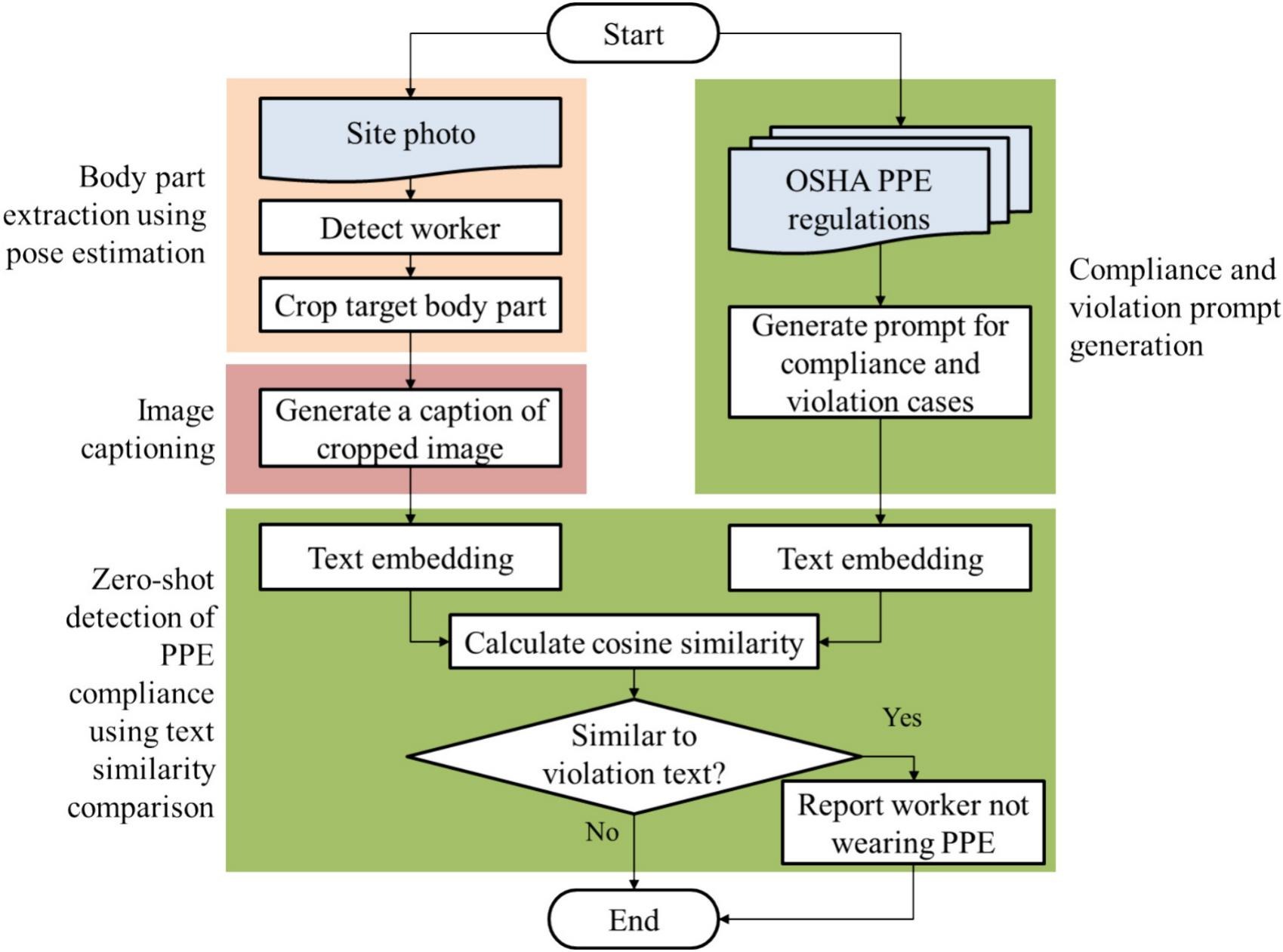
Previous studies have deployed object-detection-based approaches to automate personal protective equipment (PPE) safety monitoring. However, previously proposed methods require large amounts of labeled data for different PPE items. This study proposes a zero-shot PPE monitoring method that does not require a training process to overcome this problem. The proposed method comprises three steps. First, it detects workers onsite from images and crops body parts using human-body key points. Next, the cropped body images are described in text using image captioning. Finally, the extracted text is compared with prompts describing body parts wearing PPE, and safety is determined based on cosine similarity. Compared to the F1-score of 73.5% achieved by traditional object detection approaches trained on 50 images for hardhat monitoring, the proposed zero-shot approach demonstrates significant improvement with an F1-score of 82.6%. It also surpasses the previous zero-shot monitoring performance (an accuracy of 53%). Learn more…

view
D. Gil and G. Lee, Zero-shot monitoring of construction workers’ personal protective equipment based on image captioning, Automation in Construction 164 (2024) 105470.

view
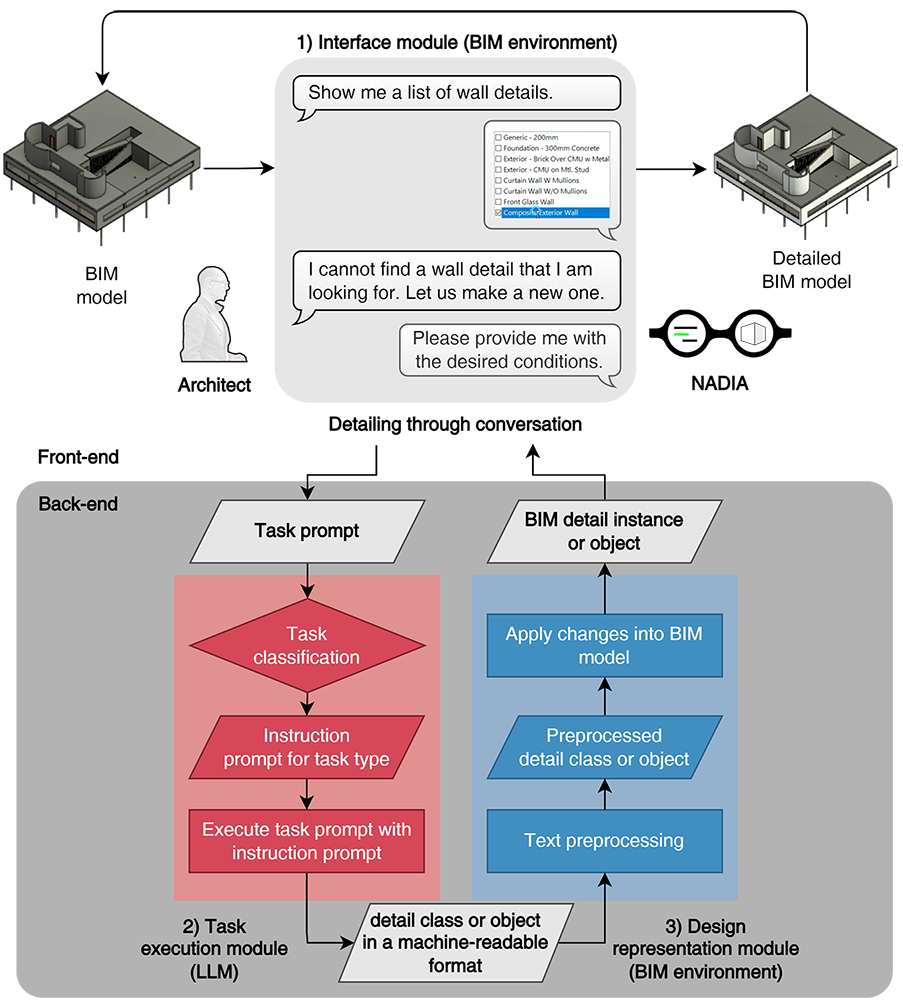
S. Jang, G. Lee, J. Oh, J. Lee, B. Koo, Automated detailing of exterior walls using NADIA: Natural-language-based architectural detailing through interaction with AI, Advanced Engineering Informatics 61 (2024) 102532.

view
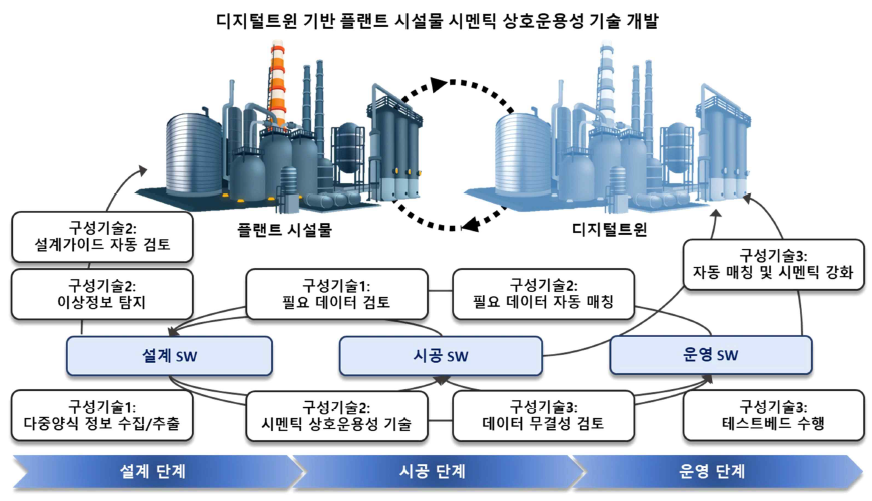
디지털트윈 기반 플랜트 시설물 시멘틱 상호운용성 기술 개발


view
Strategies for Decarbonization of Construction through Offsite Construction and Automation
MORE