeling (BIM) even when they use BIM tools. This study investigates why some non-BIM users believe that they are not BIM users by analyzing their perceptions of BIM. To this end, a survey was conducted with BIM and non-BIM users in the Republic of Korea. The survey consisted of questions about the perception of BIM and non-BIM users toward BIM use, process, organization and policy. The results show that suspicious non-BIM users account for 65% of non-BIM users. The analysis of the survey reveals that the non-BIM users who actually use BIM tools have a higher expectation of the level of overall BIM adoption than BIM users have. They believe that they are not BIM users because they currently deploy only basic BIM uses that do not require a high level of collaboration. and do not have a BIM specialist (BIM manager) in their group. Further research on the global view of BIM users is recommended.
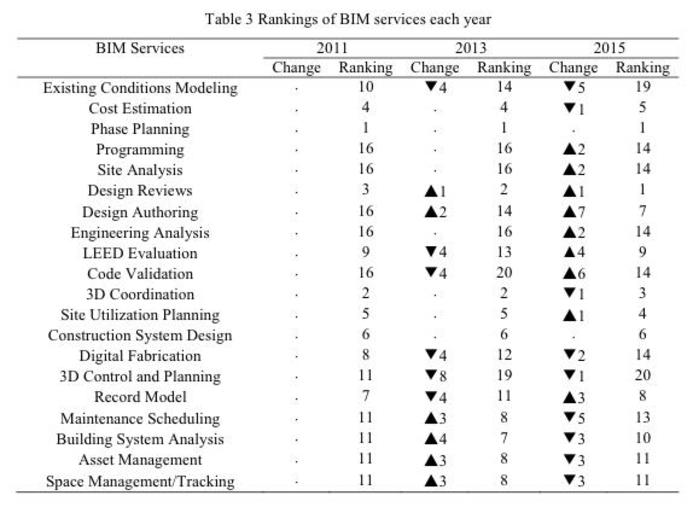
This paper presents the results of a five-year longitudinal study conducted to analyze the changes in the building information modeling (BIM) services provided by top contractors from 2011 to 2015. Many previous studies analyzed the trend of BIM adoption through questionnaires, case studies, or interviews, all methods that are subject to respondents’ perspectives. To objectively analyze the changes in BIM services throughout the years, the research team tracked the BIM services provided by top contractors, which were selected using the 2011 to 2015 Giants 300 reports. The BIM services that each company provided were collected in 2011, 2013, and 2015 from the company’s websites, brochures, and/or reports about its BIM projects. The collected BIM services were regrouped using the BIM use classification suggested by Pennsylvania State University. The frequency of BIM services and the correlations between the BIM service types were analyzed. The results showed that the average number of BIM services provided by one company increased from 5.16 in 2011 to 10.91 in 2015. The top five BIM services provided by the top BIM companies include phase planning, 3D coordination, design reviews, cost estimation, and site utilization. While about 70% of the top BIM companies provided these services in 2011, these services were provided by most companies (approximately 85%) in 2015. It is expected that the results of this study will help the industry to overview trends in the BIM market and decide which technologies they need to adopt in order to keep pace with major BIM companies.
Despite the widespread use of building information modeling (BIM)—including BIM-based design review, which is known as an early step of BIM adoption—many regions and small companies struggle with using BIM effectively. Many existing studies have provided industry- and project-level statistical data on the impact of design errors in construction, as well as an industry-level statistical analysis of the effectiveness of BIM-based design review, but such studies are often challenged by professionals who strongly believe in the effectiveness of drawing-based design review. This study conducted four design review experiments with eight experienced professionals to provide an inherent personal-level cognitive limitation of drawing-based review. The experiments reveal that due to an overwhelming number of potential errors to review, drawing-based design review only allows professionals to deploy a targeted search strategy, which might be an effective information search method within a given or predefined search space but is limited in finding unanticipated design errors. As a result, experienced professionals could not even detect 5% of known errors on drawings during the experiments. The result confirmed that experience cannot overcome such cognitive challenges in drawing-based design review.

This paper aims to analyze design errors prevented by building information modeling (BIM)-based design validation to identify consideration factors for successfully implementing BIM-based design validation in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) projects. More than 1,300 design errors detected by BIM-based design validation in three BIM-based projects in South Korea are categorized according to its causes, work types, and likelihoods to cause project delay and cost overrun. Each design error is analyzed by conducting face-to-face interviews with practitioners in the three projects.

This paper proposes a methodology to analyze the impacts of building information modeling (BIM)-based design validation on reduction of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in architecture, engineering, and construction projects. In order to validate the applicability of the proposed methodology, case studies of two BIM-based projects in South Korea were conducted. Through the BIM-based design validation process, 381 and 136 design errors were detected and 108 and 21 rework were prevented in Case 1 and Case 2, respectively. As the results, 384.2 tonne (0.5%) and 79.9 tonne (0.7%) of total GHG that might be emitted in the production stage of construction materials of the two projects were prevented by BIM-based design validation.
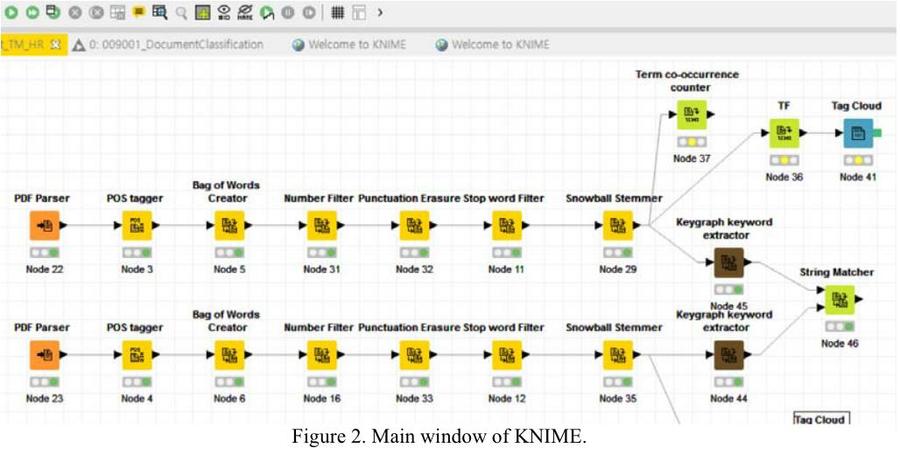
Even engineers who have the same job title and are working on the same project have different skills and backgrounds. However, despite the importance of assigning the right person to the right job to ensure successful project delivery, current human resource (HR) allocation practices are only concerned with the list of projects in which a candidate has been involved, years of experience in a discipline, and their previous job titles. As a result, some engineers lack the knowledge and experience to perform the tasks they are assigned on a project. This study demonstrates the need for a long, descriptive résumé rather than the commonly used short, brief résumé. When the job candidates who participated in this study were asked to describe their work experience in several sentences on their curriculum vitae (CV) instead of describing them using a few words composed of just the job title and roles, the contents of the CVs were clearer and showed less bias. This paper therefore presents a text-mining algorithm and a semantic résumé analysis system that we developed to automatically extract and analyze the work experience candidates write about on their résumés. This algorithm and analysis system can help HR managers control the significant amount of information found on prospective employees’ long résumés. To validate the algorithm and the system, six sample résumés were collected anonymously. These résumés were then reviewed both manually and by the developed system. In a subsequent study, we expect to apply the text mining–based HR resource allocation algorithm to select construction engineers for a real project and measure the job-matching rate.
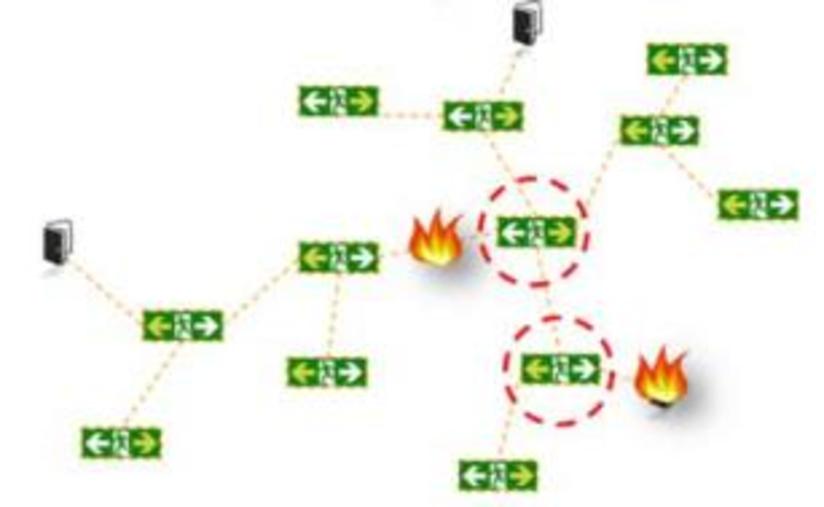
This paper presents the factors that could potentially affect the reliability of a serverless smart exit sign system, namely an evacuation guidance system based on a wireless sensor network (WSN) without a central server. Serverless smart exit sign system dynamically changes the directions of signs to indicate the shortest safe evacuation paths. Thus, the reliability of these systems is critical. Nevertheless, no research has been conducted to test the reliability of serverless smart exit sign systems. As a first step, we conducted a literature review to analyze the factors that could degrade the network performance of serverless smart exit sign systems. The identified factors were grouped into three categories: physical obstacles, environmental factors, and WSN properties. We plan to develop a prototype of a serverless smart exit sign system and then to conduct experiments to validate the influence of these factors on its network performance.
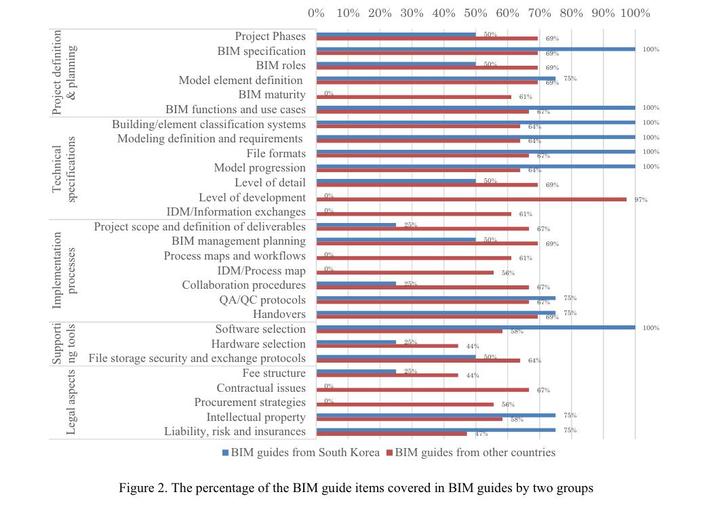
The aim of this study is to identify the future direction of Korean building information modeling (BIM) guides by comparing the Korean BIM guides with those of BIM-advanced countries. Although quite a few BIM guides are currently available in Korea, new and updated BIM guides are required to cope with the Korean government’s plan to expand the scope of the BIM mandate from the public projects under 50 billion won to all public “customized-service” projects in 2016. A customized-service project is a type of project that a public organization commissions the Public Procurement Service (PPS) to manage partially or fully from the planning phase to the maintenance phase. First, BIM guides—the four major public BIM guides in Korea and 58 BIM guides from 10 countries worldwide—were collected and analyzed. The results of the study indicate that the Korean BIM guides still lack clauses regarding BIM workflows, information delivery guidelines, and contractual and intellectual property issues, and clear definitions on the level of development. The results also show that the Korean BIM guides mainly focus on BIM implementation during the design and construction phases, but place little emphasis on the facility management phase. On the other hand, the Korean BIM guides include details on how BIM models should be developed incrementally throughout the schematic design, design development, construction documentation, and construction phases. In addition, the Korean BIM guides clearly describe the minimum requirements for various cases relating to BIM data use, such as design review, 3D coordination, and cost estimation. Like many of the BIM guides in the Northern European countries, all Korean BIM guides recommend that BIM models be submitted in the Industry Foundation Classes (IFC) format. This study will contribute as a basis for developing the direction of the next series of Korean BIM guides.
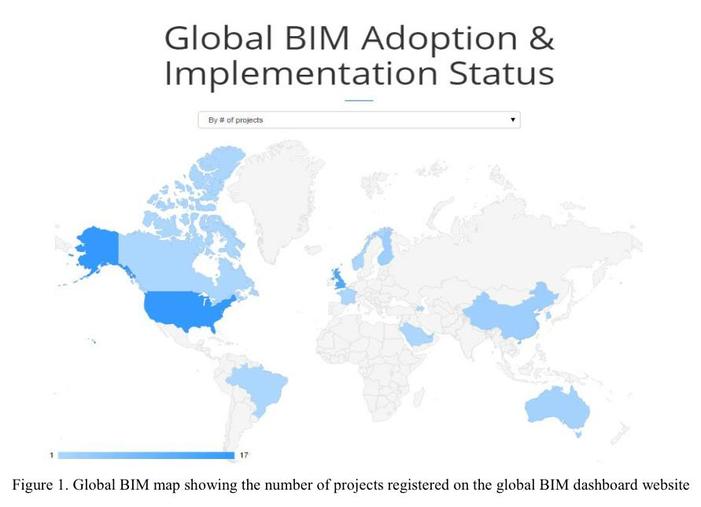
This paper introduces the global building information modeling (BIM) dashboard project, a three-year government-funded project in South Korea. The global BIM dashboard is an online system that collects and provides real-time information about the status of BIM adoption and implementation in each participating country as well as BIM projects across the globe. The most commonly asked questions about BIM usually involve the status of BIM adoption and implementation in a specific region, namely whether a particular type of BIM project is ongoing in a region or which companies are most active in a specific region. The global BIM dashboard aims to answer these questions. The global BIM dashboard uses slim BIM charts for visual and quantitative representation of the BIM adoption and implementation levels in each country. It employs the four most commonly used indices: BIM adoption rate, depth of BIM implementation, level of BIM proficiency, and years using BIM. In addition, the number of BIM projects and the number of BIM users in a region are used to represent the BIM implementation status of that particular region. The global status of BIM adoption and implementation is visually represented using what we call the global BIM map—a color-coded global map divided by region and implementation status. BIM project information is collected and stored in a BIM casebase (database) using a project information classification based on the information classification for best practice projects. The BIM project information stored in the global BIM dashboard database is also used to automatically generate BIM rankings.

When starting a new project, generally similar existing projet are searched. As Building Modeling Information(BIM) has short history and experience, the dependence on similar project is high. Small and medium sized design companies are depending on website search tool for information of BIM project besides companies maintaining the Database(DB) from lots of project experience. However, the information level and contents provided by websites differ drastically from each other which makes it difficult to utilize the information and apply cases. Furthermore, the different classification system of the sites makes the situation even worse. Therefore, we collected and analyzed over 100 BIM cases from 18 global websites, to develop a system for BIM case application. Result showed that over 90% of our subject pool provided basic information including the construction type, characteristics of the client (public/ private), location of the project, and detailed information such as primary usage. Moreover, the reasons for applying BIM where to solve problems of geometric design, building system like MEP and construction. Furthermore, there was a contrast between cases conducted only within Korea and cases conducted with other countries. While there was almost always helpful information regarding the administrative steps for Korean BIM cases, there was close to no information for projects carried out outside of Korea. These results could contribute to verifying the trend of information provision of the websites for BIM projects data, and this is believed to be helpful for developing an application system for BIM cases which have an organized information provision system and level as well as for bench marking.
This paper aims to identify patterns in users’ requests for facility management (FM) services in higher education facilities. We analyzed data collected from 309 service request forms, made available via a department office and an enterprise resource planning system, at a private university in Seoul between May 2009 and February 2015. We found that the number of user requests were the highest in September and October. Requests for electronic and communication (E/C) services outnumbered those for architectural services and mechanical and plumbing (M/P) services. Repair requests for doors and windows were the most common under architectural services; repairs for air-conditioners and radiators were the most commonly under M/P services; and installation of electrical outlets, telephone wires, and internet services were the most sought-after E/C services. Maintenance requests were received every three months, while repair requests were received every six or seven months.
This paper conducted a network analysis of two BIM project cases — one a large-sized project and the other a small-sized project — using the Ucinet6 software program, aiming to identify BIM project success factors for collaboration according to organization size. The results show that the organization size and the knowledge of BIM experts have no influence on project performance or on the improvement of a network. Rather, as the centrality of a network increased and the closeness of participants decreased, construction was delayed. However, even if the centrality increased, the project was well performed when the possibility of structural holes was lower and density was higher.
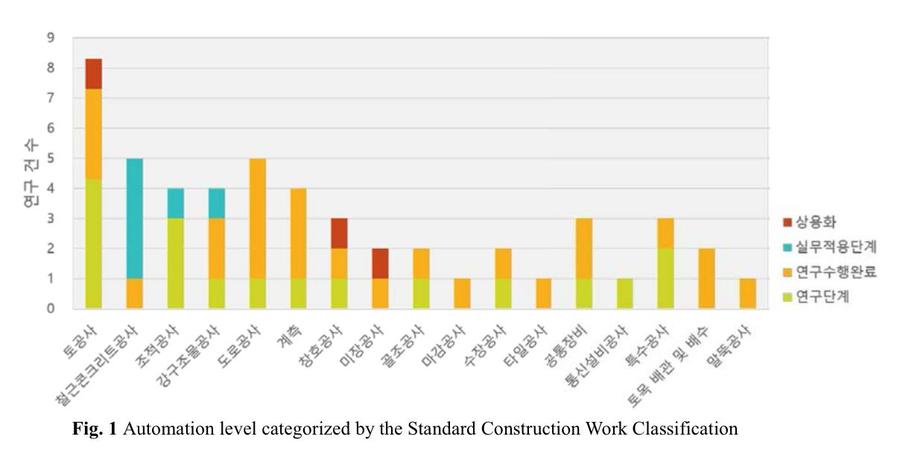
This study surveys the construction robots developed for the past twenty years through literature review and web search. In these two decades, many studies have been conducted in construction automation, and recently, three-dimensional (3D) printing and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have become new trends. We collected and analyzed 54 cases conducted in the last twenty years in order to technology and development trends. We classified the construction robot research according to the standard construction work classification. In addition, we evaluated development level through comprehensive of four levels: research stage, research completion stage, practical application stage, and commercialization stage. The analyzed results show that only a few projects succeed in commercialization or practical application limited to only three work categories. Eight counts of earth excavators, four counts of reinforced concrete construction, and four counts of steel structure construction work. Moreover, all research cases, which we collected, focused only on the development of the individual robots. In conclusion, the requirements for the development of integrated control systems or coordination systems are encouraged to automation research in terms of leading successful cases. Key Words: Construction robot, Automation
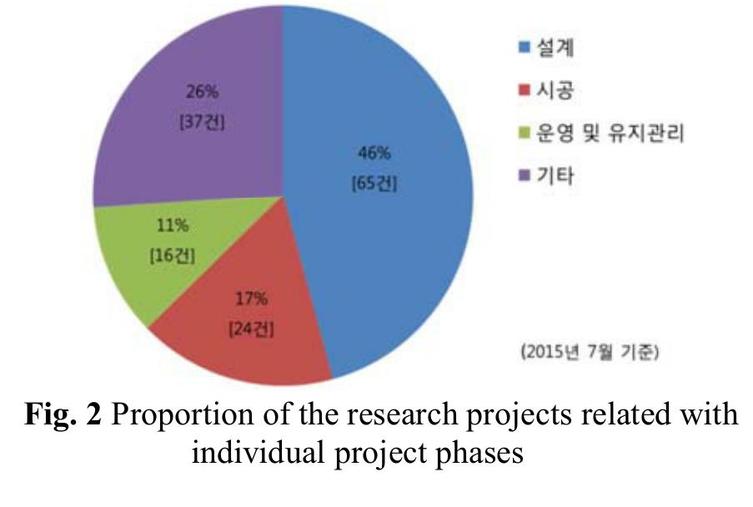
This study surveys national research projects in South Korea from 2004 to 2015 related to building information modeling (BIM) and analyzed the trend by project phase. For the analysis, we have collected 136 BIM-related research projects in South Korea from the National science & Technology Information Service (NTIS) website, which provides information about national research and development projects. The research projects were categorized by construction project phase. A keyword analysis has been conducted to understand detailed BIM research areas. The phase analysis shows that over 60 percent of the BIM-related research projects in South Korea focus mainly on the design phase. The keyword analysis shows that a majority of the BIM research projects have been conducted in the areas of ‘decision making support’, ‘automated quality assessment’.
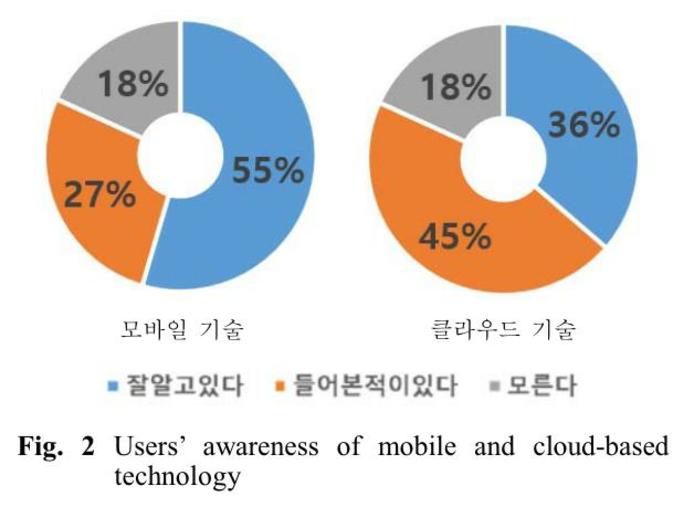
This study aimed to survey users’ awareness of mobile- and cloud-based technology for the Highway Bridge Management System, to improve work efficiency and reduce maintenance expense for the Korea Expressway Corporation (EX). It also suggests ways to activate the implementation of the technology. More civil appeals have been reported because of the inconvenience of using old infrastructure, and maintenance costs have increased. Many concerns are also voiced about safety issues; thus, maintenance performance has become more important. Since the EX was partially privatized, it has provided and maintained major infrastructure such as highways, tunnels, and bridges; it seeks ways to improve work efficiency, and the increased maintenance of old infrastructure has become a burden. The EX has started developing mobile- and cloud-based technology to solve these problems. This study surveyed EX employees regarding their awareness of this technology. The mobile-based technology is more readily recognized by respondents than the cloudbased technology, but the survey showed that both technologies have high feasibility. The respondents mentioned that continuous training, server security, validation of existing data, and intentions to improve processes are needed to implement the technology.
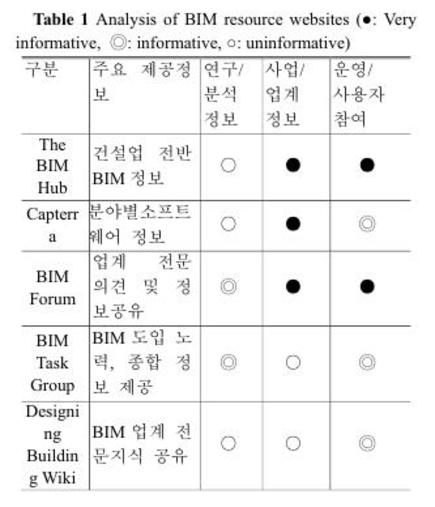
This study surveys and analyzes informational websites for building information modeling (BIM) projects. Designers often look for existing projects similar to their own projects when they begin new projects. Benchmarking similar projects is tactically important, especially for BIM projects, because BIM is new to many designers. Small and middle-sized design firms, which do not have much data, rely heavily on web searches to acquire this type of benchmark project information. This study surveys and reviews websites that provide BIM project information. The survey shows that the currently available BIM project websites simply list project information or BIM-related news and articles and do not provide analytic (statistical) data or indepth project reviews that could benefit designers or managers in establishing their design directions or strategies.
The purpose of this study is to specify the information required by a web-based BIM case database system to develop an information delivery manual (IDM) for a BIM case database system to provide a clear definition. We analyzed the BIM project information required by the case database system by deploying ISO 29481-1 Part 1, a methodology for specifying an Information Delivery Manual (IDM). The methodology from the latest version of the ISO 29481-Part 1 mandates that an IDM should comprise at least: 1) an interaction map/transaction map; 2) a process map (PM); and 3) one or more exchange requirements (ERs). We defined an interaction map, a PM, and ERs for the BIM case database system throughout the BIM process using this approach. As a result, in order to support the BIM case database system development process, we could identify the relevant roles involved and transactions between roles, define the flow of activities from relevant roles within the process, and extract ERs that need to be exchanged.
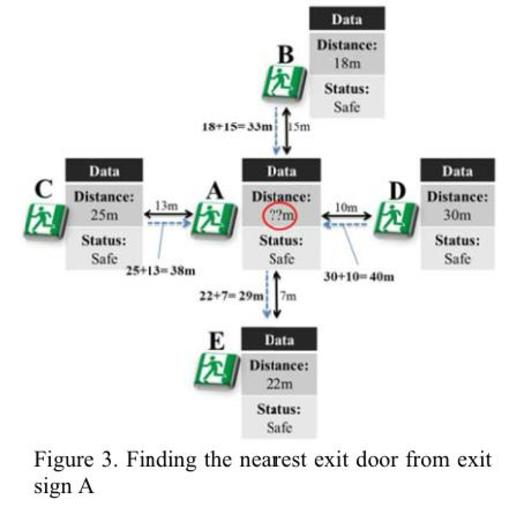
A smart exit-sign system is an exit-sign system that can proactively orient the direction of an exit sign toward the shortest safe path in fire situations. In a previous study, an automated direction setting algorithm for a smart exit sign was proposed that assumed the exit signs were controlled by the main central server. This study proposes a new direction setting algorithm for a server-independent smart exit-sign system. The server-independent direction setting algorithm (SIDSA) can be divided into four main steps once the smart exit-sign system is installed and initialized: (1) update of the fire-status information detected by a sensor; (2) sharing of the fire-status information with neighboring exit-sign modules; (3) update of the shortest-path (distance) information according to the fire situation; (4) update of the direction on the display board. SIDSA has been validated through multiple simulations.

This paper introduces an effort to develop a building information modeling (BIM) knowledge base system that includes various BIM-related statistics and best practices. This study is currently being conducted as part of a US$5,800,000 national research and development project in South Korea to build open BIM-based building design standards and information technology (IT) infrastructure to improve design and construction efficiencies. The project consists of three phases and is currently in the first phase. The main goals of our study within this project are to develop a standardized format for the collection of BIM project cases and BIM key performance indicators (KPIs) so that data can be sustainably collected and easily searched for via the Web. The indexes are to be used to rapidly and intuitively show the status of national- and international-level BIM projects. The first version of the standardized format for collecting BIM project cases has been developed by analyzing existing BIM projects. The format has been disseminated to several contractors, architects, and BIM consultants to ascertain the completeness and usefulness of the format. A web system, which we refer to as the “global BIM dashboard,” is also being developed. It will allow national and eventually international BIM users, researchers, and BIM-related decision makers to rapidly and intuitively acquire BIM information, including BIM statistics, BIM KPIs, and the lessons learned from best practices. The first phase of the BIM knowledge base project will not include a reasoning algorithm. As the system and data grow, however, we plan to add more intelligence to the system so that users can more easily and rapidly access the data they would like to acquire.
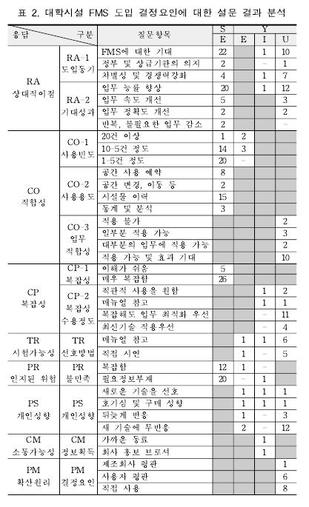
The aim of this research was to identify the factors influencing the adoption of facility management system (FMS) in higher education facilities from the perspective of innovation resistance. We conducted surveys at two universities: one utilizes FMS, the other is planning to adopt it. Respondents were classified into three groups depending on their experiences. The respondents favored business compatibility over ease of use. Abundant information directly influenced FMS satisfaction. We identified the respondents’ willingness and tendency to adopt innovation technology.
Currently, the number of BIM projects and related studies have been increasing, however, the data collection and analysis studies have tend to be conducted independently and sporadically. So, it is difficult to compare the factors included in such resources with each other. Moreover, the inconsistency between indices and/or between criteria make it hard to construct an integrated database. In this study, various indices for performance measurement and best practice using in the field of project management (PM) as well as in the field of BIM project case studies were investigated and analyzed. Based on the analyzed results, we proposed a ‘Classification template and a standard collection form of BIM cases’ which could be applicable as references about similar tasks, as the feasibility analysis on the use of BIM during the early stage of project management. This study was conducted as a preceding research for the development of the BIM case database.
A method has been developed for automatically generating a phylogenetic tree of architectural plans based on graph theory, according to the properties of the plans and the timing of their appearance. A phylogenetic tree of architectural plans is a branching diagram that shows transitions of the architectural plans by period. In previous studies, researchers analyzed structural similarities and differences between architectural plans by comparing one floor plan to another. Such manual classification processes sometimes result in inconsistent classifications and are inefficient, especially when a large number of plans are compared and analyzed. Herein a new algorithmic approach is proposed, termed the time-based joining (TBJ) method, for quantitatively evaluating structural similarities between architectural plans and creating a phylogenetic tree of the analyzed architectural plans. The validity and consistency of the TBJ method’s results were tested by generating a phylogenetic tree of 422 collective housing unit plans in Seoul, South Korea, constructed from 1970 to 2010.
null

Existing Building Information Modeling (BIM) evaluation methods focus on the maturity of BIM rather than how successful a project is because of BIM implementation. This study proposes a goal-driven method for sustainable evaluation of a BIM project's success level on the premise that a project's success cannot be evaluated without identifying its goals.We first identify candidateKey Performance Indicators (KPIs) required for measuring the success levels of goals and those that can be derived using certain types of BIM uses. Then, the final KPIs are selected by reevaluating the candidate KPIs with respect to collectability, measurability, and comparability. The final step involves identifying and developing processes and forms for collecting data while conducting daily tasks.The proposed method has been applied to two projects.The projects showed the possibility of using the goal-driven method as an effective means of assessing the BIM project's success level.
Previous studies on automated fire-egress guidance systems have focused on providing the shortest path information from a specific person at a certain point to the closest exit mostly using a mobile device. This study aims to develop a Smart Exit Sign system that can detect dangerous areas in real time and direct evacuees to the shortest safe evacuation path by dynamically changing the direction signs to the safe egress. The challenge was to provide the shortest safe egress to any evacuees at any point. We have developed a sensor network and algorithm that could exclude unsafe paths and calculate the shortest safe path from multiple starting points to multiple exit points based on Dijkstra’s algorithm—the most commonly used algorithm for finding the shortest path. The validity of the proposed system was tested through simulations of test cases.
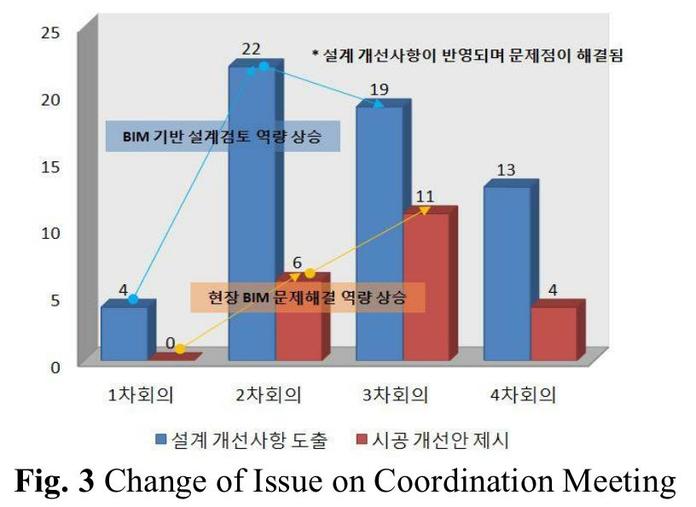
Lean construction came from lean manufacturing. The basic goal of lean manufacturing is to eliminate muda, mura and muri. Nowadays BIM is changing construction site and management methods. And BIM based MEP coordination is considered as essential process for complex building which has many kinds of MEP elements. Many researchers indicate usage of BIM with lean concept can make synergy. This paper focus on development of BIM and lean based process innovation for MEP coordination. Through case study, some changes which was made by BIM are presented. Owner, CM, G.C and subcontractor could be collaborated by coordination meeting. And stakeholders are quickly accustomed to BIM environment.

null
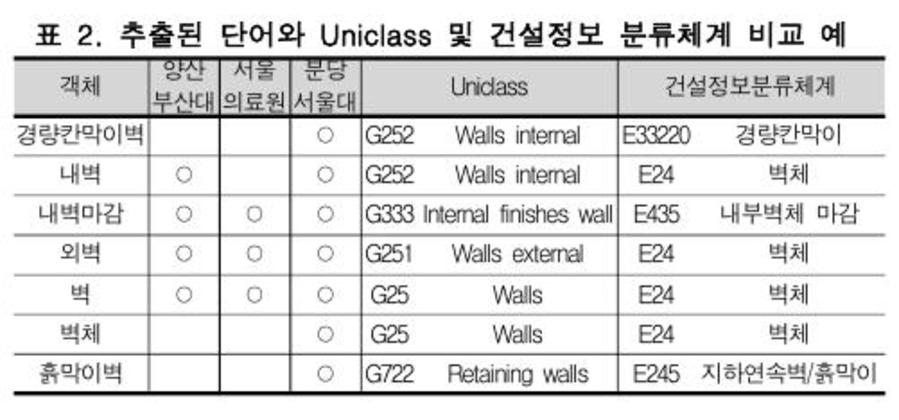
null

null
null
The purpose of this paper is to propose a subset of business process modeling notation (BPMN) to improve the information delivery manual (IDM) development process. The information delivery manual (IDM) (ISO/DIS 29481-1, 2008) currently recommends using BPMN for describing process maps (PM). The BPMN model is a generic graphical representation standard for specifying business processes targeted at a wide range of industry sectors. In its present form, it includes an unwieldy number of symbols and rules (currently over 160 notations) in order to cover a wide range of uses. Consequently, many process models use only a small number of these notations. This study collected and analyzed BPMN notations used in 54 processes in 14 existing PMs developed by various organizations. It was found that only 36 notations are used in IDM development. Based on these 36 notations, a subset of BPMN for IDM development is proposed.
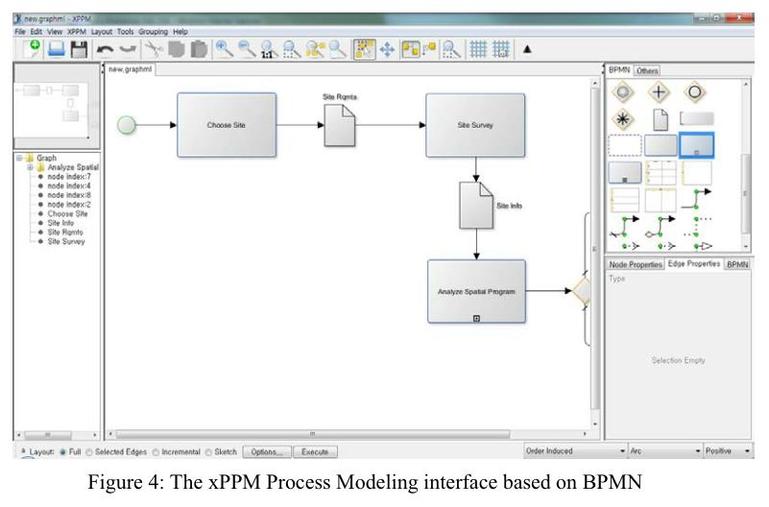
This paper introduces a new “extended Process to Product Modeling (xPPM)” for efficient Information Delivery Manual (IDM) development. The current IDM development typically uses Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN) to represent a Process Map (PM). However, the resultant Process Map is isolated from the development of Exchange Requirements (ERs) and Functional Parts (FPs). ERs and FPs specify the information required when information is exchanged between different activities. The extended Process to Product Modeling (xPPM) method is proposed to provide a tight connection between PMs, ERs, and FPs. The theoretical framework is based on the Georgia Tech Process to Product Modeling. An xPPM tool is being developed in Java to support several IDM development efforts in South Korea.
This paper proposes a new quantitative sight area rate analysis algorithm based on the “sight area rate” of a stage from the audience seats in the theater. The current sightline analysis checks whether a sightline from a seat is blocked by front-row seats from a cross-sectional and plane view at the center of a theater. Although this method is a commonly accepted practice, it is not uncommon to find people who have their view blocked by the front-row seats in a theater. The newly proposed algorithm analyzes and quantifies the actual view area from each seat. The sight area rate is the actual sight area divided by the total unblocked sight area (or screen area) from each seat. The proposed algorithm provides quantitative results which make it easier to design a theater. Since the proposed algorithm can derive sight area at the early design stage of theater utilizing a set of plan and cross section drawings, it can be applied to analyze view of audiences though a 3D BIM model is not fully developed.
This research proposed two algorithms, which may reduce the size of IFC files, by extracting only the information requested by each project participant. The extraction algorithms could help to increase the productivity related to the exchange project information between them. One of the algorithms extracted entities related to the required building elements and instances recursively explain these entities from an IFC file. The other one eliminated the unnecessary entities and instances from the file. This research compared the IFC file extracted by the two algorithms to identify the more efficient algorithm. The extraction algorithm was more efficient than the elimination algorithm because the size of an IFC file through the extraction algorithm was almost 1/11 of the file size when the elimination algorithm was used. The identified algorithm could reduce the file size to 8.7% of the original size when extracting information related to the slab element in an IFC file.
The purpose of this paper is to identify consideration factors for successful building information modeling (BIM) projects. Such factors include critical success factors, criteria for determining BIM software, BIM function, and BIM pilot projects. Each of these was evaluated by using a survey of 61 international BIM experts. The survey was based on literature reviews and face-to-face interviews. This paper presents the results of the survey and identifies important consideration factors for BIM projects.
The rotation-controllable tower-crane book block is the automated construction equipment able to rotate a steel beam in a horizontal direction. This paper estimates the economic impact of safety improvement when this equipment is deployed at construction fields. An analysis on industrial accidents shows that accidents related to steel structures make up 4.78% of total building construction accidents. This paper employed real discount rate and present worth. For this, the economic benefits were analyzed by including a reduction in the accident rate compared wuth menufacturing costs. The cost-benefit ratio was 1.142, demonstrating the economic feasibility of the equipment. In addition, sensitivity and qualitative benefits analyses were conducted.
This study suggests a new spatial network midels (SNMs), called the space-connector model, for improving the representation of the relations between spaces. Previous models had shortcomings of not being able to express the differences in the spatial connection relations between spaces: e.g., the differences in the type and size of openings and as the differences caused by whether a wall is solid or transparent. A new notation for representing these differences is proposed.
Many IFC servers, based on RDB systems, suffer from poor processing speed and performance. We suggest that an ORDB, which is based on a concept similar to EXPRESS, is a suitable alternative database management system (DBMS). This paper reports the results of a preliminary performance evaluation between an object-relational database (ORDB)-based IFC server and a relational database (RDB)-based IFC server by using the BUCKY benchmark method. The results showed that an ORDB-based IFC server was faster than an RDB-based IFC server. Since we have not yet conducted the full-model test, this result has not been confirmed. However, the benchmark test showed the potential for improvement in the performance of the IFC server. More reliable results should be observed through a full-model test in future work.
Formwork layout is perceived as important due to its strong tie to site works. But, most formwork is done manually and influenced by worker’s skill and thus, a lot of construction errors occur. The introduction of BIM (Building Information Modeling) enables acquiring more precise information on the building shape, dimension, structure, etc. than 2D-based drawings and thus, the increased productivity, such as reduction of workload and work times, and the economic efficiency, such as reduction of formwork types and form dimensions with the consideration of constructability, are expected. This study reviewed the previous studies and formwork layout systems to derive this study’s differentiations and factors to be first considered for formwork planning were derived by analyzing priorities against consideration factors. Last, a flow chart and algorithm were developed to apply the derived factors to the formwork layout module.

null

null

null

null

건설 생애 전 주기 중에서 기획단계의 지반 조사로 시작되는 흙막이 공법의 선정은 잘못 선정될 경우 해당 프로젝트의 공사비와 공기에 끼치는 영향이 매우 크다. 그렇기 때문에 공법 선정의 요인 및 프로세스에 관련된 연구가 많이 발표되었지만 일반인들의 활용이 어려워 실용화되지 못하고 있다. 본 연구에서는 본 연구의 선행연구에서 개발한 흙막이 공법 선정 프로세스에 기반하여 웹 기반 의사결정 지원시스템을 개발하였다. ASP.NET을 이용하여 사용자들의 접근성을 높이고 자료의 보완 및 수정이 용이한 웹 기반 시스템인 Dr. Underground로 발전시켰다. 이 의사결정 지원 시스템은 일반인들이 쉽게 접근하여 건축물 기본 요구 사항과 대지 조건, 인접 대지 조건을 입력하면, 해당 프로젝트에 적절한 흙막이 공법을 선정해주고 그에 대한 상세 정보를 제공해준다. A retaining wall system suitable for a construction project is selected on the basis of subsoil conditions. If the decision-maker selects an improper system, it has a negative effect on the cost and schedule of the construction project. There have been many studies related to the models and processes for selecting optimal retaining wall systems. However, engineers who are not familiar with formal analysis methods could not easily utilize the formal methods proposed by previous studies. . In order to overcome this problem, we developed a web-based decision support system called Dr. Underground, which is both physically and technically easily accessible by engineers. Dr. Underground was developed based on a selection method developed from a precedent research project. It was developed using a server-side web language ASP.NET and MS Access as a database. Decision-makers can input data about the building’s condition, construction site conditions and adjacent site conditions in this system. Based on the input data, Dr. Underground recommends an optimal retaining wall system for the inputted conditions and provides detail information on the system.

최근 건축물이 대형화, 복잡화 되면서 예기치 못한 상황에 대한 안전성 문제가 이슈화 되고 있다. 그러나 초대형 건물의 경우 규모가 커서 수작업으로 방재 및 안전성과 관련한 법규 검토에 시간이 많이 걸리고, 실수가 일어날 가능성도 높다. 이러한 문제로 한 조사에 따르면 건축 및 건설관련자-실무자의 83%가 자동법규검토 시스템이 필요하다고 응답하였다. 본 연구는 기존의 자동법규검토 시스템 및 연구현황을 살펴보고, 기존 BIM기술을 이용하여 국내 방재 및 피난 관련 법규를 자동으로 검토하기 위한 시스템개발 가능성을 검토하고자 한다. 이밖에 자동법규검토 시스템의 필요성과 그 기대효과를 분석하고 기존 연구사례를 통해, 국내 적용가능 여부를 검토하고, 지역적 특수성에 대한 문제점, 한계를 논의한다. 또 그러한 문제점들에 대한 해결책과 향후 발전방안을 제시한다. 본 연구에서는 피난관련 법규로 그 범위를 제한하였지만 앞으로 전체적인 법규 자동검토시스템이 구축되기 위해 필요한 노력과 작업에 대해 알아보고 연구해 나가야 할 것이다. Recently, the trend has been for buildings to become larger and more sophisticated, and this has created safety issues. Because the buildings are big it takes lots of time to check building codes related to anti-disaster and safety manually, and there is the high possibility of making mistakes. Due to these problems, according to a study, 83% of architecture and construction workers believe that an automated code-checking system is needed. This study researches past automated code checking systems and research activity, and using Building Information Model (BIM) technology, determines the feasibility of developing a system to automatically check domestic codes related to egress and anti-disaster. This paper describes the necessity of an automated building code checking system and expected effects. It then reports whether the methods used in previous studies can be deployed in domestic building code checking and discusses problems and limitations. It also suggests an alternative approach. Although this study covers limited codes related to egress, we need to find out what is needed for automatic general code checking system and do further studies for that.

지난 10여 년간 건설 분야에서 데이터 마이닝(data mining) 기법을 이용하여 실적 데이터의 패턴을 찾고 이를 바탕으로 다양한 예측 모델을 개발하려는 연구들이 다수 진행되어 왔다. 그러나 데이터 마이닝 기법의 경우, 일반적으로 수천 또는 수만 개의 데이터를 사용할 것을 추천하고 있으나, 건설 분야의 선행연구들을 살펴보면 데이터 마이닝에 사용된 데이터의 수가 최대 이백 개 표본 정도에 그치고 있다. 그 결과 데이터 마이닝 기법을 이용하여 선행연구의 방법 및 결과를 재현하려고 하여도 같은 결과를 얻기 힘들고, 아예 패턴추출이 힘들거나 도출된 패턴에 오류가 있는 경우도 있다. 본 연구는 소수의 표본수에 기초하여 보다 신뢰성 있는 공법선정 모델의 개발에 관한 대안적인 방법을 모색하고자 한다. 먼저 건설 분야에서 데이터 마이닝 기법을 활용한 연구의 범위에 대해 살펴보고, 특히 흙막이 공법선정 모델 구축에 관한 선행연구 고찰을 통해 소수의 데이터에 의존함에 따라 발생하는 문제점들을 알아보고, 이를 극복할 수 있는 방안에 대해 논의 하고자 한다. In the past decade, various data mining techniques have been used in construction engineering as a means to make informed decisions through the aid of useful knowledge discovered from historical data. Researchers in the construction domain are often confronted with a challenge to derive a meaningful conclusion with a limited sample of data. However, when the data size is small, the proposed results are often illogical. Even if the derived results are technically flawless, sometimes it is difficult to reproduce these results by using the same analysis method when a different set of data is used. This paper reviews some problems that stem from limited data size, and discusses several recommendations for dealing with these problems.

거대해지고 복잡해진 건설프로젝트에서 건설 생애주기 동안 필요한 모든 정보를 효과적으로 관리하기위한 BIM에 대한 관심이 증가하고 있다. BIM을 이용한 협업에서 정보의 교환과 공유는 이윤을 극대화할 수 있는 중요한 요소이다. IAI에서는 건설프로젝트의 모든 참여자가 사용할 수 있는 표준 파일포맷으로 STEP기반의 IFC모델을 제시하고 있고 현재 2x3버젼이 게시되어 있어서 이를 지원하는 BIM소프트웨어에서 IFC포맷으로 내보내거나 들여올 수 있다. 하지만 실험결과 IAI로부터 IFC호환성 인증을 받은 BIM소프트웨어들이라도 IFC포맷의 파일을 내보내거나 들여올 때 정보가 손실되거나 변형되는 오류가 발생하였다. BIM소프트웨어 사용자들은 정보공유를 위해 IFC파일을 사용했을 때 자신도 모르게 에러가 발생해서 프로젝트에 큰 손실을 입을 수도 있다. 본 연구에서는 호환성 검사에 대한 기존의 연구를 살펴본 후 IAI의 검사 과정을 조사하고 문제점을 도출한 후 문제점에 대한 해결방안을 제시하고자 한다. The Architecture, engineering, & construction (AEC) industry domains have grown more complex and larger. BIM is a digital representation of a building to facilitate the exchange and development of construction information integration and interoperability. Industry Foundation Classes (IFCs), under development by International Alliance for Interoperability (IAI), represent the part of buildings or elements of a process. IFC has been adopted as a central information repository in order to deliver integrated building information. Other BIM software could open the IFC file, recognize standard objects such as walls, window, and doors as building components. The IFC standard is generally agreed to be of high quality and is widely implemented in software. However, sometimes, information distortion or information loss occurrs during information exchang. The IAI Model Support Group (IAI-MSG) offers the opportunity to certify IFC-compliant applications based on a structuralized approach. However, IFC interoperability error also have occurred by using certificated tools. As project participants exchange BIM information by using BIM software they will need a reliable and efficient exchange of information. In this paper, previous interoperability tests were analyzed, and we propose a new concept in interoperability test.

null

null
In this paper, new filtering method for sensor registration is provided to estimate and correct error of registration parameters in multiple sensor environments. Sensor registration is based on filtering method to estimate registration parameters in multiple sensor environments. Accuracy of sensor registration can increase performance of data fusion method selected. Due to various error sources, the sensor registration has registration errors recognized as multiple objects even though multiple sensors are tracking one object. In order to estimate the error parameter, new nonlinear information filtering method is developed using minimum mean square error estimation. Instead of linearization of nonlinear function like an extended Kalman filter, information estimation through unscented prediction is used. The proposed method enables to reduce estimation error without a computation of the Jacobian matrix in case that measurement dimension is large. A computer simulation is carried out to evaluate the proposed filtering method with an extended Kalman filter.

It has been recognized that a system that facilitates efficient communication and interaction is critical in order to improve coordination between AEC project participants. Various research literatures show that migration of conventional AEC work processes, which have relied heavily on two-dimensional drawings, to more convergent processes that share a single common information source based on three-dimensional object-oriented data or BIM, can yield better outcomes and improve productivity. However, several problems made it very difficult to collaborate and share information between project participants. Some of the problems include legal liability issues, a reluctance to share inside information with others, maintenance of a master model, a dynamically changing organizational structure of a project group, and a collaboration-support system that can support these issues, etc. Therefore, the objective of this paper is to propose a conceptual scheme of a "session-based" collaboration environment, called Construction Project Life Cycle Management (CPLM). CPLM is a system intended to help project participants make better decisions and to facilitate coordination between various stakeholders in a project by providing virtual collaboration groups called "sessions" and methodology to support the open information policy between both horizontal and vertical organizations within those sessions. Additionally, this paper introduces a system to be developed using the proposed conceptual scheme of a session-based CPLM and its development plan.

As the land price in the downtown area increases, buildings are becoming bigger, deeper and higher. Consequently, the importance of underground construction has increased. Although construction engineers make every effort to complete underground construction without any problem, construction failures like landslides and the collapse of a retaining wall occur because of the uncertainty of the soil conditions as well as the unexpected risks of excavation work. In order to prevent potential excavation accidents, it is essential to understand the causes and impacts of such accidents. However, there are only a few examples of construction failures, which show the economic impact on accidents during excavation because of the sensibility of the information. This paper presents two cases of excavation accidents, which were investigated by construction insurance company. The compensation for the accidents paid by the insurance company was compared with the estimated costs calculated based on the estimation method for excavation accidents proposed by our previous study. The comparison results showed that the estimate calculated by our method was much less than the actual compensation because the estimate solely focused on the construction costs whereas the compensation included other external factors.

An IFC Server is a database management system that stores data complying with a standard data format, called IFC, and keeps track of data transactions, modifications, and deletions. It plays a role as an information hub for storing and sharing information between various parties involved in construction projects. There have been several efforts to develop an IFC Server, however, they suffered from slow performance and long transaction time due to a complex mapping process between IFC files and relational database structures. In this study, we aim to develop an IFC Server using an object-relational database system. Since IFC has an object-flavored data structure, we expect to have a simpler and faster mapping process from IFC to the IFC Server. This paper reviews existing studies and describes the overall framework of the OR-IFC Server.

대부분의 상용 데이터베이스 관리시스템은 관계형 데이터베이스 (relational database) 기술에 기반하고 있다. 그러나, 객체지향언어인 Express로 정의된 IFC(Industry Foundation Classes)를 일반적으로 많이 사용되는 관계형 데이터베이스로 매핑하려면 서로 구조가 달라 매핑과정이 매우 복잡해진다. 한편 IFC를 객체기반 데이터베이스(object-oriented database)나 객체관계형 데이터베이스 (object-oriented relational database)와 같은 객체기반의 데이터베이스로 매핑하게 되면 그 과정이 비교적 단순해지고, 많은 장점을 가질 수 있다. 본 연구에서는 장기적으로 IFC와 객체기술에 기반한 통합정보교환기술을 실용화하기 위하여 먼저 관계형, 객체지향형 데이터베이스의 개념에 대해 살펴보고, IFC를 객체관계형 데이터베이스로의 매핑 방법에 대하여 알아본다.

건축물 수명주기 동안 생성되는 정보를 통합관리하고 재활용하여 경제적 손실을 줄이고 이윤을 극대화하려는 과정을 Building Information Modeling (BIM)이라고 한다. 기존의 건설관리기법들과 비교하여 양질의 건물을 더 싸게 빠르게 지으려고 한다는 점에서 그 궁극적인 목적이 다르지 않지만, 기존의 기법들이 경영관리기법척인 측면에서 접근하였다면, BIM은 시스템적인 면에서 접근을 하고 있다는 데에 그 차이점이 있다. 본 논문은 BIM의 정의와 배경에 대해서 고찰하고, BIM을 위하여 필요한 핵심기술들의 현재와 미래에 대하여 논의하였다.

null

3D parametric modeling technology was first introduced about 15 years ago, but still only a few sectors in Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) have successfully adopted the technology in production. This paper reports the second phase of an early successful collaboration project between an industry sector, academia and a CAD vendor to develop an intelligent 3D parametric CAD system for the precast concrete industry in North America.

We review the transition now being undertaken from 2D drafting to 3D parametric modeling and the development of Building Information Modeling (BIM). We examine the functionality of BIM platforms, using an example from precast concrete structures. We formulate the development of parametric modeling of building systems from the context of SFB modeling and characterize most parametric modeling as function-form mapping, with optional behavior-driven detailing. We examine the implications of this kind of technology for future building software development and the future delivery of design expertise in building.

3D parametric modeling systems are now beginning to replace the age-old medium of drawings (whether manual or CAD) for compiling information for building design and construction. In order for users to efficiently develop building designs using 3D modeling, systems must incorporate both practice- and engineering-based parametric assembly modeling. Parametric assembly modeling lays out collections of objects at a time, and defines how the assemblies should automatically adjust themselves in response to any edits to the parameters that determine their lay out. Defining and implementing the specific practice- and engineering-based knowledge needed to support parametric modeling is an expensive and risky affair, especially when the market is not well educated or prepared for such a revolutionary product. This paper presents a case study for development of such a product for the North American precast concrete industry. The parametric modeling software was developed through collaboration between precast concrete producers, proposal winning software companies and a university advisory team. The case study outlines the issues of risk and their resolution, the need for strong collaboration among a diverse group of often competing industry players, and a strategy for educating the future users of such a system while at the same time utilizing their expertise to develop an outstanding product. This type of detail collaboration of industry experts, modeling experts and a high tech software company was shown to be an effective extended business organization to develop such an industry-based high-tech product.

The downstream production sectors of the construction industry are developing powerful parametric modeling design and engineering tools for fabrication modeling. This paper reports an effort by the North American precast concrete industry toward developing such tools. Some implications for architectural design and practice are outlined.

The information collected in the requirements analysis phase of data modeling must be accurate and consistent. Existing procedures, graphic languages and tools support mostly limited checks of syntactic consistency of diagrams. We introduce the logic and rules for dynamically checking and maintaining consistency in the information itself. The logic is implemented in GT PPM, a tool designed for capturing required information for medium- and large-scale organizational process and product modeling.

We explore the reasons why advanced information technology applications have not been adopted by the AEC industry. Within the industry, however, some sectors have made significant moves toward adoption of advanced IT. By examining these areas of success, we propose a framework for the incremental conversion of the AEC industry to fully incorporate advanced IT.

Thirteen detailed process models of precast producer companies’ engineering design, production and erection procedures have been prepared as part of an effort to re-engineer the information-dependent processes of precast design and production. Under the guidance of the research team, precast company experts each modeled their company’s processes using the custom-built ‘GT-PPM’ process-modeling tool. The tool allows modelers to define detailed information inputs and outputs for each process activity and produces models that are machine-readable. We present and discuss methods of comparison and extraction of common information items from the heterogeneous process models collected. We also discuss the advantages and difficulties encountered in using the Design Structure Matrix and other methods to analyze the models and to track the information flows through the activities. The project is ongoing: a second round of process modeling to capture the companies’ future processes, incorporating the envisaged software and data model, will begin once an upgraded version of the GT-PPM tool is completed.

We outline a new approach to process modeling in support of development of product data models. It is based on the definition of process models with far greater detail than have been used previously, and on the automated mapping of these models to product model schemas. A new process-modeling tool was developed for this purpose along with applications for structuring and analyzing the data collected with it. Examples are provided from the domain of precast concrete design and fabrication.

This paper discusses the possibility of using the GTPPM (Georgia Tech Process to Product Modeling) method, which was initially developed as a systematic approach to product modeling, as a method to generate IFC views or CIS/2 conformance classes. A view is a valid subset of a product model. The view generation method is discussed in the context of the IFC Information Delivery Manual (IDM).
A current research project within the North American Precast Concrete Industry aims to integrate information both within precast producer companies and between the companies and their suppliers, consultants, contractors, and clients. The first step was to undertake a process modeling study of the activities performed within each consortium company, so as to form the basis for the software specification and later data model. Existing process modeling methods and tools were considered . They do not support: · extraction of information used in the activities, · analytical validation of the process model and its information flows, · comparison of models collected from separate companies across an industry sector, · effective use of process model information in deriving a product model. To these ends, we developed an analytic modeling methodology, and implemented a new tool for its use.

-

-

-

-

-

-
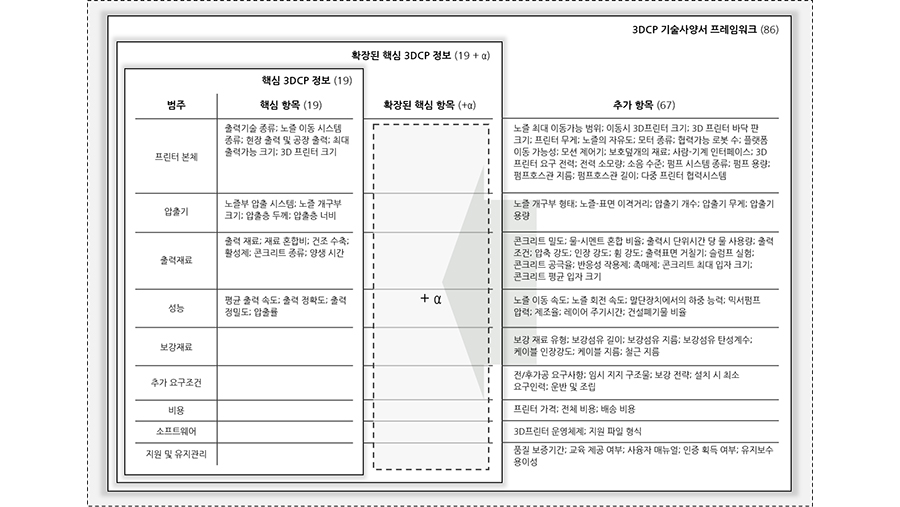
This paper proposes a technical specification framework for three-dimensional concrete printers (3DCP) through an analysis of 139 academic papers published from 1997 to 2020, 98 3DCPs identified from them, and three rounds of a Delphi survey with 22 3DCP experts. Despite the fast growth of the 3DCP research and market, there is no commonly acceptable technical specification framework for 3DCPs to comparatively analyze 3DCPs with diverse characteristics. Technical specifications for existing 3D printing systems, however, are unsuitable for 3DCPs because they do not include concrete properties, reinforcement information, and construction information. To derive a common technical specification framework for various 3DCP types, this study first developed a new classification system of 3DCPs and complied 1,604 technical specification items through systematic literature review and document analysis. The technical specification items were restructured into 9 groups and 90 items by removing identical terms, merging synonyms, and excluding outliers. A series of Delphi surveys was conducted to validate the definitions, classifications, and importance of the items with 3DCP experts in construction management, hardware, software, and concrete material. Statistical tools were employed to evaluate the consensus arrived by the expert panel. The results shows that the experts identified 86 items out of 90 items as significant 3DCP properties. Overall, the printing materials group was considered the most important, followed by extruder, mainframe, and the other groups. Based on the analysis results, this study proposes a 3DCP technical specification framework with the 19 core and 67 supplementary technical specification items in 9 groups. By deploying the core 3DCP information, existing technical specifications of the major 3DCPs were comparatively anaylzed. In consequence, it enables to analyze more balanced than the comparative analysis in existing studies by including six groups of items, and it contains key information that experts in each field consider important. The findings could be a basis for developing standards of 3DCP technical specification framework. In addition, it can be used as references and guidelines for 3DCP developers to write technical specification or for 3DCP users to make comparative analysis and decision making. Nevertheless, the limitation of this study are that current 3DCP technology does not have enough cases worldwide applied to actual construction projects, thereby limiting relevant experts and knowledge. In the future, when 3DCP technology becomes more commercialized and skiiled professionals are sufficient, its usefulness in the actual projects will be validated.

-

-
According to the population census of 2016, apartment housing makes up 60.1% of all housing types. One of the most pressing problems among apartment tenants is defects in the apartments where they live. The existing research on housing defects is focused on domestic rather than international studies. The existing studies on apartment defects have focused on the types of defects and factors for improving them. The research related to defect type classifies the defects by construction work or symptom. These defect studies mainly analyze whether defects are related to factors such as area, type of plane, number of exposed surfaces, floors, shape of building, and structure. However, existing studies lack systematic statistical analysis, so they have lower reliability than desired. In addition, these studies are limited by the lack of a uniform defect classification system. The purpose of this study is to construct a defect big data system, enable information to be recycled, and re-verify the existing defect studies by analyzing defect occurrences by apartment characteristics. In order to overcome the limitations of previous studies, this study examined data of 30,000 defects in 8 apartment buildings in South Korea from 2002 to 2010. This study organized a defect classification system, which had not been unified in the previous studies, and constructed a defect big data system. Using this constructed defect big data, we re-examined the existing research results and derived the factors to be considered for each apartment characteristic. Our results will be helpful for contractors to prevent and manage defects in the future by examining the defect big data. The reasons for re-verification of the existing research results are as follows. 1) The existing hypotheses are considered to be important for design, construction management, and apartment maintenance. 2) It is necessary to secure reliability through re-verification using ANOVA tests, t-tests, etc., because the existing data analysis is limited by its reliance on descriptive statistics. 3) Based on the results of the existing research, it is necessary to draw out the factors for careful management of defects. 4) Apartment design technology changes with time, so it is still necessary to revalidate the previous research results. This study re-examined the hypotheses of previous studies on whether apartment characteristics affect defects through the following hypotheses. H1: Larger areas will have a greater frequency of defects. H2: The complexity of the floorplan shape will increase the frequency of defects. H3: Complex planes (mass overlap type) will have fewer defects as time passes. H4: A greater number of exposed surfaces will cause a greater number of moisture-related defects. H5: As time passes, the correlation between moisture-related defects and the number of exposed surfaces will decrease. H6: The rate of defects will differ for each floor section (low, middle, high). H7: The more complicated the shape of the building, the higher the defect rate will be. H8: The tower type will have fewer defects as time passes. H9: The tower type will have more moisture-related defects than the other village arrangement types. H10: Apartments with SRC and RC structures will have different defects. H11: In RC apartments, defects will decrease with time. As a result of the defect big data hypothesis testing, the frequency of defects was only found to have a high correlation with the area (“Number of defects/Number of households/Number of rooms”: r = 0.690, n = 29, p = 0.000), plan type (“Number of defects/Number of households/Number of rooms”: r = 0.609, n = 17, p = 0.010, “Number of defects/Number of households/Area”: r = 0.635, n = 17, p = 0.006), and the shape of the building (“Number of defects/Number of households/Number of rooms”: r = 0.427, n = 1805, p = 0.000, “Number of defects/Number of households/Area”: r = 0.361, n = 1805, p = 0.000). The SRC structure was about twice as likely to have defects as the RC structure. The number of exposed surfaces and the floor type were not correlated with the frequency of defects. The results for H1, H2, H7, H9, and H10 were statistically significant, and hypotheses H3, H4, H5, H6, and H8 were rejected. This study verifies the results of defect occurrence according to apartment characteristics through big data analysis and suggests defect management as a center of defects in each apartment characteristic. In addition, it is meaningful that the study has solved the statistical reliability problem of previous studies and constructed a defect big data system. This study has contributed to identifying the factors (floorplan, tower type) that affect the occurrence of defects. The study also found that attention should be paid to shape-related characteristics in the design stage. Also, through the analysis of time, it was revealed that defects must be prevented from the design phase or steadily managed rather than solved through the development of technology. Acknowledgments This work was supported by “Human Resources Program in Energy Technology” of the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning (KETEP), granted financial resource from the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy, Republic of Korea. (No.20174010201320)
With the global trend of BIM applications shifting from technical development to practical adoption and domestic policy to adopt BIM, government facilities and companies in the architecture, engineering, and construction industries are eager to learn the proper way to use BIM from case studies. However, hands-on workers, such as architects and construction managers, find it difficult to collect case studies of BIM-applied construction projects (BIM projects). Despite the presence of various websites (e.g., Global BIM Dashboard, the BIM Hub, BIM+, and AECbytes) and literature (e.g., The BIM Handbook, The BIM magazine, and journal papers) that offer case studies of BIM projects, it is hard to find structured information, as case studies are scattered everywhere and described in natural language. Applying the text-classification method, a subcategory of text mining, can help solve this problem. But when we directly apply the text-classification method to the construction field, it creates other problems regarding BIM-related documents, because optimization of the method is required. The purpose of this study is to develop a BIM document ) categorization method for BIM use. The BIM use proposed in the BIM Project Execution Planning Guide v2.1 was used as a classification category, and text classification methods were applied for categorization algorithms. Also, a web-based information system was developed to update and manage machine learning algorithms. More specifically, the study answered the following questions: (1)How can we manage multi-word features, numbers, punctuation, and stop words when we generate a local dictionary for text preprocessing of BIM documents? (2)What are the machine learning algorithms and algorithm variables that show the best performance in the text classification of BIM documents? (3)How can we maintain optimized text-classification methods if the corpus is continuously changed by adding new raw data? In this study, 240 BIM documents written in English were collected from BIM-related websites and literature. Each BIM document was labeled 1 (yes) or 0 (no) in regard to 22 items related to the presence of BIM-related description and 21 BIM uses to validate the performance of machine learning algorithms. The Porter stemmer was used for stemming. Features that showed the same order 2–5 times repeatedly, such as “Building Information Modeling,” were defined as multi-word features. Also, the rules to handle numbers and punctuation shown in features like 3D, 3-D, and quantity take-off were defined. To reduce the amount of calculation for text classification of BIM documents, 21 BIM-use items were tested after the presence of BIM-related description was tested. Feature weighting, feature selection, and the number of features were used as variables for supervised learning. For unsupervised learning, the document-segmentation method, feature selection, a dimensionality-reduction parameter, iteration of estimation, the number of topics, the width of the word window, the minimum word count, and similarity thresholds were used as variables to estimate the performance of each algorithm. The performance of unsupervised learning algorithms was tested by comparing the cosine similarity between the definitions of each BIM use described in BIM Project Execution Planning v2.1 and testing the document with thresholds. Precision, recall, and F1 score were estimated to validate the performance of machine learning algorithms. In the study, support vector machine (SVM) with ¬term-frequency (TF), chi-squared statistics, and 60% of the total features (3,171 features) showed the best performance for the classification of the presence of BIM-related description. The result was precision: 80.26%; recall: 82.99%; and F1 score: 81.61%. The unsupervised learning algorithm for the 10 BIM use items that have more than 10 samples showed the following F1 scores: existing conditions modeling: 84.52%; cost estimation: 85.71%; phase planning: 77.81%; design reviews: 85.02%; design authoring: 84.98%; engineering analysis: 84.57%; 3D coordination: 82.99%; digital fabrication: 79.10%; record model: 79.76%; maintenance scheduling: 78.53%. Each test extracted the best variable combination for the algorithms. The average F1 score of the unsupervised learning algorithms was 82.30%, and the unsupervised learning was better than supervised learning. The web-based information system to maintain optimized algorithms was constructed based on the study’s results. In conclusion, text classification applied to construction will make it possible to collect tacit knowledge more efficiently thanks to reducing the time required to find the proper documents that contain the required information and allow workers to focus on their own interests. Also, the results of this study provide a chance to challenge the tracking the BIM-adoption trend and learn how to use BIM by categorizing a large number of BIM documents automatically.
OH, H. (2016). The development and reliability validation of serverless smart exit sign system using a wireless sensor network. Seoul, Yonsei University. Master: 1-93. A smart exit sign system is an evacuation guidance system that dynamically changes the directions of the signs to indicate the shortest safe evacuation paths. A serverless smart exit sign is a smart exit sign that communicates data between the exit sign nodes using a wireless sensor network without a central server. When a fire breaks out, evacuees are more likely to rely on exit signs when they are in a venue they do not know well than when they are in a familiar place. Traditional exit signs show fixed direction signs to the nearest exit; however, this can lead evacuees to areas of greater danger if the fire has spread. To solve this problem, several researchers have proposed smart exit sign systems. Nevertheless, most of these studies have focused on the development of algorithms to find the shortest safe path to an exit based on the assumption that a central server exists. Some researchers have proposed smart exit sign systems using smartphones or portable appliances; however, these systems cannot guide evacuees if they are not carrying the required equipment. Serverless smart exit sign systems have several advantages over the earlier server-dependent smart exit sign systems. First, serverless smart exit sign systems are more reliable than server-dependent ones because the entire server-dependent system fails if the central server stops working or any line between the server and the individual exit sign nodes is disconnected due to a fire, physical damage, or other reasons. On the other hand, exit sign nodes in serverless systems are not reliant on the status of the server because they do not use a server at all and can still communicate with neighboring nodes even if some nodes are damaged. The second advantage is that a serverless smart exit sign can be installed in an existing building without complex wiring work, whereas a server-dependent smart exit sign system requires complex and expensive wiring. Thus far, a few groups of researchers have independently developed serverless smart exit sign systems; however, they have focused only on the development of algorithms for serverless smart exit sign systems and have not considered the hardware aspects of serverless smart exit sign systems. Thus, the proposed systems have not been validated in terms of reliability, which is a key requirement for smart exit sign systems. By reliability, we mean the extent to which the system stably and consistently operates under various internal and external conditions. For example, doors and walls that could potentially deteriorate network communication are considered external factors, while the specifications of the network modules such as network packet size are deemed internal factors. Reliability is an important requirement for any emergency evacuation system, including serverless smart exit sign systems, to prevent system failure. The reliability of wireless communication (networking) in particular is key to the successful operation of a serverless smart exit sign system because, if individual exit sign units cannot send and receive data reliably, the entire system may malfunction. In this sense, this paper focuses on the development and reliability validation of a serverless smart exit sign system with due consideration of various potential interference factors. The limitations of previous smart exit sign systems were investigated via a literature review, and an applicable network structure was developed for a serverless smart exit sign system. In addition, the factors influencing the network performance of serverless smart exit sign systems were ascertained. The identified factors then were analyzed in terms of data transmission reliability and network reliability by conducting experiments using a hardware prototype. When considering data transmission reliability, the results of our experiment showed that a 15-millisecond transmission delay and five times the packet re-transmission redundancy were required. In terms of network reliability, we determined that node installation intervals of 8 meters and no blocking concrete walls were needed for the serverless smart exit sign system. We developed a set of requirements for the serverless smart exit sign system and conducted a full-scale simulation to test the system’s operational stability. The simulation results showed that the operational speed of the developed system was stable when determining the shortest and safest exit path, regardless of the detected location of the fire. To determine the commercialization of the proposed system, we interviewed experts to discuss further steps that would need to be taken. According to their feedback, it is highly probable that the serverless smart exit sign system could be commercialized; however, more validation tests need to be conducted. One of the experts pointed out that the serverless smart exit sign system would need to be constructed using a hybrid network of wired and wireless connectivity to obtain commercial approval from the government. A hybrid network and operational scenario is thus being investigated for the developed serverless smart exit sign system. Another expert proposed that a back-up appliance configuration be considered in the event of fire detection sensor and module unit failure. Accordingly, the more validation testing will need to be carried out as the next step. Even though additional research is needed to refine the serverless smart exit sign system, this study makes a few contributions to the current literature. The reliability of the developed serverless smart exit sign system was verified through experimentation. Furthermore, the system was evaluated via expert interviews to fill the gap in the knowledge between previous conceptual studies and practical system development.
JEONG, W. (2016). An analysis of the key indices for accessing levels of BIM adoption and implementation and their application methods. Seoul, Yonsei University. Master: 1-57. There have been proactive movements within many governments around the world to facilitate the use of building information modeling (BIM). Understanding the current adoption and implementation levels of BIM in organizations and even countries and determining directions for future development have therefore become increasingly important. Diverse reports and research about BIM adoption and implementation have generally been ongoing; however, the indices that are most widely used have some limitations. For example, BIM adoption rate is criticized for the inherent inadequacies of sample surveys and the fact that it does not represent actual daily use, while other indices show the fragmentary results. For this study, we selected the most representative indices for understanding levels of BIM adoption and implementation and proposed a chart to demonstrate the comprehensive levels of BIM adoption and implementation. Awareness of BIM (including the reviewing of BIM for adoption), BIM adoption rate, years of using BIM, level of BIM proficiency, depth of BIM implementation, and BIM effect(return on investment) are the indices that are widely used to report on BIM adoption and implementation through the technology adoption process from awareness of the new technology to the actual use of the technology. This research focuses on BIM status after BIM adoption, so the BIM awareness index, including the reviewing of BIM for adoption, was excluded. An expert survey was conducted to research the representativeness, collectability, and consistency of BIM adoption, depth of BIM implementation, level of BIM proficiency, years of using BIM, and effects of using BIM. The BIM effects’ results were lower than the others, so it was also excluded; the other four indices were subsequently called the slim BIM indices. According to results, BIM adoption rate and years of using BIM represent adoption status more than implementation status, while level of BIM proficiency and depth of BIM implementation reflect implementation status more than adoption status. The correlation analysis between years of using BIM, level of BIM proficiency, and depth of BIM implementation showed that level of BIM proficiency and depth of BIM implementation are highly correlated. The slim BIM charts reflect the representativeness and relations between the slim BIM indices and provide visual and quantitative representation of the levels of BIM adoption and implementation. Three types of slim BIM charts were developed according to their individual purposes. In the diamond chart, all four variables are used, while the triangle chart utilizes the depth of BIM implementation, level of BIM proficiency, and years of using BIM variables, and the ball chart employes the BIM adoption and depth of implementation(or level of proficiency) variables. The triangle chart excludes the BIM adoption rate variable to focus only on BIM users’ implementation and the ball chart was developed to simplify the diamond chart. We applied the slim BIM charts to three regions, namely North America(2009 and 2012), Western Europe(2010), South Korea(2012), and India (2014). BIM had been most widely adopted and implemented in North America in 2012 but most deeply in Western Europe in 2010. In 2012, South Kora had widely adopted BIM, but implementation had been shallow. India in 2014 shared a similar status with Western Europe in 2010, but the overall level was lower than in Western Europe. The quantitative results of the slim BIM charts were compared with the BIM Engagement Index for its validation. Generally, the results were similar, but the Indian case revealed some fluctuations. Nevertheless, the slim BIM charts compensated for this through the visualization of the results. To improve the slim BIM charts’ accessibility and use, a Global BIM Dash board website (globalbimdashboard.org) was established. On this website, the slim BIM charts represents the levels of BIM adoption and implementation. Additional surveys will be performed via the website as well. The slim BIM charts have the advantage of being able to collect data due to the use of the smallest possible number of variables with three types of variables being utilized based on their purpose and the available data. The visualized results offer instinctive representation, and comparisons can be deliveredvia the quantified results. In the future, the accumulated data and results will provide tendencies toward BIM adoption and implementation and will suggest appropriate strategies for implementing BIM. The contributions of this paper are to comprehend and select representative indices (the slim BIM indices) to understand status of BIM adoption and implementation, and to analyze the characteristics and correlations between the slim BIM indices. The slim BIM charts enable a comprehensive, visual understadning of levels of BIM adoption and implementation.
Won, J. (2014). A Goal-Use-KPI Approach for Measuring the Success Levels of BIM-Assisted Projects. Seoul, Yonsei University. PhD: 1-220. The obligation of implementation of building information modeling (BIM) in public projects in many countries and the increased client interest in BIM has expedited the growth of the BIM market. Pike Research (2012) forecasted that the BIM market would increase from US $1.8 billion in 2012 to US $6.5 billion in 2020. This increased number of BIM-assisted projects has increased managers' interest in learning how to efficiently manage BIM-assisted projects and how to determine what should be measured in order to successfully execute, manage, and improve these projects―because what cannot be measured cannot be managed. Therefore, this dissertation aims to develop a sustainable methodology for measuring BIM performance of a project for the successful preparation and management of BIM-assisted projects. Performance management of BIM-assisted projects helps improve project performance by evaluating the maturity and strength of BIM business practices. Previous studies that evaluated BIM performance of projects failed to indicate which performance indicators could be used to confirm whether the BIM goals of a project were achieved and which took into account the BIM goals and BIM uses for BIM-assisted projects for performance measurement. Evaluation of the performance of BIM-assisted projects using consistent evaluation methods can lead to a meaningless assessment of effects that were not obtained by implementing BIM in the project. The fuzzy Delphi method and the grey Delphi method are simultaneously applied concurrently to identify a set of meaningful BIM key performance indicators (KPIs) and to establish relationships between BIM goals and BIM uses, BIM uses and BIM KPIs, and BIM goals and BIM KPIs. This research verified the identified BIM KPIs and the established relationships between BIM goals, uses, and KPIs by conducting a triangulation method. The triangulation of sources―surveys, documented accounts, follow-up interviews, and participant observation―was the primary method for comparing the data from the qualitative measures. The proposed goal-use-KPI approach is additionally applied to four actual BIM-assisted projects in order to check its applicability. Three findings related to application of the developed model were determined in face-to-face interviews with project participants from the four projects: (1) usability of the developed model is enhanced more than previous ones; (2) checking the achievement of BIM goals established in the planning phase is possible by providing a list of BIM KPIs mapped with the selected BIM goals; and (3) continuous monitoring of BIM performance is possible by carrying out BIM-assisted projects. The key contribution of this research is the development of a sustainable methodology for diagnosis BIM performance levels for successfully preparing and managing BIM-assisted projects by considering BIM goals and BIM uses of projects. Sustainable performance measurement for the preparation and management of BIM-assisted projects helps when comparing evaluation results across various types of projects by continuously measuring the BIM success level after completion of projects using the same set of evaluation criteria. An additional contribution is the derivation of 19 BIM KPIs for the efficient management of BIM-assisted projects, whether during the projects or after completion; these KPIs help to consolidate and prioritize scattered success factors. If everything is important, then nothing is manageable.
개성공업지구는 2003년 6월에 토목 단지조성공사를 시작하였고, 그 이듬해인 2004년 6월부터 시범단지에 건축공사를 시작하였다. 건축공사는 노무비의 비율이 전체 공사비의 20~30%를 차지하기 때문에 인건비가 남측근로자에 비해 상대적으로 저렴한 북측근로자를 이용하여 공사를 진행하고자 노력을 많이 하였지만 남측과 북측의 건설시공 방법이 다르고 작업환경이 달라 서로를 이해하는데 시간이 많이 소요되었고 남측근로자와 북측근로자를 얼마만큼 투입하여 작업을 진행하여야 하는지 인원투입을 예측할 수 없어 전체 공사비에서 노무비의 투입예산을 작성할 수 없었다. 때문에 남측근로자와 북측근로자의 구성 비율이나 생산성에 의한 인원투입 자료가 절실하게 필요하였지만 그 동안 북한 지역에서의 축적된 공사자료가 부족하여 실적공사자료를 가질 수 없었다. 이 때문에 본 연구에서는 2005년부터 2012년까지 개성공단에서 이루어진 건축공사의 남북인원 실 투입현황을 분석하여 향후 개성공단 및 북측공사에서의 건축공사 진행시 노무비 산정의 기본 자료를 만들어 활용하고자 하였다. 개성공단에서의 건축공사는 총 21개 현장의 자료를 정리하여 그 중에서 20개 현장의 자료로 분석을 실시하였다. 건축공사의 수많은 공종 중에서 노무비의 비율이 높은 형틀공사 공종을 분석의 대상으로 삼았고, 형틀공사 한 개의 공종만 집중적으로 분석하여 분석결과를 도출하면 나머지 공종의 공사들도 같은 방법으로 분석이 가능하여 건축공사 전체 공종에 대한 남북 인원비율이 계산될 것으로 판단하였다. 연도별 분석결과 2005년, 2006년의 형틀공사 투입인원은 20:80의 인원비율을 보였고, 2007년에는 8:92, 2008년에는 4:96을 보여 시간이 지나면서 남측근로자의 비율이 급격하게 감소하여 북측근로자가 남측근로자를 대신하여 작업을 하였다고 볼 수 있다. 남북관계가 원만하지 않아 공사물량이 줄었던 2009년에는 5:95를 보였으나 북측근로자를 대부분 철수시키고 소수의 인원만으로 공사를 진행하였던 2010년에는 12:88, 2011년은 20:80의 비율을 보여 북측근로자가 철수하여 빈자리를 남측근로자가 대신 채웠다고 할 수 있다. 이는 남북관계가 원활하게 풀린다 해도 철수한 북측근로자가 건설현장에 다시 투입된다는 보장이 없기 때문에 남북근로자의 투입 인원비율은 당분간 낮아지지 않을 것으로 판단되며, 오히려 남북관계가 원활하게 되어 개성공단의 건축공사가 활성화 된다면 남측근로자의 인원비율은 30%이상 더 높아질 것으로 판단된다. 하지만 북측근로자가 건설현장에 원활하게 보충된다면 협력업체의 시간이 지남에 따라 남북근로자의 인원비율이 급격하게 변화하듯이 개성공단 초기에서와 같이 2~3년 뒤에는 5:95의 인원비율이 유지될 것으로 판단되며, 기존의 북측인원을 약간이라도 보유하고 있는 업체의 경우에는 1~2년 이내에 예전 2008년도의 인원비율을 유지할 것으로 보인다. 또한 오랜 시간이 지나더라도 남측에서 자재가 공급되고 남측에서 설계가 이루어지는 한 전체적인 품질이나 공정관리를 위해 최소한의 남측기술자가 필요하다고 판단되며 지속적인 자료의 축적으로 점점 더 정밀한 투입인원의 추정이 필요하다고 판단된다.
KIM, S. (2014). Extraction of object information for rule-based design validation on healthcare building design. Seoul, Yonsei University. Master: 1-49. BIM을 이용한 설계 검토는 시공의 정확성 등의 이유로 전 세계적으로 활발하게 연구되고 있고, 실제 건설 현장에서 폭 넓게 활용 되고 있다. 건축 시설물의 유형 중 병원 건축물은 타 시설물과 비교를 했을 때, 설계 요구사항이 복잡하고 다양하기 때문에 여러 객체정보를 추출 할 수 있다고 판단하였다. BIM을 이용한 룰 기반 설계 검토를 위해서 필요한 객체정보를 국제병원설계가이드로 꼽히는 FGI 병원시설물 설계 가이드 분석을 통하여 필요한 객체 정보를 추출하고 국내 병원의 설계요구사항 RFP에서의 객체정보와 IFC 엔티티(entities)와 비교분석을 함으로써 병원 시설물의 BIM을 이용한 룰 기반 설계검토에 필요한 최소 객체 정보들을 알아보고 IFC스키마에서의 적용 범위를 분석하고자 한다. 텍스트기반의 병원설계가이드와 설계요구사항요청서들은 룰 기반 설계검토를 위해서는 자연어문장에서 컴퓨터가 인식할 수 있는 규칙언어로 변환을 해주어야 한다. 이를 위해서는 자연어 문장을 단순화하고 컴퓨터가 인식할 수 있는 서술어(method)와 주어, 목적어(object)로 분해를 해야 한다. 본 연구에서는 룰로 사용할 수 있는 주요 객체정보 즉, 주어, 목적어의 오브젝트로 정의하여 객체정보를 분류하였다. 분석결과 FGI 병원설계 가이드에서는 공간객체의 정보가 가장 많이 제공되고 있으며, 국내 병원 세 곳의 설계요청서를 분석하여 얻은 결과 역시 공간객체의 정보가 가장 많이 언급되었다. 이를 통하여 BIM을 활용한 규칙 검토를 위해서는 최소한 공간객체의 구성이 우선 필요하다는 것을 확인 할 수 있었다. 추가적으로 본 연구에서는 IFC2x3와 IFC4의 엔티티들을 추출 된 객체정보들과 비교한 결과 IfcSpace 객체 중심으로 모델이 구성되고 이를 바탕으로 BIM을 이용한 룰 기반의 설계 검토에서 대상이 되는 BIM 모델의 구현 수준을 제안하였다.

There are various elements that is necessary for adopting and executing BIM (Building Information Modeling). A voluntary adoption by private company is ideal. In reality, it has limits without public institute support. So government and public institute need to help private company adopts BIM. One of supports is a development of BIM guideline. BIM guideline standardization for collaboration is necessary. Because it brings out purpose of BIM that creates and reuses data used for various parties. Participants should discuss development of BIM guideline. Development of BIM guideline is a difficult as it has to be used widely in construction industry. If government and public institute develop BIM guideline standardization, private company easily adopts BIM. And it helps that government build management standardization of construction industry. The USA, UK and Singapore that aggressively adopt BIM recognize importance of BIM guideline standardization. So their government development BIM guideline for private company to establish management standardization that applies with each company's purpose of BIM adoption. In Korea, Ministry of Land and Public Procurement Service announce BIM guideline in 2010. And many researching about BIM guideline are done by academia. But these BIM guidelines don't suggest specific contents. So as to utilize BIM guideline in practice, BIM guideline should be more specific and practical. Through studying previous research about BIM guideline, this study is suggested practical standardization of BIM guideline. BIM guideline based on this study help private company build BIM guide. This BIM guide that is in accordance with each company's standard should contribute to establishing roadmap and adopting BIM.
According to the National Emergency Management Agency, most fires are caused by negligence. In addition, the negligent use of various devices can be considered in terms of wasted energy. To solve this problem, this study develops a thermal camera to replace the conventional context-aware system. The principle of the developed system is to measure the change in situation, depending on differences in the target temperature. These changes in temperature are detected by measurements taken with the thermal imaging camera system, which is is more objective and quantitative way than the existing context-aware system is. Various systems are related to the context-aware system. However, an investigation by the National Emergency Management Agency found that fire-prevention equipment using a variety of sensors was either not operational or had a failure rate of 30%. The current situation means that the use of context-aware systems has reached a critical point. Therefore, the objective of this study is to solve this problem by introducing a thermal camera designed according to the configuration of context-aware systems. The thermal camera has both benefits and drawbacks. The accuracy of the thermal imaging contrasts the relatively narrow field of view. In order to resolve this situation, additional devices were connected. For example, the servomotor can be rotated up, down, left or right, and the angle of rotation can be adjusted precisely to the device. In addition, the programming language can be controlled through the motor unit, which has the advantage of a relatively small size with great power. Connection to a servomotor enabled the thermal camera to pan and tilt, thus providing it with a wide range. The developed system was verified through experiments, which were carried out in various 50 places, such as the hallway of a building, laboratories, and houses. The situations differed with respect to the characteristics of the target objects. Hence, the system was applied depending on the characteristics of each object, which confirmed the results of different experiments. Experiments were performed in which not all objects could achieve the purpose of the experiment. However, the thermal camera developed for use with a context-aware system made it possible to detect changes in the temperature of the target object. The results showed that the thermal camera responded with rapid and accurate situational awareness. Of course, we progress through various experiments conducted under constraints. However, under these conditions, the results showed that cognitive performance of the developed camera was excellent. In addition to overcoming the limitations of existing systems, subjectivity, and labor-consumption was improved. In future studies, seasonal factors and circumstances could be considered, with the objective of conveying to the user in real-time results that are even better than in real life.
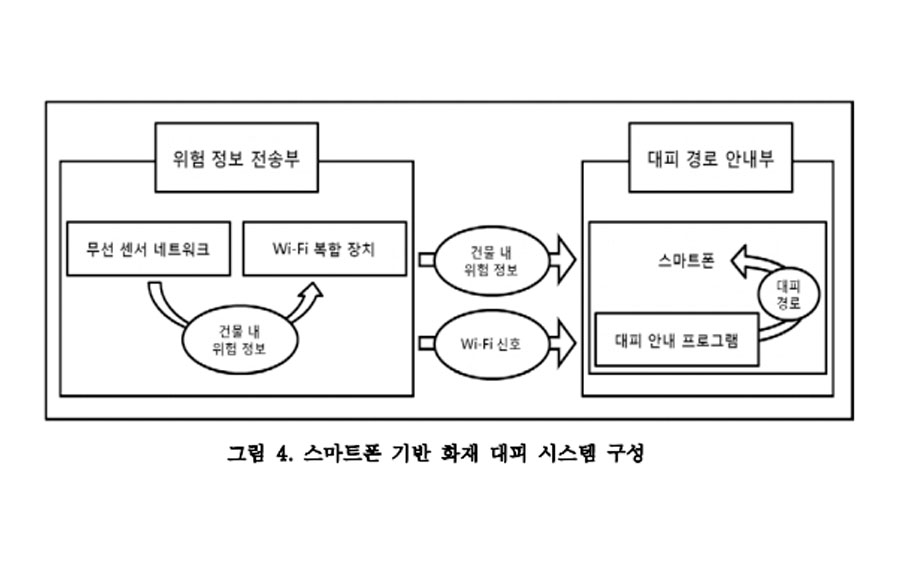
The purpose of this study is to develop a mobile-based fire evacuation system, designed for supporting evacuation process. Mainly Zigbee and Wi-Fi technology is used for indoor location tracking of the system users and for locating hazardous spots. Proposed system deploys existing methods, but developed and applied them focusing on fire evacuation system. Due to short evacuation time limit in most fire emergency situations, real-time recognition of hazardous location and an accurate positioning of users is very important for evacuation system by means of avoiding congestion and providing faster evacuation route. In order to achieve this we decided to utilize 802.11 standard (Wi-Fi) throughout the evacuation process since there are no such evacuation system that is able to share sensor data and track users on a same kind of wireless network. By developing a composite Wi-Fi device, harzadous information from sensor network, which is commonly constructed with Zigbee standard, can be sent directly to users equipped with smartphones through Wi-Fi network that is used for tracking users as well. A composite Wi-Fi device operates as an access point for indoor localization as well as a medium for sending sensor data to users. In order to enhance the indoor positioning accuracy and the performance of the evacuation system based on the tracked position, existing KWNN fingerprint method was improved. The proposed KWNN method was analyzed and showed 80% reduction in constructing the database for indoor tracking. The tracking position accuracy of proposed method was tested in Engineering building of Yonsei university and the result showed that the proposed method is 39% accurate than traditional KNN fingerprint method
The Public Procurement Service (PPS) of Korea announced that, from 2016, every public facility construction must adopt Building Information Modeling (BIM) and the official product of the BIM data must be submitted in the format of Industry Foundation Classes (IFC). This indicates that it has become important to effectively manage the IFC model data file. The aim of this study is to develop algorithms that can efficiently input an IFC model file into an IFC model server (or IFC server). The IFC model server is a database management system that uses the IFC schema as the underlying database structure (IFCWiki, 2011). Previously, several model servers were developed for using and exchanging building model data efficiently among project participants. Typical model servers are IMSvr, EMS, SABLE and the BIMserver. Most of them were developed based on relational database (RDB) principles. However the mapping process between IFC and the internal data structure of the RDB based database was complicated, which led to slow performance of the IFC server. There was a complex problem expressing the object-oriented IFC information since the RDB based IFC servers do not support the inheritance function of an object. To solve the problems of the RDB, an IFC server based on an object-relational database (ORDB) was developed and the performance of the ORDB based server (OR-IFC server) was relatively better than that of the RDB based server (Jeong, 2010). However there were still limitations in managing model data files larger than 100MB, which is the common size of a BIM model’s data in the construction industry. It took 90 minutes to input a 5MB IFC model file into the ORDB based IFC server. This study proposes algorithms to efficiently import large IFC model data into an ORDB based IFC server. The core task was to decrease the number of times the entity was searched for when translating the IFC file to an object file without losing any entity id attribute information. To efficiently translate the massive texts of an IFC file, reducing the number of times the entity id was searched for was important, because reducing this number is a way to increase the mapping speed and consequently this means the server has high performance. Therefore this study covers algorithms that can decrease the number of times the entity id is searched for when mapping the IFC file to an object file. Four algorithms are introduced in this study and each algorithm was developed when solving the limitations of the previous step algorithm. 653 IF statements were repeatedly used in algorithm 1; the IF statements were divided into ten modules in algorithm 2; IFC schema were read into the mapping process in algorithm 3; and arrays were declared in algorithm 4. To verify the import performance improvement of the algorithms, a test was conducted. The mapping process times of the four alternative algorithms were measured and the results were analyzed. Three IFC models were used for the test with different sizes. Small size file (5MB), middle size file (60MB), and the large size file (110MB) were used to measure the mapping process times. Among the four algorithms, the array-based algorithm outperformed the other algorithms. By using the array-based algorithm, compared to algorithm 1, the time required to import a 5MB IFC model was reduced from 90 minutes to 24 seconds, and in the case of a 60MB IFC model, from 10 days to 344 seconds. Moreover, the 110MB IFC model, which is the common BIM model size that is used in the construction industry, took 769 seconds using the fourth algorithm to input into the OR-IFC server. The mapping process time translating the IFC file was considerably decreased by improving the importer algorithm. This is an advantage of the OR-IFC model server which can efficiently manage large IFC data files within the server. Furthermore, the algorithm suggested in this study can be said to have contributed greatly by providing the basis of efficient data sharing environments to manage BIM model data in the construction industry. On the other hand, when there were errors in the IFC model file itself, a problem occurred importing the model data file into the OR-IFC server. The model data file was not normally stored. The number of text lines in a 60MB IFC file is approximately 900,000 lines. To check manually for errors in 900,000 lines costs a lot of time and effort. Therefore, automatic error checking module which can find errors efficiently in the IFC file should be developed for future works.

-
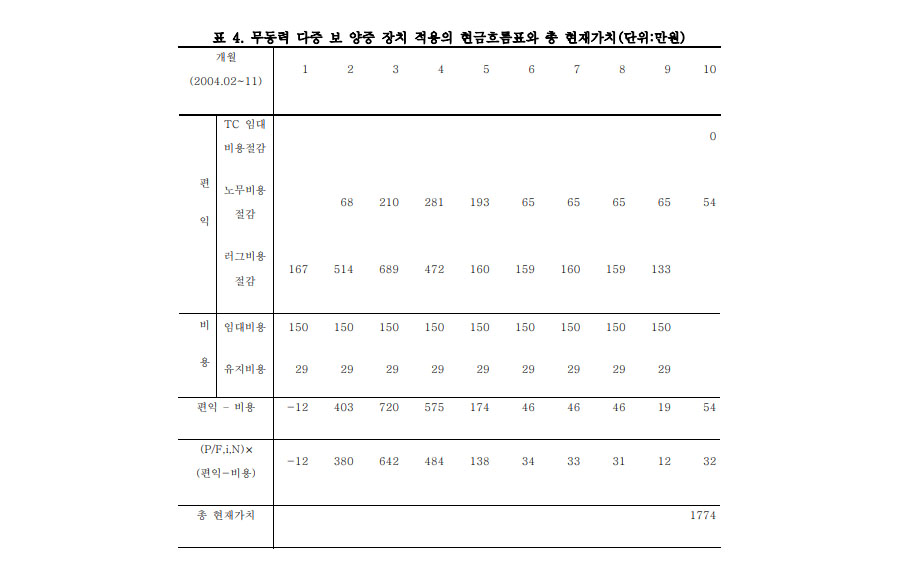
In steel building sites, productivity has been improved by tying and lifting multiple small steel beams. But, while bolting or welding a beam, the remainder of the tied beams can collide with already installed columns and girders. Moreover, the practice can be dangerous because it requires workers to untie the rope(s) while standing on an unstable beam and being secured only by a safety lanyard. In order to overcome the deficiencies of traditional lifting practices in multi-beam situations, several designs for motorized multi-beam lifting systems have been proposed. A multibeam lifting system is a tower crane accessory that mechanically and subsequently secures and subsequently releases two to three beams in order to shorten the lifting cycle time and improve productivity. However, for a variety of reasons, none of the multi-beam lifting systems has been adopted by industry. One critical drawback common among the proposed multi-beam lifting systems is the need for a large amount of electricity to power motorized systems capable of holding several beams. Such electrical capacity can be difficult to supply due to the required cable length or large number or size of batteries. In addition, the proposed systems lack sufficient safety mechanisms to prevent beams from falling. Non-powered multi-beam lifting system is proposed in this study to overcome the limitations of powered multi-beam lifting system. This new system satisfied the functional requirement by three main mechanisms. First, The Non-powered multi-beam lifting system uses self-weight (gravity) as the source of energy and does not use any electricity. Second, The Non-powered multi-beam lifting system includes a lever-based safety device to prevent beams from slipping and falling. Finally, The Non-powered multi-beam lifting system’s frame is designed to automatically adjust to beam widths within the acceptable range when the safety devices are engaged. The Non-powered multi-beam lifting system was tested three times at three different locations with different goals. It was first tested at a factory to verify system safety. After confirming the safety of the system, the system was brought to a construction site and used to move beams to and from various locations within a stockyard. This experiment was designed to further verify system safety in a low-risk environment while also allowing the systems performance to be compared with traditional lifting methods in terms of LCT. Finally, the Non-powered multi-beam lifting system was deployed in actual steel beam installation. Based on the data collected form the experiments, the quantitative analysis and the qualitative analysis were conducted. First of all, three factors were analyzed in the productivity analysis: the LCT, the number of workers, and the additional costs for the lug-welding activity. And then, to analyze the economic impact of the LCT reduction afforded by the NPMLS, we sought the economic equations and conducted case benefit-cost analysis by using pilot project data. The fieldapplicability of The Non-powered multi-beam lifting system and ease of operation were also evaluated qualitatively through observations and interviews with workers. The result is as follows. Time and work for installing beams were reduced and the safety was improved. It was possible to reduce the cost of labor and welding lugs. The Non-power multi-beam lifting system was faster and offered better load control than the traditional method, and specifically cited a reduction in beam strikes with already installed building components, which is a common problem with the traditional method. Tower crane operators and steel workers were accustomed to operations within the given range of precision and easily learned how to release a beam after several trials. In this study, the non-powered lifting device for steel H-beams was developed and the field applicability and economic feasibility of the technology were analyzed through field tests. Future research is to develop the other lifting device for other materials. However, such all-purpose devices are generally very difficult to develop, and once achieved, may lose the initially intended benefits due to the complexity of the final solution. A practical solution may be to adopt the concept of “robot-oriented design”.

-

-

-
JEONG, M. (2011). (A) study on the customer satisfaction and loyalty in construction management. Seoul, Graduate School, Yonsei University. PhD. This research aims to verify the cycle of customer satisfaction in construction management (CM) that leads to repurchase and referral. It also attempts to determine the level of satisfaction that can promote repurchase and enthusiastic referral within the customer satisfaction cycle. Toward this end, it analyzes the relationship between CM selection factors, expectation, customer satisfaction, and customer loyalty by surveying 135 project managers with influence over CM selection and experience with CM services. The results support the formation of a customer satisfaction cycle by revealing that customer satisfaction with CM leads to customer loyalty. In other words, satisfied CM customers contribute to new customer acquisition through repurchase and referral. An analysis of the differences between new and repurchasing customers was conducted with the purpose of promoting repurchase in the customer satisfaction cycle. The results revealed that customers in a long-term transactional relationship with CM services tend to be concerned with management skills, staff skills, and past performance, while new customers are more concerned with brand image and word of mouth. In addition, there are certain patterns in CM selection according to customer and project type, such as past performance being preferred in projects for residential facilities. According to an analysis of the differences between new and repurchasing customers in their expectation and satisfaction, repurchasing customers’ expectations of CM services are higher than those of new customers. The analysis also indicated that repurchasing customers perceive their satisfaction level as higher than new ones in the pre-design and design phases. Therefore, in order to increase repurchase rates, high-level positive disconfirmation between expectation and performance of services is needed, and the services should focus on meeting customer expectation in the early phases. With the purpose of promoting enthusiastic referral in the customer satisfaction cycle, the relationship between the satisfaction level and referral intentions was examined. The results revealed that the likelihood of highly satisfied customers becoming promoters was 71.3% higher than for moderately satisfied customers, which indicates the importance of the satisfaction level in attracting promoters. In addition, it was revealed that the initial services and the ethical attitude of CM play a role in customer satisfaction and loyalty formation, respectively, in the early phases of a project.

-
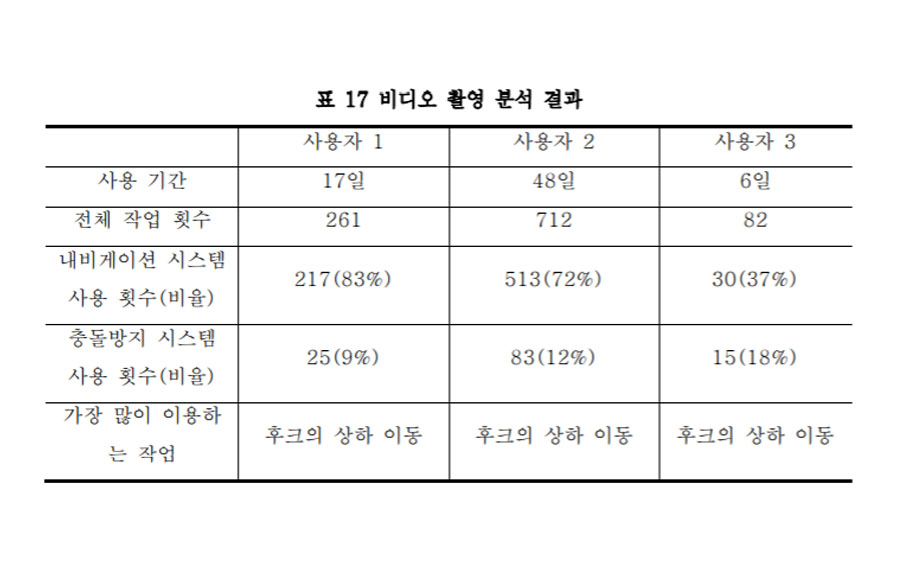
The tower crane work has possibilities of big accidents because the work is to move the heavy materials. In construction sites, the tower crane moves carefully following the signal from the workers to prevent the accidents. However, the collision of the materials and the building or the crash occurs because of the dead zone when the crane moves materials. The crane driver is in the high place but he feels a danger from the work because the blind spot still exists even in the high place. The tower crane navigation system was developed to prevent the accidents and to help the tower crane driver to work easy and safely. The tower crane navigation system was developed to prevent the accidents from the blind spot, and the system reflects the demand of the users by the interviews and surveys. The system developed lastly established in actual site to the tower crane driver use the system and the usability test was conducted. Use frequency analysis and screen mode preference was evaluated. The result showed that the driver used the tower crane system more against existing system. The driver especially used the system when the blind spot occurred. The screen which the two crane drivers prefer was different. It is analyzed that the function which can rotate the view mode easily is necessary for the crane drivers who have different preferences. The tower crane navigation system is developed on the crane drivers conducting interview and survey. In the usability test, the users showed high frequency of using the tower crane navigation system. The result shows that the system improves the usability and safety for real tower crane work. In this study, the test aimed at limited drivers. Therefore, we need to apply this system to many sites in the future study so that we can get more reliable data.
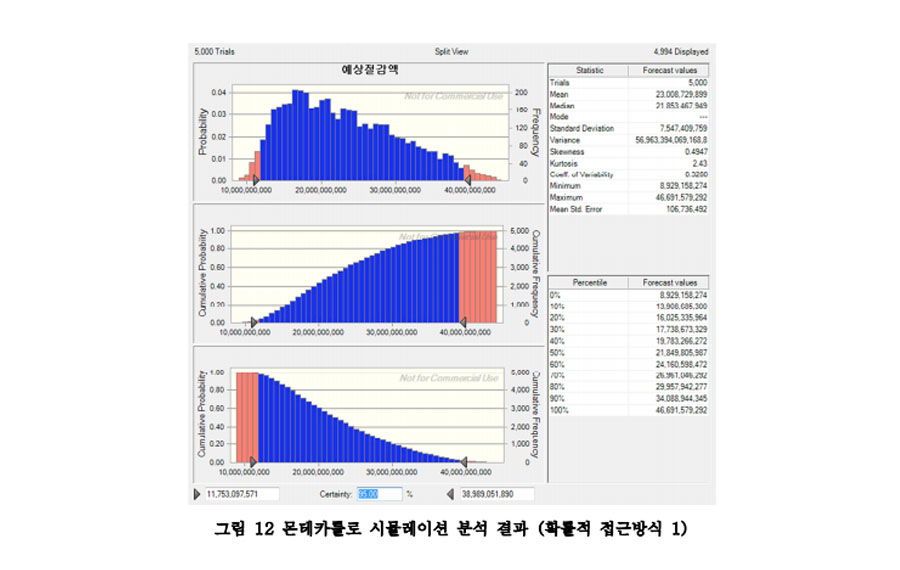
PARK, K. H. (2011). (A) study on the effect of pre-detecting errors using BIM in the pre-construction phase. Dept. of Architectural Engineering. Seoul, The Graduate School Yonsei University. PhD. Constructing a building requires the constructor to materialize and give form to the architect’s intended design laid out on two-dimensional piece of paper. Not only is this very complicated but also has many segmented processes that give rise to many issues. Among them are re-working, delayed completion and exceeding of production costs, which also are key determinants of success of the project. With the recent rise of more complicated buildings, free forms and the participation of stakeholders, the aforementioned problems are becoming more significant. This study presents the use and application of BIM (Building Information Modeling) as a solution to resolve some of these problems. In this study, a design validation process using BIM was conducted for a 2D blueprint. Then, the errors that were discovered were translated to a ROI (Return on Investment) analysis to demonstrate the effect of pre-detecting design error in the preconstruction phase. For this ROI analysis, the amount of material that would have been used to correct for the mistakes is multiplied by the unit rate of the material to calculate the expense that could have been avoided. In the first step, the types of design errors were observed in reviewing existing literature. The types of errors were then re-categorized into logical, blue print discrepancy, omission errors to be more relevant to the case study used in this study. Using BIM, 158 logical errors, 358 blue print discrepancy errors and 193 omission errors were discovered. Among the 709 total errors discovered, 401 were associated with direct costs while the remaining 308 were not. The direct costs associated with the 401 errors amounted to around 4 billion (ROI 250%). However, this is the case with the assumption that not a single error is found using the traditional method. Since this assumption is unrealistic, the following two methods are employed. First is the use of static value. The probability of error detection was analyzed in three situations: under 28.3%, 50% and 73.3%. Employing this method, the net ROI of 1.4 billion won (11%) was calculated. The second employed the Monte Carlo simulation which is a stochastic approach. Using this method, the revenues calculated from utilizing BIM ranged from 1.2 billion won being the lowest to 3.9 billion won being the highest, translating into a net ROI ranging from 4%~244% (average of 104%). These two methods show that there is a postive net ROI from 4% to 244% with the early detection of design error. When indirect costs (associated with delayed construction) are calculated, an additional 8.5 billion won can potentially be saved. There are two limitations to this study. The first is the lack of case studies available for the analysis. The second is that the assumptions are based on the errors that have not occurred. Nevertheless, an ROI of 104% gives considerable support to the benefits of introducing and using BIM in the pre-construction phase. In previous literature, the process of ROI analysis and methodological approach are not presented. Additionally, there are significant differences in results from different institutions. This paper contributes to the existing literature by resolving these shortcomings: it introduces a never before introduced methodological approach that allows for a more reliable assessment of BIM implementation effects. With the proliferation of methodological BIM analysis, this paper additionally hopes to expedite the introduction of BIM. There are still many avenues for future research as more case studies become available. Among them are 1) making research results more pervasive and universal through repeated analysis, 2) standardizing and accurately calculating delayed construction time due to construction errors and 3) a more in-depth analysis of transaction costs.
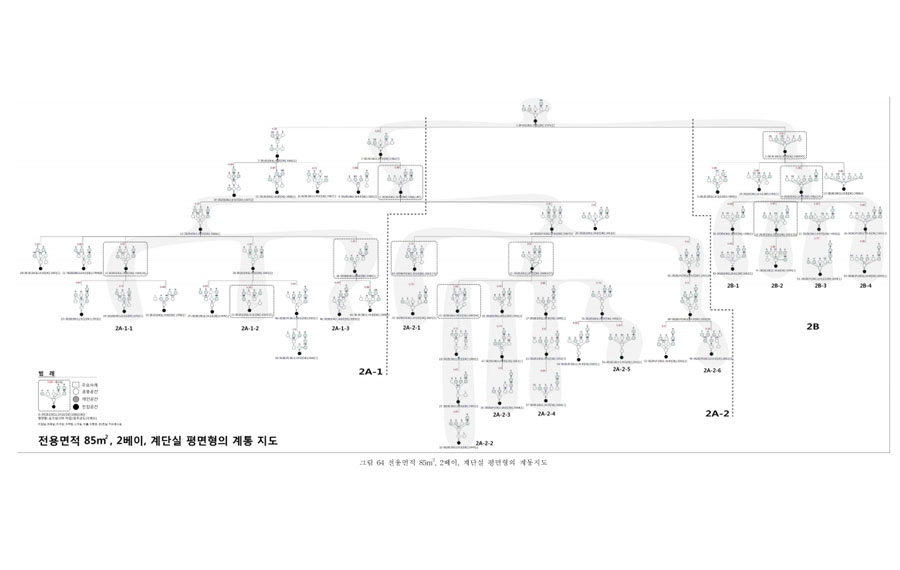
This study deals with methods of making a phylogenetic tree, that presents the types of space and the relationships between them, based on phylogenetic ways of thinking and research methodologies. As qualitative factors in architecture, the types of, and relationships between, architectural spaces have mostly been dependent on researchers' standards and decisions. Lack of information about when these spatial types came about has also caused limitations to research on changes of types over time and correlations between them. To overcome these limitations, this paper proposes a methodology which can quantitatively evaluate types of architectural space and the changes of the relationships between them. A method of drawing a phylogenetic tree that presents the transitions of plan composition is suggested based on an index of similarity between types of spatial compositions using existing graph theories. For further analysis of the index of similarity for spatial composition graphs and various quantitative, a space connection model and ASpace have been designed. The space connection model is based on a network model of space that can efficiently express plans of buildings. ASpace is a space analysis program that was developed to automatically analyze data collected from the space connection model. This study aims at four achievements: First, a time-based joining method(TBJ) was proposed considering similarities between spatial compositions and the times of plans' occurrence. TBJ can cover the problem of existing methodologies’ incapability of considering occurrence time, while producing consistent results just as the existing biological joining method. It also established a theoretical for the premise that systematical thinking can be applied to architecture, especially to living space. Second, limitations of existing spatial data, which have been collected and applied by models selected based on the ways and types of space analysis, are. The proposed space connection model, which is capable of various analyses with one set of space data, can compute property values of connectors that connect spaces and can also analyze differences in spatial relations that are dependent on the property values(size and transparency). This space connection model is capable of transformation into other space models as well. Third, a space analysis program is developed in order to carry out various space analyses. The strongest point of the program, ASpace, is that it can perform analyses contemporarily with design processes, including the space analysis function and the blueprint generation function. ASpace is built on an object-based system, so that it can be developed and utilized consistently, along with various emerging space analysis methodologies. Fourth, historical change in space composition over the past 40 years is studied thoroughly by a similarity analysis on types of apartment. Each plane figure’s branch shape in this delivered phylogenetic map changed and maintained its space structure in a certain direction. From the common genotype plane figure, a plane figure that has a particular genotype branch shape has been derived. This plane figure space is composed of genetic trait and prototype. The next generation plane figure changes based on this prototype. By social, economical and legal factors, the similarity and variety between these plane figures is altered. Furthermore, in space composition and location appearance, variety and conformity have repeatedly increased and declined. Finally, the proposed method is more reliable compared to the existing qualitative method of apartment housing analysis, since it deals with about 1,300 data resources. Especially in a time series analysis of space, data is divided by the year and time, so a small number of certain cases can cause distortion to the whole result. Therefore the amount of data analyzed is a significant factor for enhancing the accuracy and reliability of the analysis.

-
As the number of high-rise construction project increases since the 20th century, use of tower crane has also increased and the notion on the safety accident and productivity has become widespread. Automated tower crane began to receive more attention, accompanied by related studies. Previous studies can be divided into hardware development such as semi-automated crane using wireless controller, path planning in virtual space and development of optimal algorithm. Most studies have been conducted in a lab or virtual space. This research is a follow-up to Lee’s study (2009) on the sub-elements of tower crane automation, a system that uses laser sensor to measure vertical distance of lifting. In addition to the laser sensor, this research adopted encoder sensor and GPS sensor to develop Lifting Path System. These were applied to tower cranes in project sites to test performance. The research consisted of three stages. First, previous studies were examined to define function and role of the system. Multi-sensor based Lifting Path System and its algorithm was designed. Next, a module test was conducted based on the design to develop Lifting Path System. Lastly, to verify accuracy and safety of the system, it was installed on a 12ton Luffing jib type tower crane at a construction site. Its accuracy was tested using the total station and laser distance sensor module, and the test contained four steps with the following results. The first stage tested a jib’s up-and-down movement and it showed error of 0.66°. Next, the accuracy test for vertical distance that measures up-and-down movement of the hook block yielded error of 0.07m for four sheets of A1-sized laser reflecting plates. For precise measurement of the hook block’s movement, third and fourth stages of the accuracy test were conducted. Development of the Lifting Path System and performance evaluation led to advancement in tracking technology that is required for automated tower crane. It also enabled real-time measurement of lifted load and real-time location of the tower crane. Furthermore, the on-site accuracy test can facilitate field application of hardware for automated tower crane. This research is expected to contribute to future research on automated tower crane as it covers subjects including collision prevention, automated crane control processing technology and tower crane navigation.
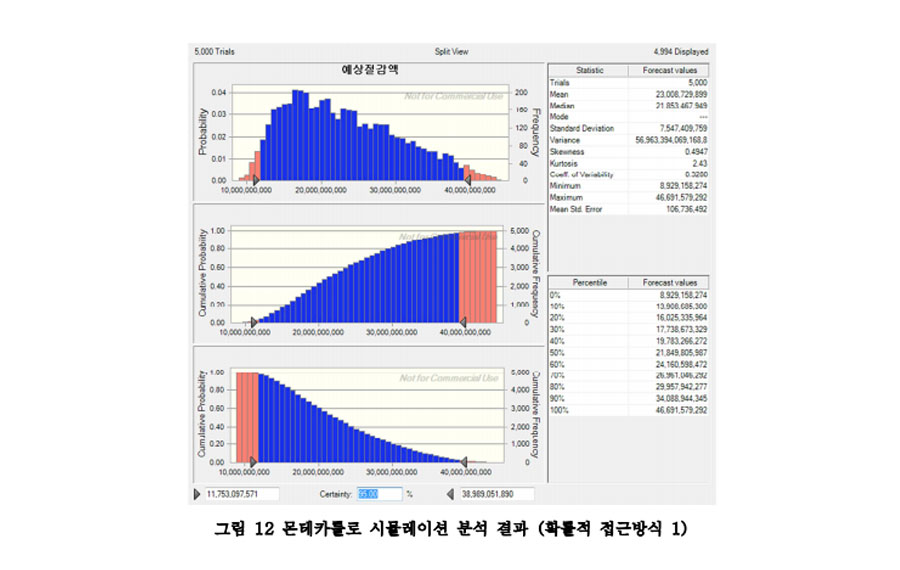
Constructing a building requires the constructor to materialize and give form to the architect’s intended design laid out on two-dimensional piece of paper. Not only is this very complicated but also has many segmented processes that give rise to many issues. Among them are re-working, delayed completion and exceeding of production costs, which also are key determinants of success of the project. With the recent rise of more complicated buildings, free forms and the participation of stakeholders, the aforementioned problems are becoming more significant. This study presents the use and application of BIM (Building Information Modeling) as a solution to resolve some of these problems. In this study, a design validation process using BIM was conducted for a 2D blueprint. Then, the errors that were discovered were translated to a ROI (Return on Investment) analysis to demonstrate the effect of pre-detecting design error in the preconstruction phase. For this ROI analysis, the amount of material that would have been used to correct for the mistakes is multiplied by the unit rate of the material to calculate the expense that could have been avoided. In the first step, the types of design errors were observed in reviewing existing literature. The types of errors were then re-categorized into logical, blue print discrepancy, omission errors to be more relevant to the case study used in this study. Using BIM, 158 logical errors, 358 blue print discrepancy errors and 193 omission errors were discovered. Among the 709 total errors discovered, 401 were associated with direct costs while the remaining 308 were not. The direct costs associated with the 401 errors amounted to around 4 billion (ROI 250%). However, this is the case with the assumption that not a single error is found using the traditional method. Since this assumption is unrealistic, the following two methods are employed. First is the use of static value. The probability of error detection was analyzed in three situations: under 28.3%, 50% and 73.3%. Employing this method, the net ROI of 1.4 billion won (11%) was calculated. The second employed the Monte Carlo simulation which is a stochastic approach. Using this method, the revenues calculated from utilizing BIM ranged from 1.2 billion won being the lowest to 3.9 billion won being the highest, translating into a net ROI ranging from 4%~244% (average of 104%). These two methods show that there is a postive net ROI from 4% to 244% with the early detection of design error. When indirect costs (associated with delayed construction) are calculated, an additional 8.5 billion won can potentially be saved. There are two limitations to this study. The first is the lack of case studies available for the analysis. The second is that the assumptions are based on the errors that have not occurred. Nevertheless, an ROI of 104% gives considerable support to the benefits of introducing and using BIM in the pre-construction phase. In previous literature, the process of ROI analysis and methodological approach are not presented. Additionally, there are significant differences in results from different institutions. This paper contributes to the existing literature by resolving these shortcomings: it introduces a never before introduced methodological approach that allows for a more reliable assessment of BIM implementation effects. With the proliferation of methodological BIM analysis, this paper additionally hopes to expedite the introduction of BIM. There are still many avenues for future research as more case studies become available. Among them are 1) making research results more pervasive and universal through repeated analysis, 2) standardizing and accurately calculating delayed construction time due to construction errors and 3) a more in-depth analysis of transaction costs.
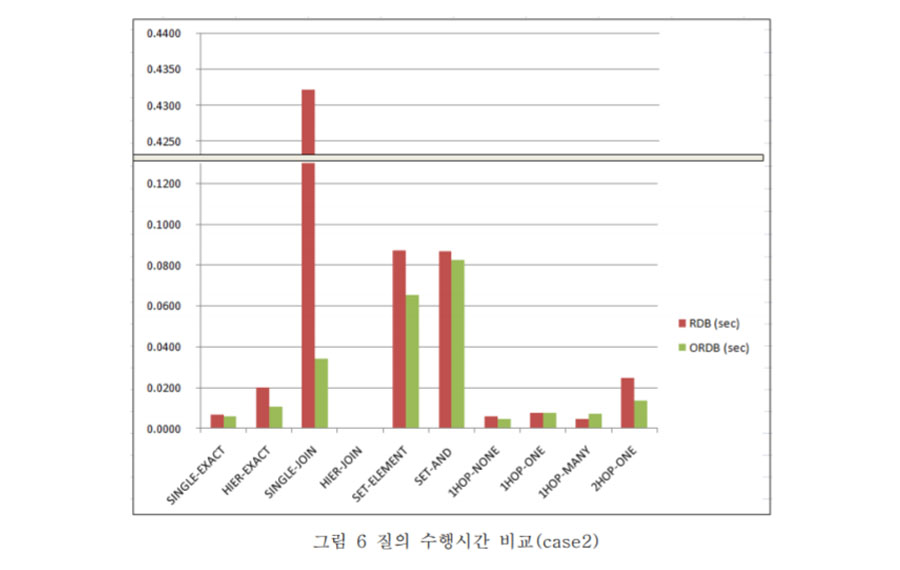
In the 1970s, there were problems with sharing and exchanging building data. Those problems still exist in today’s information society. McGraw-Hill Construction’s SmartMarket Report states that developing collaborative building information modeling (BIM) processes and improved interoperability is a top priority investment that will increase the value of BIM. The industry foundation classes (IFC) model server has therefore been developed and is regarded as a standard in the architectural, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry to solve problems relating to the sharing and exchanging of building data. The IFC model server is a management database system that can store building information as objects so it can use data partially. As building information has become increasingly complicated, so has the amount of related data. Consequently, there have been server system performance problems. In particular, the method of storage and the server data structure are directly connected to overall performance and capability. It has been revealed that the existing relational database (RDB) based on the IFC model server experienced performance problems. Another server, an object-oriented database (OODB) based on the IFC model server, had stability problems and difficulty with querying. Thus, this study aims to improve the performance of the IFC model server using an object-relational database (ORDB) that includes features of both a RDB and an OODB. We particularly focus on increasing the speed of the query process and using standard queries for object-based data exchange. We suggest a mapping rule that converts IFC2X3 schema into an ORDB. Using the rule, we developed an automated converting module to implement the database using CUBRID DBMS as a platform. We developed two IFC server systems for comparison: an ORDB system and a pre-existing RDB system. We conducted a performance test for the ORDB and RDB approaches to verify the effect of the suggested IFC server. We used the Benchmark of Universal or Complex Kwery Ynterfaces (BUCKY) benchmark method that is generally used to measure query performance for ORDBs. Using different IFC file sizes (442 KB and 5,339 KB), the results of two tests showed the ORDB-based IFC model server had better performance at 54.2% and 64.2 compared to the RDB-based one. This is because the ORDB approach includes object concepts in order to have similar data structure and to simplify the query process. A comparison of the results implies the larger data size leads the bigger difference of performance. Another words, when we use the larger data the effect of ORDBbased IFC server(OR-IFC server) is bigger. It says the potential of an OR-IFC server. Standardized queries make the system easy to use. The improved IFC model server suggested in this study needs to be further developed in order to contribute for utilizing partial model and for better data exchange.
Kyungha, L. (2010). Social Network Analysis of BIM Collaboration. Dept. of Architectural Engineering. Seoul, The Graduate School Yonsei University. Master. The main purpose of BIM is to integrate information which is needed for construction process. This helps to communicate and exchange information properly between each work section of construction process. As the government and construct industries are interested in adopting BIM process, many construction cases which are adopting BIM process are increasing. Also many studies related to adopting BIM process for construction process are increasing. Many qualitative studies concluded that more efficient construction management it can be possible by adopting BIM process. Through this adopting BIM process, collaboration of improvement was performed already. However, there are no studies about specific alternatives and comprehension of the aspect of relation with domestic BIM collaborations. This study focused on the social network analysis of characteristics of collaborations which adopted BIM process. And this study analyzed relationship properties of BIM collaboration network, characteristics of the information exchange, and major participants as information exchange hubs. According to the analysis of types of information exchange and information flow of collaboration which adopted BIM process, this study focused on differences between existing construction process and construction process adopting BIM. The qualitative interview of actual examples was surveyed in advance. Then, quantitative analysis through Social Network Analysis of BIM collaboration was performed. Since this study tried to perform quantitative analysis to existing studies which anticipate improvement of collaboration efficiency by adopting BIM, this study can be significant. As the primary stage of the BIM collaboration, this study offers comprehension on the current situation of domestic BIM collaboration, and prevent the trial and error which may occur during operating BIM collaboration. And many projects which adopt BIM process are expected to increase. On the basis of this study, it is possible to make in-depth analysis and statistical verification on the subject of BIM collaboration by the more increased social network analysis cases
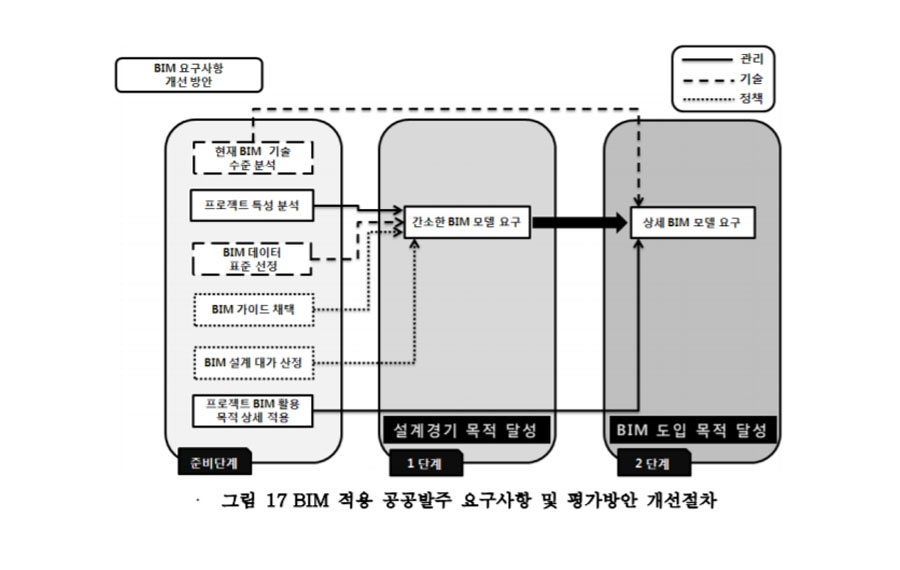
Sung, C. (2010). Analysis of Participant’s Opinion Regarding the Public Project for BIM (Building Information Modeling) Requirement and Estimation Process. Dept. of Architectural Engineering. Seoul, The Graduate School, Yonsei University. Master: 1-72. Many countries have make an effort to introduce BIM(Building Information Modeling) as their policy to raise the efficiency of productivity in AEC(Architecture, Engineering and Construction), and made it mandatory to introduce BIM particularly for public ordering. BIM has already been introduced to domestic public ordering project. However, still domestic BIM is at an early stage. Accordingly, the proper requirements and assessment have not been proposed to introduce BIM. This study aims at proposing the requirements and assessment for public ordering BIM to suggest proper direction. This study imple ented basic research with consideration of existing literature, and analysis of BIM guideline. And also this study decided the direction of interview with hands-on workers by analyzing the application domestic and foreign BIM. This study performed face-to-face interview to 20 participants in BIM project. After the interview, this study drew the general problem and improvement of BIM applied public ordering, and the problem and improvement of requirements and assessment for pre-ordered public project applying BIM. As the result of analyzing the survey for hands-on workers, there are 9 overall problems as follows: Insufficient range and standard for the introduction of BIM(26%); Uncertain purpose of BIM application(16%); Improper assessment of BIM requirements(16%); Low capability of ordering organization in applying BIM(13%); Absence of plan for applying 3D drawings(10%); Low level of applying BIM to actual work(7%); Difficulty in calculating the cost of BIM design service(6%); Insufficient understanding of BIM application by constructor(3%); and, Absence of system for the application of BIM(3%). And the plans for improving these problems were drawn as follows: Preparation of range and guideline for the introduction of BIM(20%); Simplification of the requirement and assessment of BIM(16%); Materialization of the purpose to apply BIM(16%); Establishment of policy to vitalize BIM(8%); Providing the environment for BIM education(12%); Establishment of BIM applied road map(12%); Introduction of advanced BIM ordering method(8%); and, Selection of the appropriate cost of design applying BIM(8%). According to the survey of the suitability of the requirements and assessment of pre-ordered public project applying BIM, 86%(18 persons) of participants answered that it is not proper, and 14%(2 persons) checked other items. According to this, generally they had negative opinions of the requirements and assessment of pre-ordered BIM as follows: Uncertainty of BIM requirements(30%); Subjective decision of standard and method of BIM assessment(30%); Ambiguousness of terms in order guidebook(15%); and, Insufficient capability of BIM assessment(25%). 5 alternatives were drawn to improve the requirements of BIM as follows: Simplification and centralization of assessment and evaluation of BIM requirements(36%); Suggestion of requirements for each stage of BIM(32%); Reinforcement of the capability of BIM assessment(14%); Improvement of the ordering organization's ability to apply BIM(9%); and, Application of strengths of 3D drawings(9%). This study is expected to suggest the basic direction for the requirements and assessment of future BIM applied public ordering with efficient proposal for the efficient requirements and assessment of BIM applied public ordering on the basis of the analyzed results through the interview with participants in BIM project. On the basis of this study, the future study can develop the optimum level checklist model, and verify the optimum level of the planned requirements and assessment of BIM.
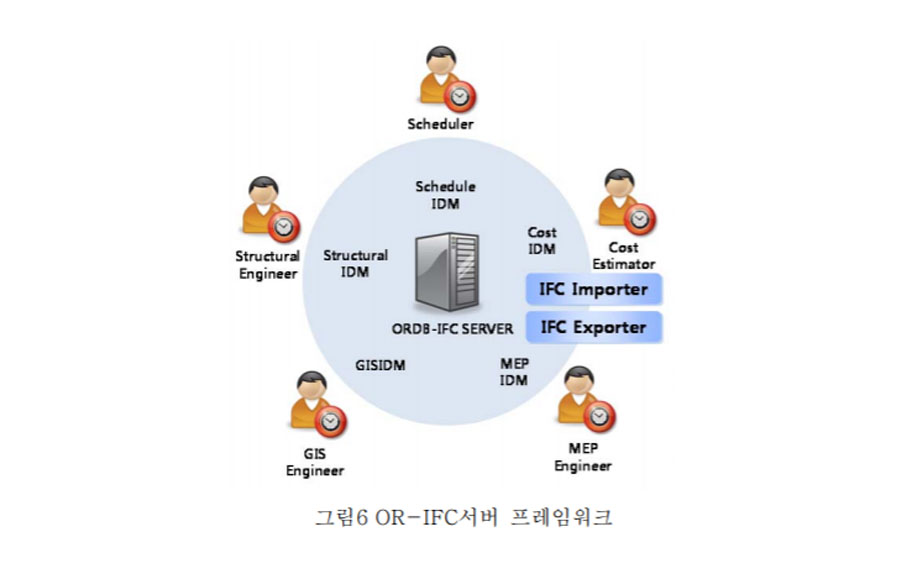
Hoonsig, K. (2009). A study of efficient Web-based BIM data exchange and sharing - Focused on development of an Object-Relational IFC Server. Dept. of Architectural Engineering Seoul, The Graduate School Yonsei University. Master. As a result of recent progress in computer technologies, BIM (Building Information Modeling, BIM) Software is presently being developed that makes each object express the forms and attributes of buildings. This is quite unlike the past 2D CAD and 3D CAD software that had only geometric models. Using BIM tools, diverse participators (architects, structure engineers, facility engineers, cost estimator, scheduler) can create and share numerous pieces of information throughout the lifecycle of a construction project. However, because each of the BIM Tools has its own file format, it becomes difficult to exchange this information. As such, the exchange and sharing of construction information are becoming salient issues in BIM Processes. To solve these problems, IAI (International Alliance for Interoperability) has presented IFC (International Foundation Classes), which expresses construction information with the EXPRESS data modeling language as a standard construction information model. IFC is one of the standard models and is the most frequently used in the area of construction at this moment. It observes ISO 10303 standards and its 2X3 version is currently posted and used. Most of the BIM Tools can export or import IFC file formats, allowing users the ability to transform each BIM model into an IFC file format to exchange and share with each other. However, when IFC models were used in actual projects, three problems emerged: 1) increased time to exchange files due to increased sizes of IFC files resulting from increases in the sizes of models; 2) loss of information in IFC files due to the use of different IFC translators in diverse kinds of software; and 3) version control issues and the authority to use files. Due to these problems, information models became less consistent and were unable to provide necessary information throughout the entire processes of the projects. And as a way to solve these problems, an IFC Model Server was proposed, which would enable multiple users to import/export IFC models through a single web-based database. The IFC Server solved the problems of version control and user authority management, but sizes of IFC files and loss of information in IFC files still remained as problems. Upload and download of models were typically performed via the internet and, for large models, this caused performance problems. To relieve these problems, this paper suggests the adoption of IDM (information delivery manual) in model exchange and the use of ORDB (Object-Relational Database) as an IFC server and report the development progress. IAI presents a method to prepare the processes of exchanges of IFC models and the information necessary for the exchanges with a manual called IDM, in an attempt to improve the compatibility of IFC files. IDM consists of Reference Processes, Process Map, Business Rules, Verification Tests, Exchange Requirements, Functional Parts, and Concepts, etc. PM expresses the processes of use and creation of model information in process models for easy understanding. ER is made in the form of a manual so that general users (architects, engineers, executors) can easily define when information exchanges are necessary in project processes. FP defines the subset of IFC models, so that software vendors can provide the ER required by users. The method to exchange IFC files using IDM does not use all of the information of IFC models. It defines part of IFC files necessary in the process of information exchanges as View, and then exchanges information through the IFC View, thereby reducing the time required for IFC file exchanges. IFC and ORDB have similar naming regulations. To store IFC files that have the concept of objects in Databases, a process of mapping with ORDB language should be carried out. IFC files have essentially 3 kinds of object concepts, as follows: 1) The concept of inheritance, such as Subtypes and Supertypes. 2) User defined attribute values may be brought in as the values of Attributes. 3) Multiple instances such as SET, BAG, LIST, and ARRAY can be inserted into one column. The method to map IFC schemas having these concepts of objects into Cubrid, a commercial ORDB, is as follows: 1) The Subtypes and Supertypes in IFC may be defined as UNDER and ADD SUPERCLASS in ORDB. 2) In object relation type databases, user defined values of Attributes can be directly used as data types. Therefore, in order to enable the use of values of a column of a table as the values of a row of another table, the use of nested tables is enabled. 3) In relation type models, a column can have one value only; thus, when multiple values are necessary, an additional table should be created and then the two tables should be combined. In contrast, object relation type databases can have multiple values using Collection Types. The SET, BAG, LIST, ARRAY types in EXPRESS can be mapped as SET, MULTISET, or LIST, respectively in ORDB, but ARRAY is not supported. In addition to the 3 types of object concepts, it is difficult for users to firsthand transform data types and Inverse Rule, Derive Rule, Domain Rule in EXPRESS into ORDB Queries. To solve this problem, a program to automatically transform EXPRESS formats into Cubrid Queries, using mapping rules, was developed. And to verify RDB based IFC Server and ORDB based IFC Server, conducts benchmark for RDB based IFC Server and ORDB based IFC Server. We implement it with cubrid commercial database system. The experimental results and analyses are also reported. IFC servers have been developed in several projects for efficient data sharing and compatibility, but they have not been commercially successful. The OR-IFC server presented in this paper, unlike existing IFC servers, uses the ORDB added with the concept of objects and the information necessary in processes is defined as IDM, in order to propose an OR-IFC server that will enable efficient data exchanges. The components necessary for OR-IFC servers and OR-IFC frameworks are also suggested. Along with the IDM, which is still conceptual, if the mapping of IFC to ORDB is successfully implemented, it will become possible to more efficiently share is and manage data. Future studies will be made on the approaches for inputting actual IFC data into ORDB and outputting them, while other studies will be made in relation to the comparison of performances between RDB and ORDB. Still other investigations will be carried out to determine the optimal way to enter extracted IFC views into ORDB using IDM.

-
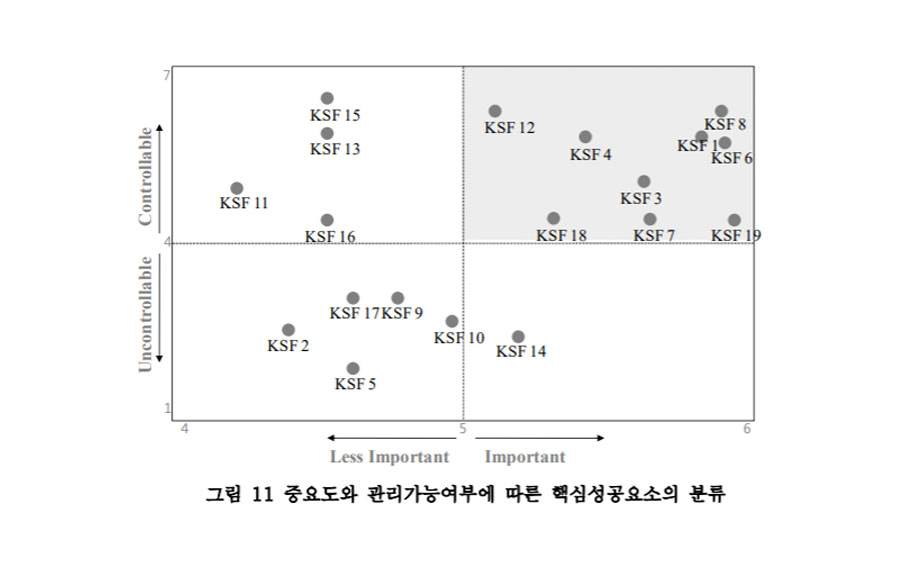
Jongsung, W. (2009). Key Success Factors for Adopting BIM (Building Information Modeling) in A/E/C Projects. Dept. of Architectural Engineering Seoul, The Graduate School, Yonsei University Master. BIM has been used widely, 62% of BIM users having plans to adopt BIM to 30% of the projects which will be carried out in 2009 and showing that it is having positive effects on several BIM projects. However, most AEC companies were not aware of the methods to perform BIM projects successfully. So, we tried to indentify key success factors (KSFs) for adopting BIM in architecture, engineering and construction (AEC) industry in this paper. The author deduced 19 success factors (SFs) carrying out a literature review and conducting face-to-face interview. Interviewees were six BIM experts in Korea. We conducted a survey which was based on results of SFs with 61 world-leading experts in BIM using a seven-point Likert scale. Finally we got the 19 KSFs because scores of all SFs were more than 4 point. In order to examine the relationship among groups of the respondents that were classified into BIM practitioners, BIM researchers and BIM consultants, we used Spearman rank correlation coefficient and multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA). Since all value of the Spearman rank correlation coefficient were more than 0.7, each groups of respondents had similar thoughts about important factors implementing BIM. And the results of MANOVA presented that BIM researchers and BIM consultants had different opinions regarding master BIM model team/manager (p-value = 0.030) and there were different thoughts between BIM researchers and BIM practitioners regarding shared liability between project participants (p-value = 0.043). Several KSFs among deduced KSFs were impossible factors for AEC companies to control. So, we proposed that following seven KSFs among 19 KSFs were prior to be improved considering the possibility to control and similarities and differences among the groups of respondents: ‘Master BIM model team/manager’, ‘Leadership of senior management’, ‘Willingness to share information between project participants ’ , ‘ Organizational structure to support BIM ’ , ‘ Continuous investment ’ , ‘ BIM training programs’ and ‘Information sharing protocols’ We expected that this research would propose a framework for an evaluation of BIM projects. In the future, we will try to develop the evaluation model of BIM projects based on the KSFs.
The most critical issue in irregularly-shaped buildings is how to construct them. Their geometric complexity presents many challenges and problems in fabricating and constructing their shapes. The high cost of such fabrications and constructions is another problem. Designs of many irregularly-shaped building projects have been altered or cancelled because of the difficulties or high costs of their fabrication and construction.To construct an irregularly-shaped building, first of all, its skin has to be chopped into small pieces, which is called panelization. After panelization, the panels go through an optimization (or rationalization) process to fabricate and construct them economically. The panels' geometries are modified or regenerated through this optimization process. To do this, fabrication methods have to be researched, and then panel types have to be classified by fabrication methods. Panels can be classified into one of 12 types by geometry, fabrication methods and type of edges. These 12 types include flat panels, one-way curved surface panels and two-way curved surface panels. Even though some types are geometrically one-way curved surface panels or two-way curved surface panels, they can be classified as flat panels by fabrication methods. Also, some types of two-way curved surface panels can be classified as one-way curved surface panels by fabrication methods. The types can be classified differently by criteria such as these. With the table classifying panels by geometry and fabrication methods, we can figure out how to classify and fabricate different types of panels.Deriving and applying the optimization algorithm considering panels' classification criteria enable a reduction in the number of splines or arcs, which reduces the number of two-way curved surface panels. Geometries can be optimized using methods such as averaging the splines, changing splines to a biarc or multi-arc and subdividing splines. Another method, which considers fabrication more than these methods does, can also be useful. The winding of curved surface panels can be presented by the concept of bending distance, which is measured by the vertical distance from one point on the edge to a straight line joining both ends of the edge. The maximum distance is defined as the maximum bending distance. We can fix the range of non-visual recognition on the building scale, and find the numerical formula for bending distance with trigonometric function. With the bending distance calculated by formula, and the length of the edges, a bending distance value table is made, which includes the range of non-visual recognition and flat panel fabrication by optimization. By comparing the bending distance in the table to the maximum bending distance of the panel's edge, we can judge whether the target panel can be fabricated as a flat panel. The edge of flat panels is a straight line; thus fabricating flat panels means altering the arc and spline of the curved panel's edges into straight lines. Applying the algorithm ther fore reduces the number of curved panels and increases the number of flat panels. This also decreases the difficulty fabricating the panels and constructing the building, thereby reducing the costs as well.Such an optimization algorithm is realized by scripting in Digital Project, which is a parametric modeling tool. Geometries are analyzed and the maximum bending distance is calculated using numerical formulas. The maximum bending distance is compared to the bending distance values from the table. If it is possible to fabricate a panel into flat panel, a straight line joining both ends of the edge is created.The classification of panels and the optimization algorithm was applied to some parts of Dongdeamun Design Plaza. When the optimization algorithm from this study was applied to the parts, the number of two-way curved surface panels was reduced from 73 to 11, and fabrication costs fell by 20%.Panel classification considering fabrication methods and the derived optimization algorithm enables the fabrication and construction of panels, which are the difficult parts of irregularly-shaped buildings. In addition, it reduces fabrication costs and plays a very important role in constructing buildings “economically.”
The most critical issue in irregularly-shaped buildings is how to construct them. Their geometric complexity presents many challenges and problems in fabricating and constructing their shapes. The high cost of such fabrications and constructions is another problem. Designs of many irregularly-shaped building projects have been altered or cancelled because of the difficulties or high costs of their fabrication and construction.To construct an irregularly-shaped building, first of all, its skin has to be chopped into small pieces, which is called panelization. After panelization, the panels go through an optimization (or rationalization) process to fabricate and construct them economically. The panels' geometries are modified or regenerated through this optimization process. To do this, fabrication methods have to be researched, and then panel types have to be classified by fabrication methods. Panels can be classified into one of 12 types by geometry, fabrication methods and type of edges. These 12 types include flat panels, one-way curved surface panels and two-way curved surface panels. Even though some types are geometrically one-way curved surface panels or two-way curved surface panels, they can be classified as flat panels by fabrication methods. Also, some types of two-way curved surface panels can be classified as one-way curved surface panels by fabrication methods. The types can be classified differently by criteria such as these. With the table classifying panels by geometry and fabrication methods, we can figure out how to classify and fabricate different types of panels.Deriving and applying the optimization algorithm considering panels' classification criteria enable a reduction in the number of splines or arcs, which reduces the number of two-way curved surface panels. Geometries can be optimized using methods such as averaging the splines, changing splines to a biarc or multi-arc and subdividing splines. Another method, which considers fabrication more than these methods does, can also be useful. The winding of curved surface panels can be presented by the concept of bending distance, which is measured by the vertical distance from one point on the edge to a straight line joining both ends of the edge. The maximum distance is defined as the maximum bending distance. We can fix the range of non-visual recognition on the building scale, and find the numerical formula for bending distance with trigonometric function. With the bending distance calculated by formula, and the length of the edges, a bending distance value table is made, which includes the range of non-visual recognition and flat panel fabrication by optimization. By comparing the bending distance in the table to the maximum bending distance of the panel's edge, we can judge whether the target panel can be fabricated as a flat panel. The edge of flat panels is a straight line; thus fabricating flat panels means altering the arc and spline of the curved panel's edges into straight lines. Applying the algorithm ther fore reduces the number of curved panels and increases the number of flat panels. This also decreases the difficulty fabricating the panels and constructing the building, thereby reducing the costs as well.Such an optimization algorithm is realized by scripting in Digital Project, which is a parametric modeling tool. Geometries are analyzed and the maximum bending distance is calculated using numerical formulas. The maximum bending distance is compared to the bending distance values from the table. If it is possible to fabricate a panel into flat panel, a straight line joining both ends of the edge is created.The classification of panels and the optimization algorithm was applied to some parts of Dongdeamun Design Plaza. When the optimization algorithm from this study was applied to the parts, the number of two-way curved surface panels was reduced from 73 to 11, and fabrication costs fell by 20%.Panel classification considering fabrication methods and the derived optimization algorithm enables the fabrication and construction of panels, which are the difficult parts of irregularly-shaped buildings. In addition, it reduces fabrication costs and plays a very important role in constructing buildings “economically.”
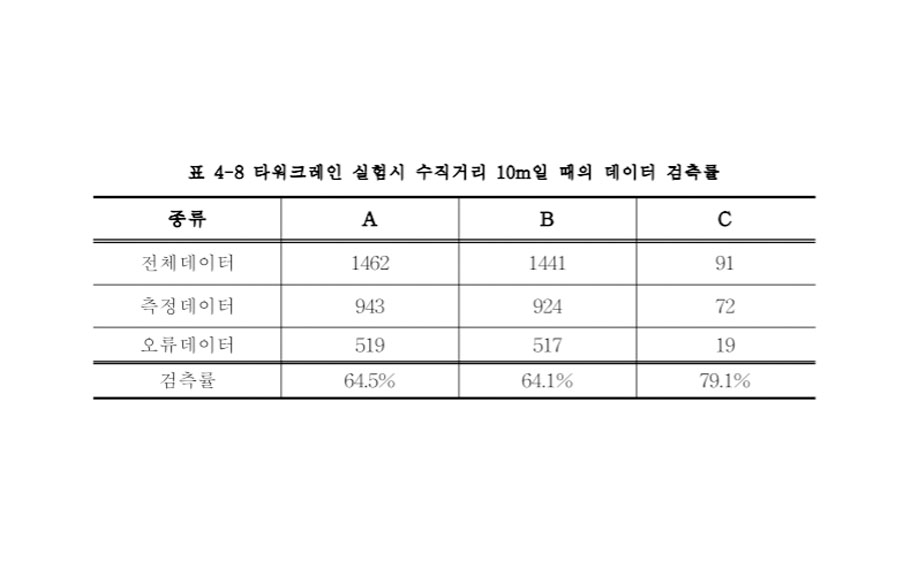
As the number of high-rise buildings after 2003 had increased by approximately 60 per year, the number of cranes has increased by approximately 200 per year, on average. This increase in the number of cranes yields the benefits of increasing employment and doing work efficiently, but also presents safety problems for workers in high places.Previous research that examined this problem focused on improving efficiency and safety with automated cranes. However, those studies were . Therefore, we are proposing the framework for a robotic tower crane system. We are proving the feasibility of applying this system in the real world through experiments using laser distance measurement during the phase of path-tracking, to reinforce our theory. Through this system, we expect to improve the productivity of lifting work by 9.9% ∼ 50%, based on previous research.The robotic tower crane system consists of a path-panning system and a path-tracking system. The process is designed with three steps, which are path-planning and tracking, CCTV (closed circuit television)-based monitoring and material separation; and we are suggesting a framework designed to lift building materials under various conditions. Also, to examine the capability of the robotic tower crane system's laser-technology-based path-tracking system, we tested the laser measurement device in indoor, outdoor and swinging conditions; and analyzed the data extracted from these tests.As a result of this process, we can acquire statistically acceptable data for the pre-configured tolerance of 10cm, proving this system's feasibility. Nevertheless, when we equip and operate this system in a tower crane, swinging will occur. This problem will be resolved by optimizing the reflector's size and installing a corner cube.

Selection of appropriate retaining wall systems is the key to the success of excavation work, especially in urban construction projects. As the excavation area became larger, the impact on urban construction projects of selecting appropriate retaining wall systems became much stronger than before. In practice, however, the selection of the retaining wall systems is often based on project engineers’ limited experience with a few familiar systems. In this regard, various data mining techniques have been used in the selection of appropriate retaining wall as a means to make informed decisions through the aid of useful knowledge discovered from historical data. Previous studies proposed using machine learning techniques that could return the most suitable system for a specific set of site conditions based on existing cases of excavation work. However, most of the proposed prediction models were black box models, which did not provide any description of why the recommended systems best suited the site conditions. Some of the prediction models generated by, for example, a rule-induction method provided a visible reasoning process. However, some of the automatically derived rules were illogical. Even if the derived results are technically flawless, sometimes it is difficult to reproduce these results by using the same analysis technique when a different set of data is used. We reviewed a series of previous studies and finally assumed that these flaws were most likely attributed to the limited number of data. In general, the data mining technique requires thousands of cases to derive a reliable conclusion, but such a large number of excavation cases are not available in construction. Therefore, this paper presents an alternate approach with logistic regression. A series of logistic regression analyses was used to analyze the 139 excavation work cases, quantifying relationships between site conditions and each of the retaining wall systems. As is well-known, statistical significance does not always guarantee the external validity of a model, especially when data size is small. In order to guarantee the external validity (i.e., generalization) of the resultant models, we reviewed the derived models by consulting domain experts and comparing the models to the findings from existing cases and relevant literature. Statistically significant and practically important relationships are then developed into a decision tree-like structure. The decision-support process proposed in this study showed around an 80% accuracy rate, which is higher than that of the decision tree built by an automated learning algorithm. Additionally, we developed a web-based decision-support system called Dr. Underground based on the decision-support process proposed in this paper. It was developed using a server-side web language APS.NET and Microsoft Access as a database. Decision makers can input data regarding site conditions, and then the system will not only recommend an appropriate retaining wall system but also construction-related details of proposed retaining wall system.
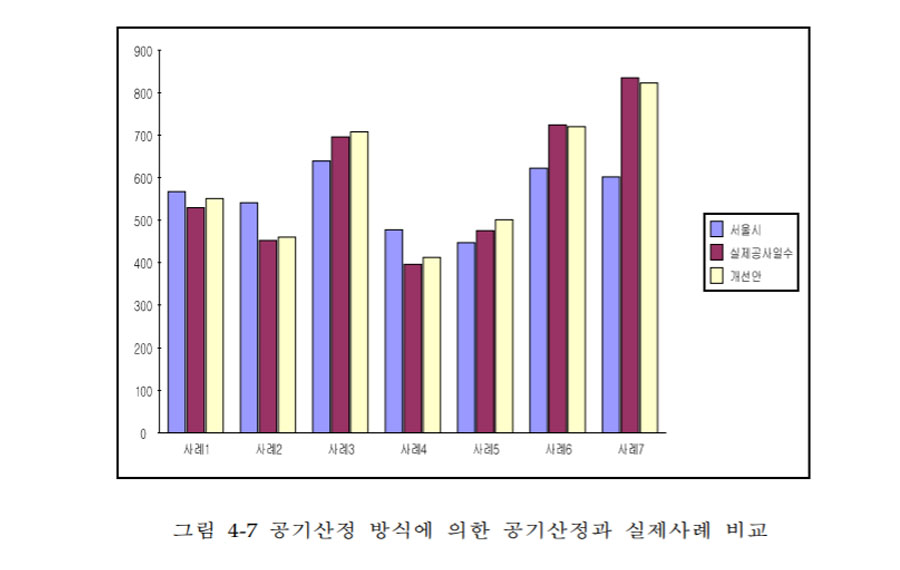
The purpose of this study is to improve the construction period estimation method for buildings in seoul in order to minimize the problems of the delayed or extended construction period due to the erroneous calculation of the construction period at the stages of basic conception and planning by the clients for the public construction projects in Korea. Since the periods of the public construction projects tend to be confirmed in the contracting process based on the construction period calculated at the stage of basic conception and planning by the clients, it is important to estimate a proper construction period at this stage. Nevertheless, since the construction period tends to be determined unreasonably depending on client's working officials' subjective judgement and experiences, their estimated construction period will differ much wide from the actual construction period. Although the clients have their own standards for estimation of the construction period, they seldom take into consideration the diversified uses and structures of the projects, while not applying some specific standards for the period when the construction work cannot be done. Namely, they tend to arrange the standards uniformly for the construction periods. This study referred to the construction period estimation methods arranged by Seoul metropolitan city and thereupon, surveyed the factors affecting the construction period to suggest some alternatives by reviewing the preceding studies, interviewing with experts and conducting a questionnaire survey. To this end, the period was divided into the net construction period and the period unavailable for work, and the former period was redivided into basement construction, frame construction and finishing construction sub-periods, and then, the period was compensated for uses and structures to arrange the standards for estimation of the construction period. The period for finishing construction was being uniformly estimated at 172 days for the parts of building with 6 stories or lower and 170 days for the parts of the building with 7 stories or higher, but this study suggested the days for finishing construction by floor. To this end, this study reviewed the weather conditions in Seoul for the last decade based on the data published by Korea Meterological Administration in association with the characteristics of the construction works, and thereby, estimated the days unavailable for work; holidays were considered by surveying the recent spot conditions. As a result of comparing the estimated periods with the actual periods of the construction works completed at 7 spots, the error was within ±5.5%, while the methods of Seoul metropolitan city administration resulted in a higher error rate or ±27.9%, which proved that the methods had been improved much. In addition, considering the criteria and conditions suggested by preceding studies as well as the diverse characteristics of the construction works, the reform measures suggested by this study for estimation of the construction period were deemed relatively reasonable.
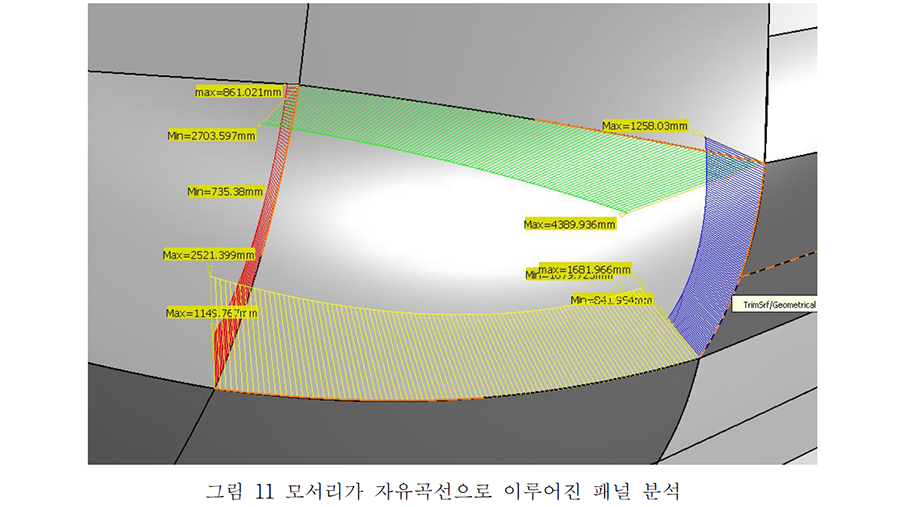
The most critical issue in irregularly-shaped buildings is how to construct them. Their geometric complexity presents many challenges and problems in fabricating and constructing their shapes. The high cost of such fabrications and constructions is another problem. Designs of many irregularly-shaped building projects have been altered or cancelled because of the difficulties or high costs of their fabrication and construction.To construct an irregularly-shaped building, first of all, its skin has to be chopped into small pieces, which is called panelization. After panelization, the panels go through an optimization (or rationalization) process to fabricate and construct them economically. The panels' geometries are modified or regenerated through this optimization process. To do this, fabrication methods have to be researched, and then panel types have to be classified by fabrication methods. Panels can be classified into one of 12 types by geometry, fabrication methods and type of edges. These 12 types include flat panels, one-way curved surface panels and two-way curved surface panels. Even though some types are geometrically one-way curved surface panels or two-way curved surface panels, they can be classified as flat panels by fabrication methods. Also, some types of two-way curved surface panels can be classified as one-way curved surface panels by fabrication methods. The types can be classified differently by criteria such as these. With the table classifying panels by geometry and fabrication methods, we can figure out how to classify and fabricate different types of panels.Deriving and applying the optimization algorithm considering panels' classification criteria enable a reduction in the number of splines or arcs, which reduces the number of two-way curved surface panels. Geometries can be optimized using methods such as averaging the splines, changing splines to a biarc or multi-arc and subdividing splines. Another method, which considers fabrication more than these methods does, can also be useful. The winding of curved surface panels can be presented by the concept of bending distance, which is measured by the vertical distance from one point on the edge to a straight line joining both ends of the edge. The maximum distance is defined as the maximum bending distance. We can fix the range of non-visual recognition on the building scale, and find the numerical formula for bending distance with trigonometric function. With the bending distance calculated by formula, and the length of the edges, a bending distance value table is made, which includes the range of non-visual recognition and flat panel fabrication by optimization. By comparing the bending distance in the table to the maximum bending distance of the panel's edge, we can judge whether the target panel can be fabricated as a flat panel. The edge of flat panels is a straight line; thus fabricating flat panels means altering the arc and spline of the curved panel's edges into straight lines. Applying the algorithm ther fore reduces the number of curved panels and increases the number of flat panels. This also decreases the difficulty fabricating the panels and constructing the building, thereby reducing the costs as well.Such an optimization algorithm is realized by scripting in Digital Project, which is a parametric modeling tool. Geometries are analyzed and the maximum bending distance is calculated using numerical formulas. The maximum bending distance is compared to the bending distance values from the table. If it is possible to fabricate a panel into flat panel, a straight line joining both ends of the edge is created.The classification of panels and the optimization algorithm was applied to some parts of Dongdeamun Design Plaza. When the optimization algorithm from this study was applied to the parts, the number of two-way curved surface panels was reduced from 73 to 11, and fabrication costs fell by 20%.Panel classification considering fabrication methods and the derived optimization algorithm enables the fabrication and construction of panels, which are the difficult parts of irregularly-shaped buildings. In addition, it reduces fabrication costs and plays a very important role in constructing buildings “economically.”

A special issue article, entitled "On what basis should we buy a 3D concrete printer?", has been published in the Building Construction magazine of the Korea Institute of Building Construction. This article proposes a technical specification framework for three-dimensional concrete printers (3DCPs) by analyzing 139 academic papers, 98 3DCPs, and a Delphi survey with 22 3DCP experts. Furthermore, it introduces 19 core technical specification items as a research result and discusses the future direction.